摘要:前几天学习了SSM项目的搭建,但是因为配置过程中出现了问题因此没有搭起来,我最讨厌不确定的事情,因此自己花费了点时间钻研搭建SSM项目的方法,终于习得了SSM项目搭建的方法,接下来我会记录一次我自己搭建SSM项目的过程。
目录- 使用IDEA搭建SSM项目
- 1.概述
- 2.项目搭建
- 2.1.创建一个webapp模板的maven项目
- 1.选择模板并创建项目
- 2.设定项目名称并设置工作坐标
- 3.设置maven路径与配置文件,之后点击finish就配置好了
- 2.2.导入jar包依赖
- 1.删除用不到的坐标依赖,我们删除掉原有的properties标签、dependencies标签和build标签中的所有内容
- 2.导入我们即将用到的坐标依赖
- 2.3.搭建项目基本框架
- 1.创建我们的Java程序目录与资源目录
- 2.创建我们的Java工作空间
- 3.创建测试区
- 2.4.创建项目对应的数据库
- 2.5.创建model层
- 2.6.Spring框架的导入以及Service层的创建
- 1.创建Service层
- 2.创建Spring配置文件
- 3.测试Spring
- 2.7.Spring MVC框架的导入以及controller层的创建
- 1.Spring MVC框架的导入
- 2.搭建相关目录结构
- 3.controller层及相关文件配置
- 4.配置Tomcat服务器
- 5.测试
- 2.8.MyBatis框架的导入以及Dao层的创建
- 1.创建数据库信息配置文件
- 2.搭建Dao层
- 2.9.测试
- 1.书写Service层的方法
- 2.书写controller层的方法
- 附录:关于编码的问题,我最终解决了,详情见下面的链接
- 2.1.创建一个webapp模板的maven项目
SSM项目的搭建实际上是Spring,Spring MVC与MyBatis三个框架的整合,听上去好像有点复杂,但是实际上其原理非常简单,就是在一个项目中先后配置这三个框架并构建相应的层,然后再在xml配置文件中加入三者的监听器,这样三个框架就能被xml配置文件联系在一起,Spring MVC中主要是提供了控制层的Servlet的方便服务,MyBatis中做的事情则主要是关于数据库的操作方便化,Spring则是提供了控制权反转和面向切面编程的功能,让这个项目的耦合度更低,达到了解耦的目的,其思想实际上是穿插在这个项目的各个层级之中的。
SSM项目中分为如下几层:controller层,这层属于Spring MVC架构的管理范围,主要是负责请求的接收与发送,也就是我们的Servlet,里边提供操作简单的传参与转发功能;model层(entity)层,关于这层在Spring MVC和MyBatis两个框架中都有提及,在MyBatis中多被称为entity层,在Spring MVC中多被称为model层,在SSM项目中我们可以二选一,因为两个名字其实是一个东西,该层中存在的内容主要是项目中需要使用到的Java Bean对应的类,也就是Java Bean的定义信息或者说是蓝图;Service层,该层主要被Spring框架管理,该层明显的使用到了IOC的对象生成方法进行解耦,这层主要负责项目中的业务处理,也就是数据的逻辑操作;Dao层,该层也可以被称为mapper层,被MyBatis管辖,两个名字实际上指的是同一个东西,但是在我们配置该层的时候实际上也使用到了Spring提供的IOC思想,并且该层会分为两部分:接口部分和实现部分,实现部分我们通常是使用配置文件实现的,因此两部分通常不会在一起,为了区分,我们通常将配置文件命名为mapper部分,将接口部分命名为dao部分,二者共同组成mapper层或者说是dao层,需要注意的是在mybatis中还存在注解开发,注解开发中的实现和接口位于同一文件中,使用注解开发我们能更清晰的意识到二者属于同一层,但是我们很少使用注解开发吗,因为这样会提升耦合度。
在SSM项目中model层有时可能也被称为java bean,而不认为它是一层,这里并不影响项目搭建,大家怎样理解都可以。
首先我们在IDEA中创建一个webapp模板的maven项目,名字随意,设定好工作坐标以及我们自己的maven路径,下面为步骤图解:
1.选择模板并创建项目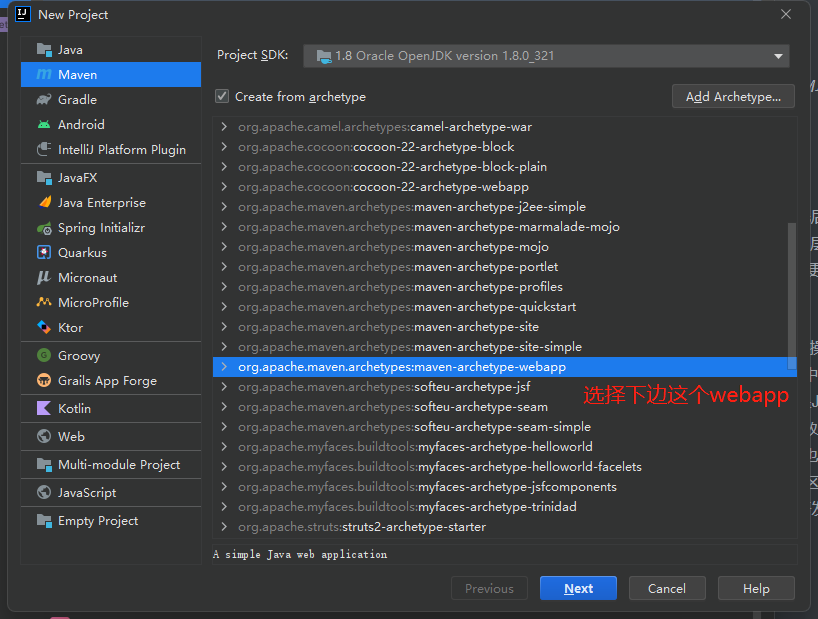
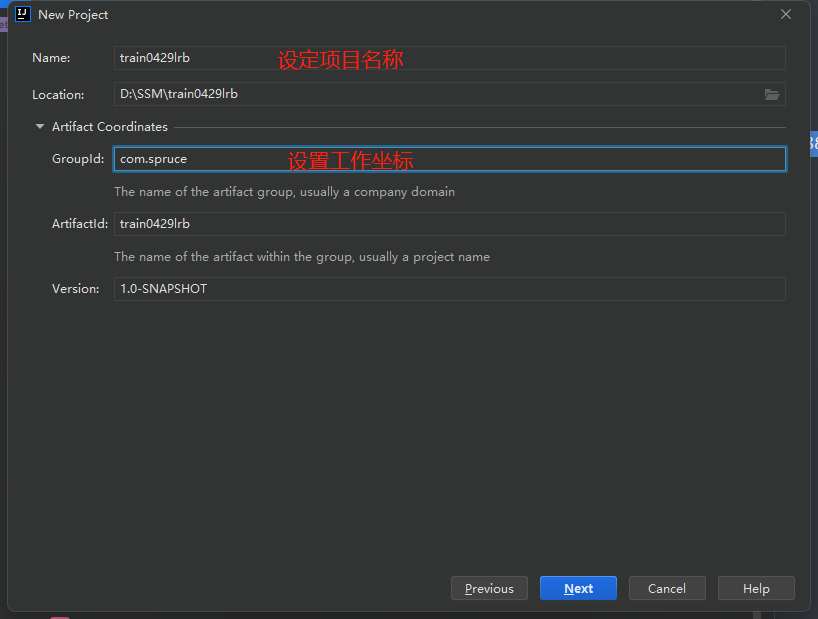
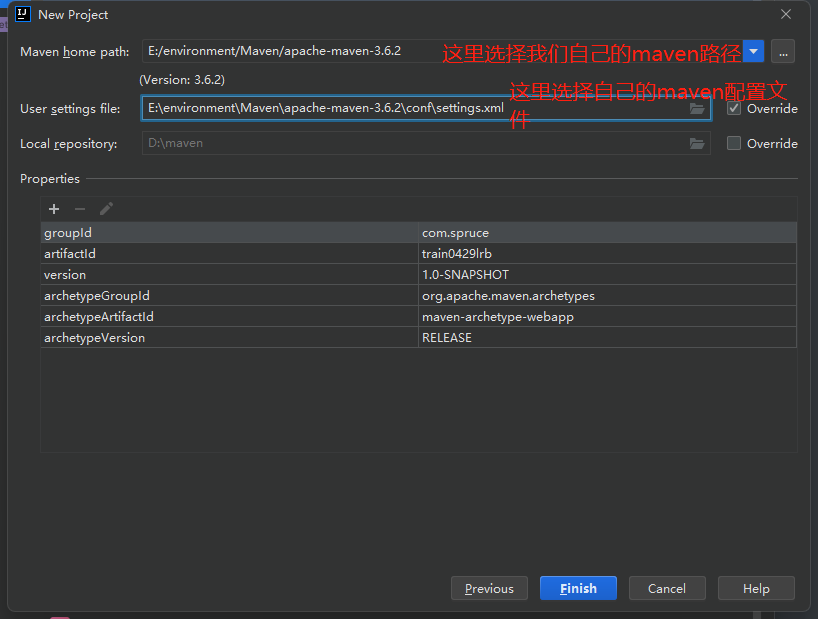
之后我们进入项目后,最先显示的就是我们的pom文件,我们接下来需要对pom文件做一些操作:
1.删除用不到的坐标依赖,我们删除掉原有的properties标签、dependencies标签和build标签中的所有内容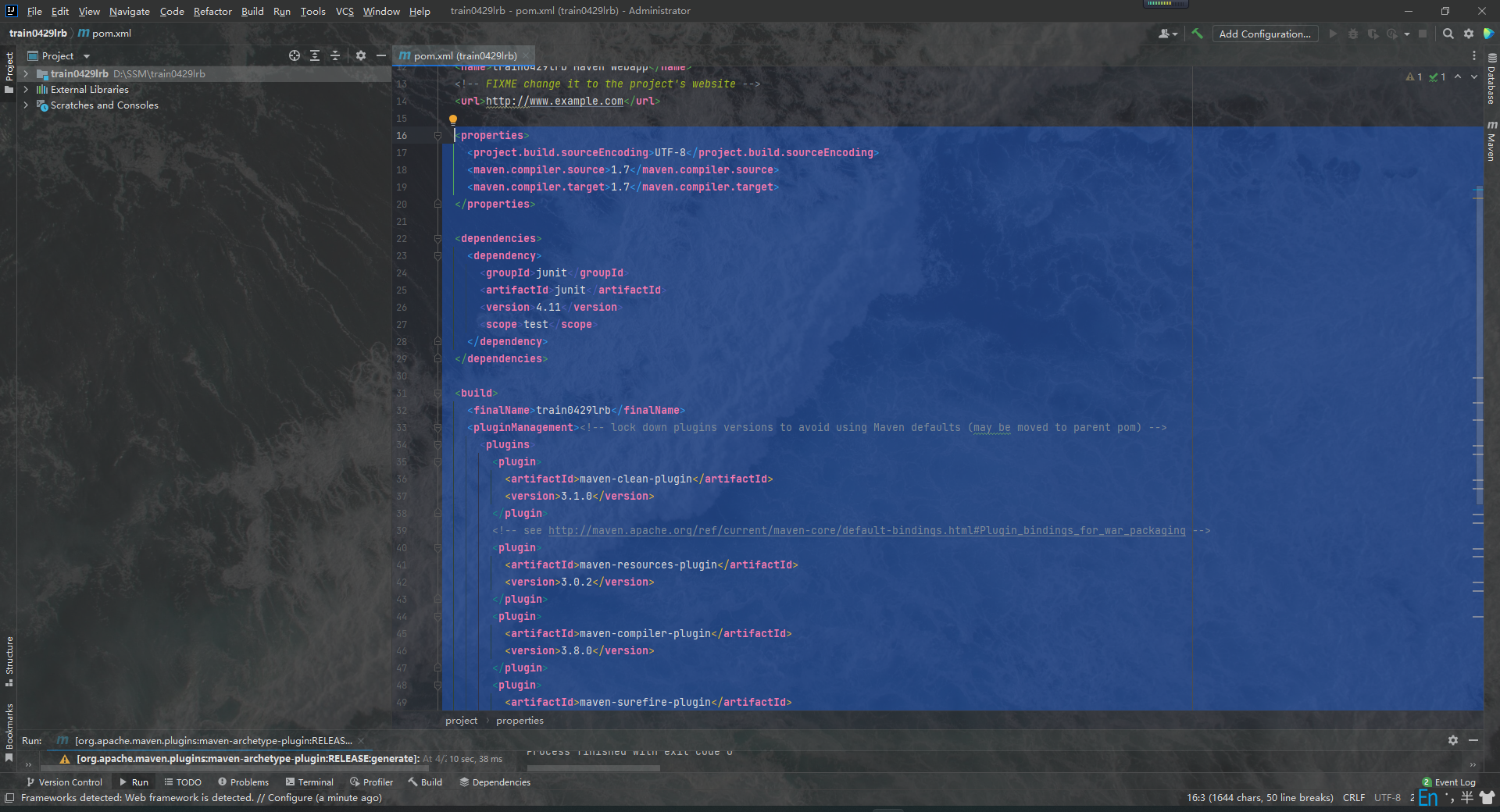
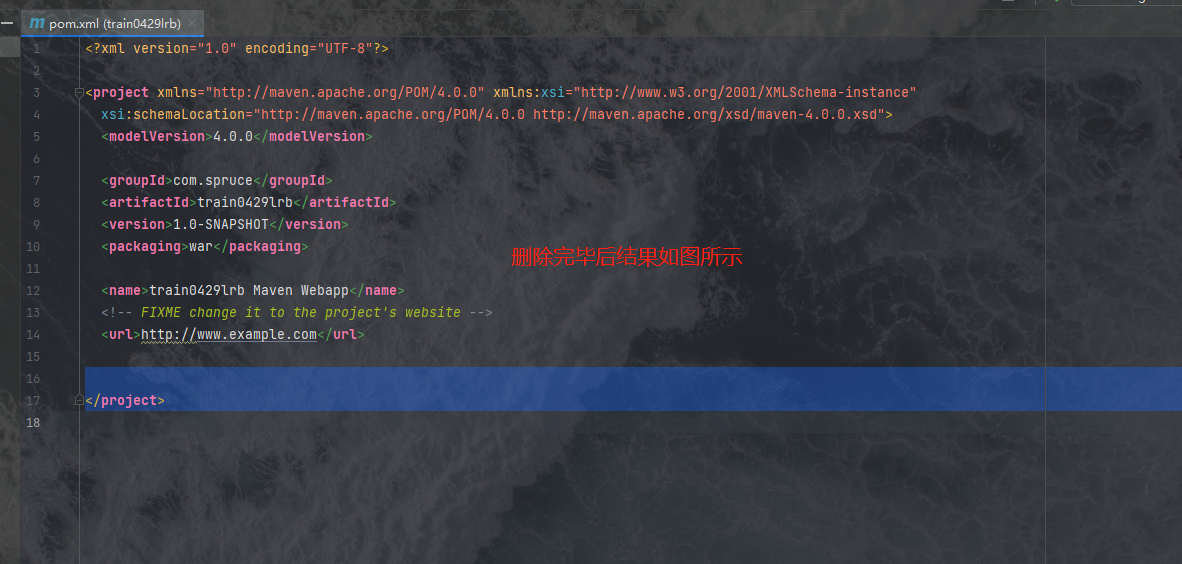
我们导入下面的jar包依赖:
<properties>
<spring.version>5.0.2.RELEASE</spring.version>
<slf4j.version>1.6.6</slf4j.version>
<log4j.version>1.2.12</log4j.version>
<mysql.version>5.1.6</mysql.version>
<mybatis.version>3.4.5</mybatis.version>
<jackson.version>2.9.4</jackson.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--spring-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.6.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency><dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>2.5</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>jstl</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!--log start-->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log end-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--连接池-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version></dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring4</artifactId>
<version>3.0.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>ssm</finalName>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.5</version>
<!--告诉插件,配置文件所在的位置-->
<configuration>
<configurationFile>src/main/resources/mbg.xml</configurationFile>
<verbose>true</verbose>
<overwrite>true</overwrite>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
导入好之后我们点击更新来进行依赖的导入:
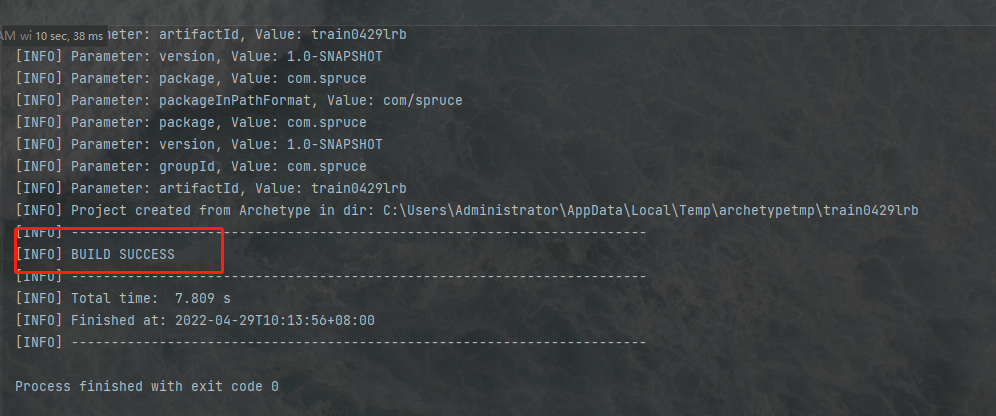
命令行中输出如下信息说明我们已经导入成功了:
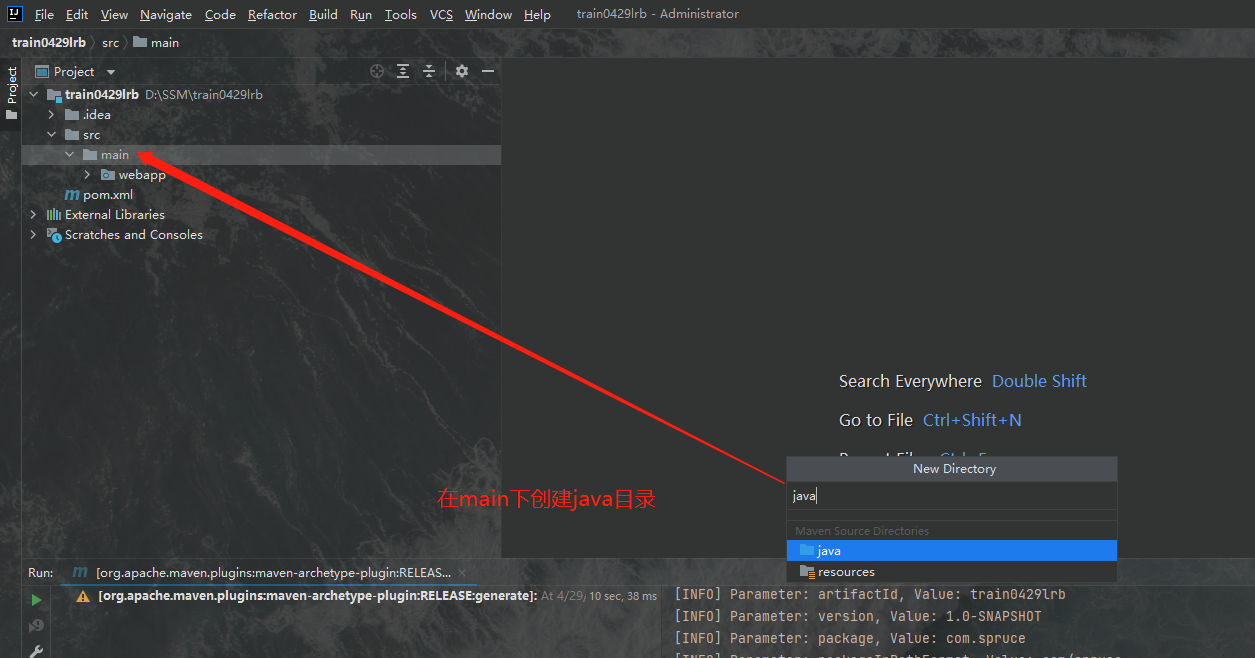
我们首先要在项目的main目录下创建两个目录,一个是java目录,一个是resource目录,两个目录都应被设定相应的角色,我们要把java目录设定成java源目录,将资源目录设定为资源目录,如下图所示我们分别创建这两个目录:
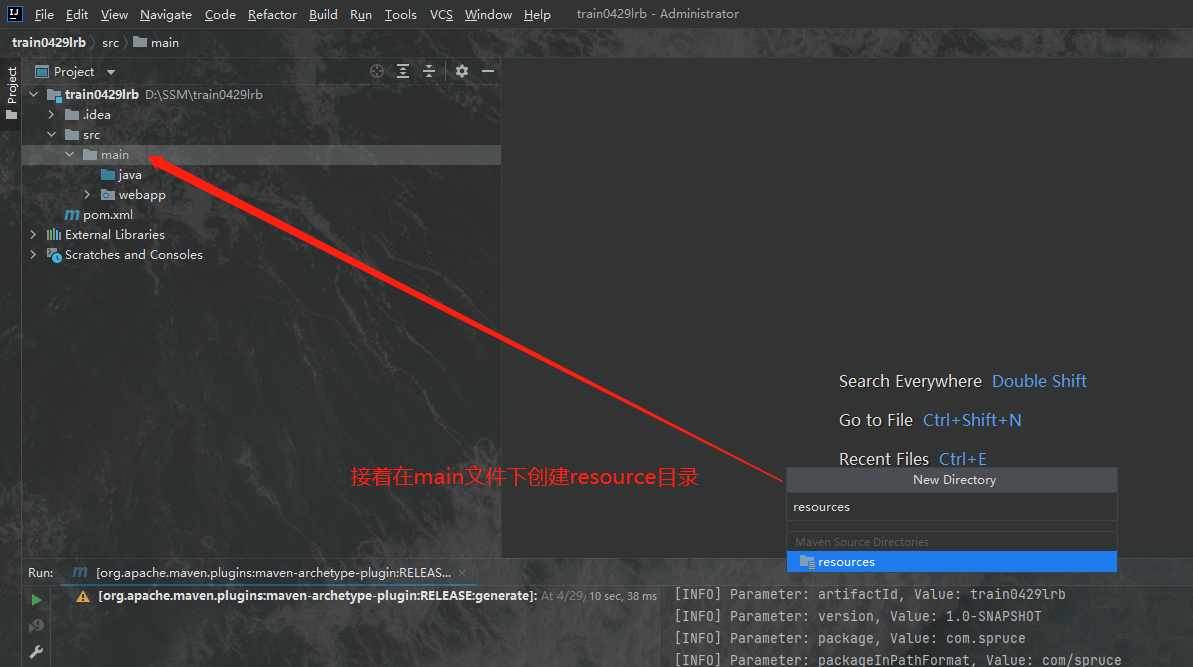
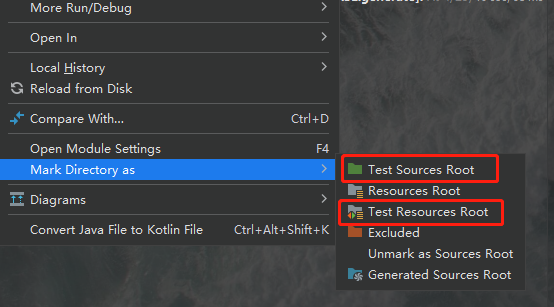
我们创建好目录之后右键单击目录,就会出现一个菜单栏,我们在最下边的Mark Directory as选项中可以看到我们可以设定目录的类型,其中java目录应为最上边的Source Root也就是源根,resource目录应为第三个Resource Root也就是资源根,如图所示:
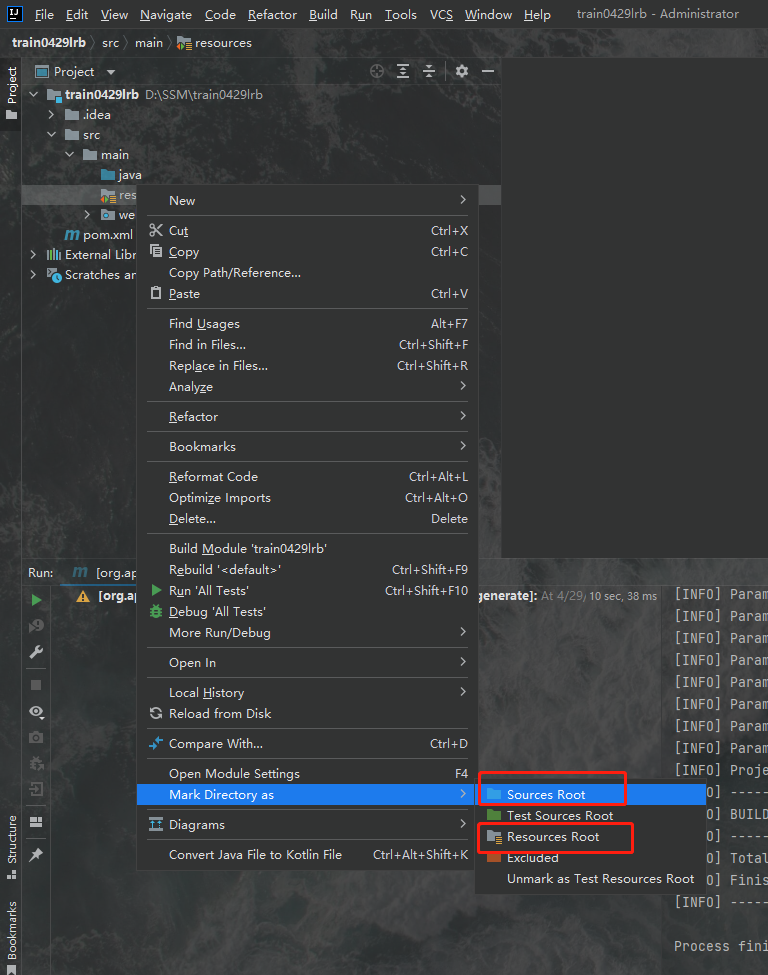
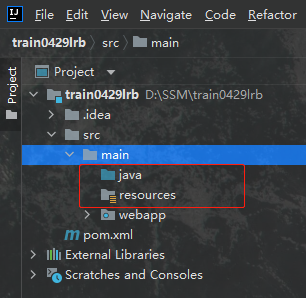
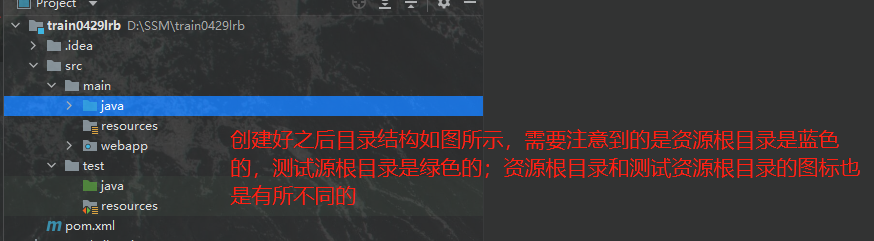
两个目录创建好之后我们便得到了一个这样的目录结构,注意两个目录的类型千万不要设置错,图标要和我一样才行:
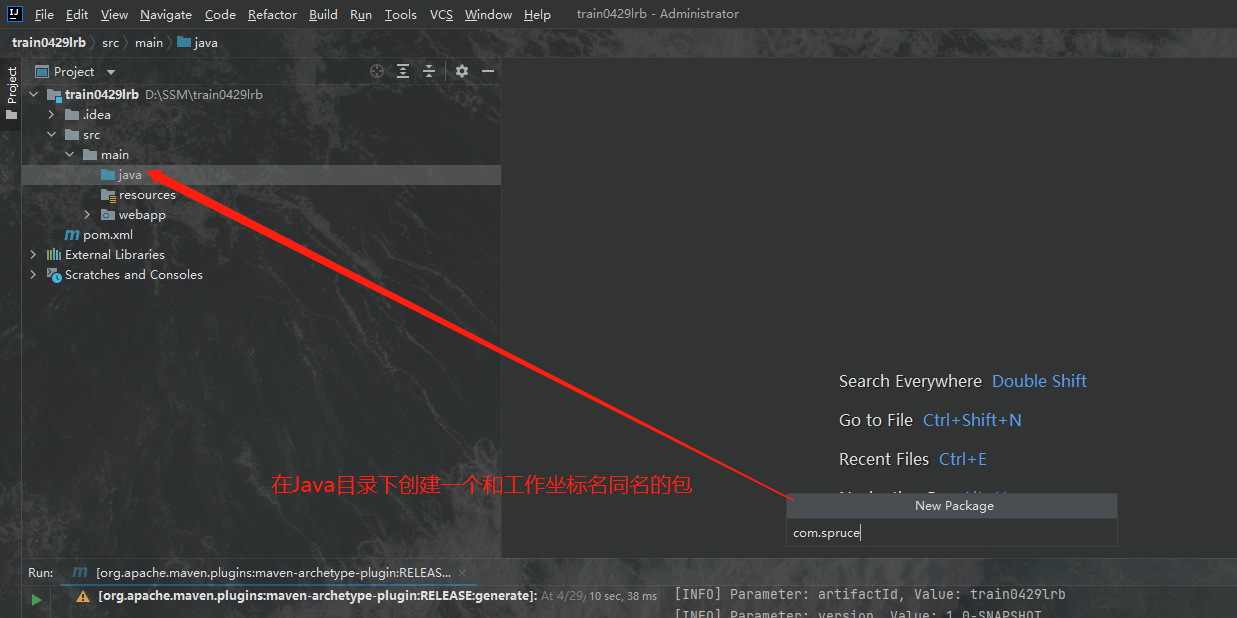
我们显然是不能直接在java目录之下直接写java代码的,我们不能直接将代码写在一个目录之下,而是应该写在有着特定命名格式的包里。尽管包也是目录,但是我们通常认为包与普通的源目录有着本质上的区别,因此我们首先在java目录下创建一个和我们之前定义的工作空间同名的包,这是规范,我们之前定义的工作空间可以去2.1中查看,我定义的坐标名是com.spruce,这个名称通常是公司名或者组名,以后我们参与到实际的开发中之后会有更深入的了解:
我们不仅仅要创建工作空间,我们还要创建测试空间,测试空间是和main目录同级别的一个目录,我们的主要测试代码都在里边书写,我们接下来在src目录下创建一个名为test的目录,并建立和main目录基本上一致的目录结构,test目录中无需创建webapp目录,只需创建好java目录与resource目录,其中,java目录的类型为Test Source Root也就是测试源根;resource目录的类型我们要定义为Test Resource Root,也就是测试资源根:
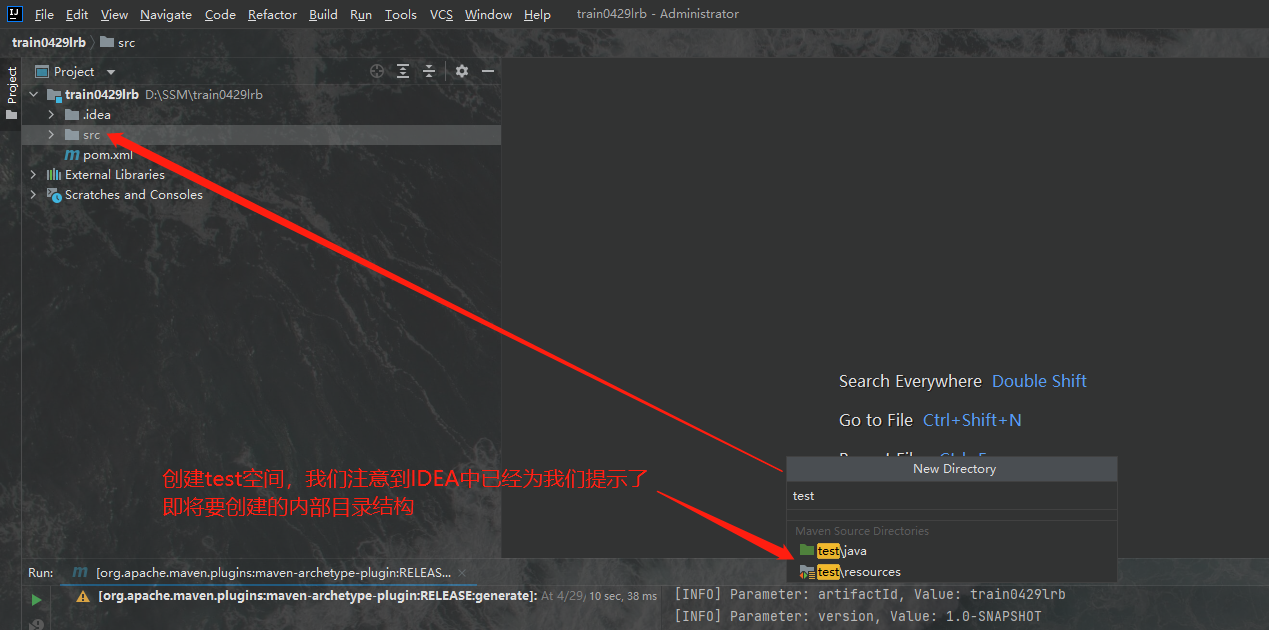
下图中的第一个选项即为测试源根,第三个为测试资源根,他们与源根和资源根的图标是不一样的:
创建好之后的目录结构如图所示:
这样一来这个项目的准备工作就基本完成了,现在就可以进行我们项目的基本搭建了。
2.4.创建项目对应的数据库 每一个SSM项目必然是要连接一个属于自己的数据库的,因此我们要专门为这个项目创建一个自己的数据库,这个数据库在之后的项目开发中必然会用到,而且在做测试的时候我们也会用到这个数据库,因此我们搭建一个和项目同名的数据库,项目名是train0429lrb,因此我们搭建一个和项目同名的数据库:
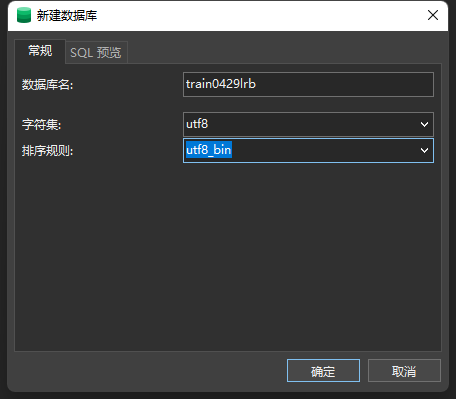
我们使用Navicat创建一个数据库,字符集如图所示,需要注意的是有时我们即使设置了utf-8的格式,编码也是总出问题,而我的电脑不知咋回事一定会出现编码问题,因此在项目搭建过程中我们先忽略这个编码问题,在项目搭建完成后我们再着重解决这个问题。
创建好数据库后我们在数据库中创建一个测试用的表,并且往里边放上一些数据,我们使用下面的数据创建表,也可以用Navicat的图形用户界面创建:
create table account(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20),
money double
);
创建好之后是这样的:
现在我们往里边插入一点数据:
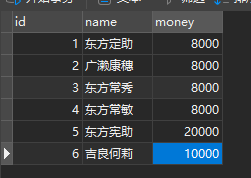
这样一来数据库就搭建好了,接下来我们根据数据库来创建我们的model层。
这里我想提的一点就是实际上每个逻辑层本质上都仅仅是一个包,其意义实际上是我们赋予它的,这里的思想实际上就是约定大于配置,对于这些层我们无需配置什么,而是我们要按照约定在里边些什么,我们在里边写的东西,就是我们赋予其真正含义的过程,我们在一个名为model的包下写Service层的代码,那这个包就是Service层的包。因此我们要是想创建一个层,必须要有代码的具体依托,而我们的代码在SSM项目中很大程度上是依托于数据库书写的,典型的如model层,接下来我们书写model层的代码。
model层代码实际上就是java bean的蓝图,我们当前数据库中存在一个实体为account,因此我们就需要创建一个account的java bean蓝图,也就是Account类,经过上面的构建表我们知道数据库中的account表有三个字段:id[类型为int]、name[类型为varchar]、money[类型为double],因此我们必须创建一个字段名和属性完全与该表一样的类,这个类在哪创建呢?我们首先应该在com.spruce下创建一个新包,名为model,然后今后它就是我们的model层了,之后我们在这个里边创建Account类:
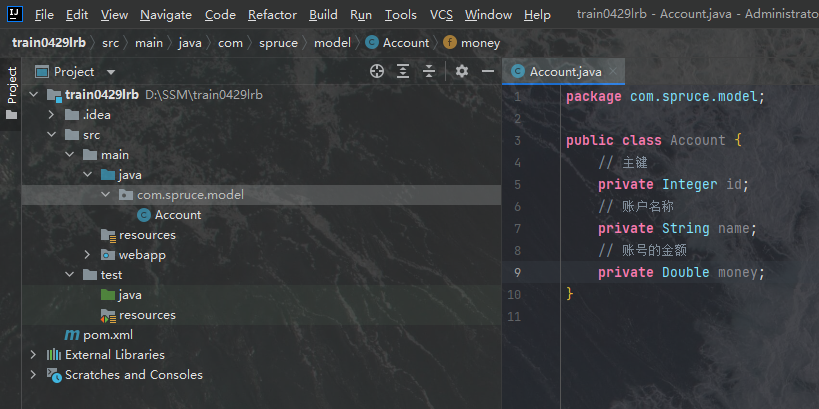
然后我们为其生成getter方法和setter方法,以及toString方法:
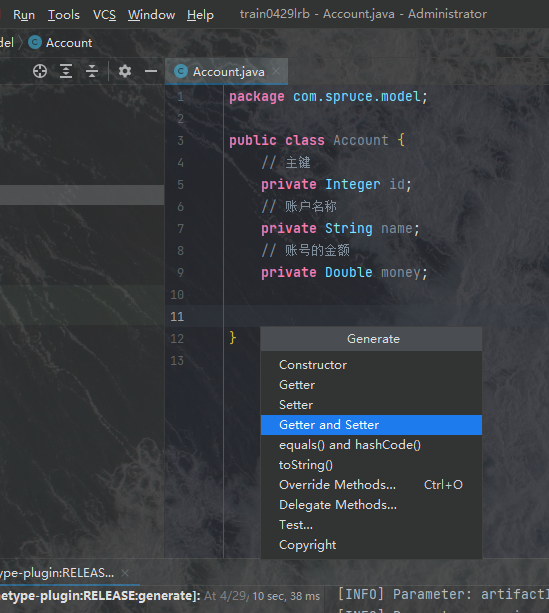
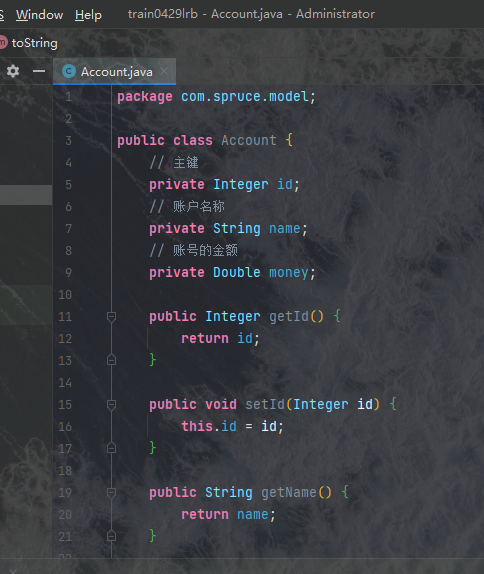
创建好model层之后,我们整体项目就算出现了第一个约定了,根据这个约定,我们就可以配置三个框架以及它们相对应的层了。
2.6.Spring框架的导入以及Service层的创建 1.创建Service层 Service是严格遵循Spring提供的IOC思路书写的,因此我们会将代码分为两部分,其中一部分是接口部分,另一部分是方法体部分,其中接口部分的作用主要是限制我们方法的声明,以及在controller层中提供生成标准bean的服务,首先我们先在com.spruce下创建一个service包:
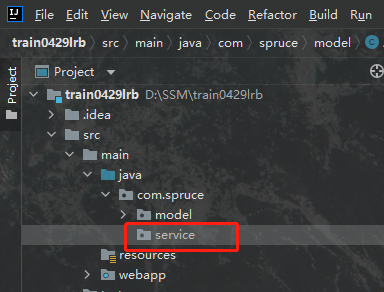
然后我们在其下边创建两个包,具体命名方式无所谓,主要是我们自己能区分就好了,一个包装接口,一个包装service层方法,如下:
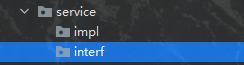
然后我们在interf包下创建一个新的接口类,名为AccountService,这里边定义的是Account这个javabean相关的业务操作的各种方法,我们书写其代码如下:
package com.spruce.service.interf;
import com.spruce.model.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface AccountService {
//查询所有
public List<Account> findAll();
}
这些代码意味着我们为AccountService的业务方法中定下了一个标准,简而言之就是说我们必须为Account这个实体提供一个查询所有数据库中的信息的方法。有了接口之后,我们就得在impl包中书写接口的实现,否则我们的方法是使用不了的。
之后我们书写接口的实现,我们在impl包中创建一个与刚才的AccountService相对应的AccountServiceImpl类,然后让这个类实现那个接口,如下:
通常情况下,我们在这个方法中是需要使用依赖注入的方式生成一个Dao层对象,然后使用Dao层对象中的那个方法的,但是现在我们还没有创建Dao层对象,因此我们先书写一个假方法,我们使用Spring提供的IOC尝试实例化AccountService类,我们现在里边书写如下方法:
@Override
public List<Account> findAll() {
System.out.println("业务层:查询所有");
return null;
}
最后也是最终要的一点,我们为这个类加上注解@Service,加上这个注解之后,Spring才会扫描到这个类并承认这个类在Spring中存在的资格,之后才能生产这个类的对象,我们可以简单的记作加上注解之后,就可以使用Spring生成它的对象了,Spring中提供的对象生成许可注解有四种:@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Repository,这四个注解的功能都一样,就是创建对象,我们有时甚至可以混用,但是在SSM中我们尽量不要混用,因为这四个注解是分别面向不同的层的对象生成的,如下所示:

因此我们在这里一定要为我们书写的这个实现类加上@Service注解,如图所示:
代码如下:
package com.spruce.service.impl;
import com.spruce.model.Account;
import com.spruce.service.interf.AccountService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Override
public List<Account> findAll() {
System.out.println("业务层:查询所有");
return null;
}
}
之后我们来正式配置Spring,我们首先创建配置文件,我们在之前在main中创建好的resource目录下新建一个spring目录,并在里边创建一个spring config类型的xml配置文件:
我们在其内部直接粘贴上如下配置信息:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--开启注解扫描,要扫描的是service-->
<context:component-scan base-package=""/>
</beans>
其中在<context:component-scan base-package=""/>中,我们为base-package添加属性,这个属性是一个包路径,内容是我们所想要让Spring托管的包,我们填入com.spruce,意思是将整个工程中的类都纳入其管理,我们可以根据自己的需求来缩小这个范围:
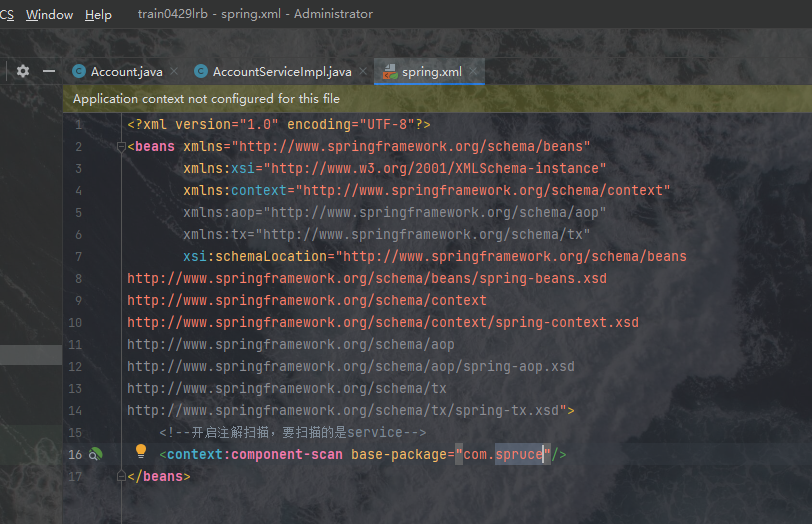
之后我们的Spring就配置好了,是的就是这么简单,接下来我们进行测试。
3.测试Spring我们使用Spring的目的在于让Spring为我们生成对象,因此我们要测试这个功能,我们在test下的Java中创建一个和工作空间同名的包com.spruce,并在下面创建一个TestSpring类,如下:
我们在里边放入如下代码:
package com.spruce;
import com.spruce.service.interf.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestSpring {
@Test
public void run(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring/spring.xml");//这里是spring.xml的路径,我们一定要书写对,该路径是以resource为出发点的相对路径,我们的目录结构中spring.xml放在了spring目录下,因此这里应该这样书写
AccountService service = ac.getBean(AccountService.class);
service.findAll();
}
}
这段代码就是测试一下Spring的IOC功能是否能用,我们点击test提供的运行按钮尝试一下:
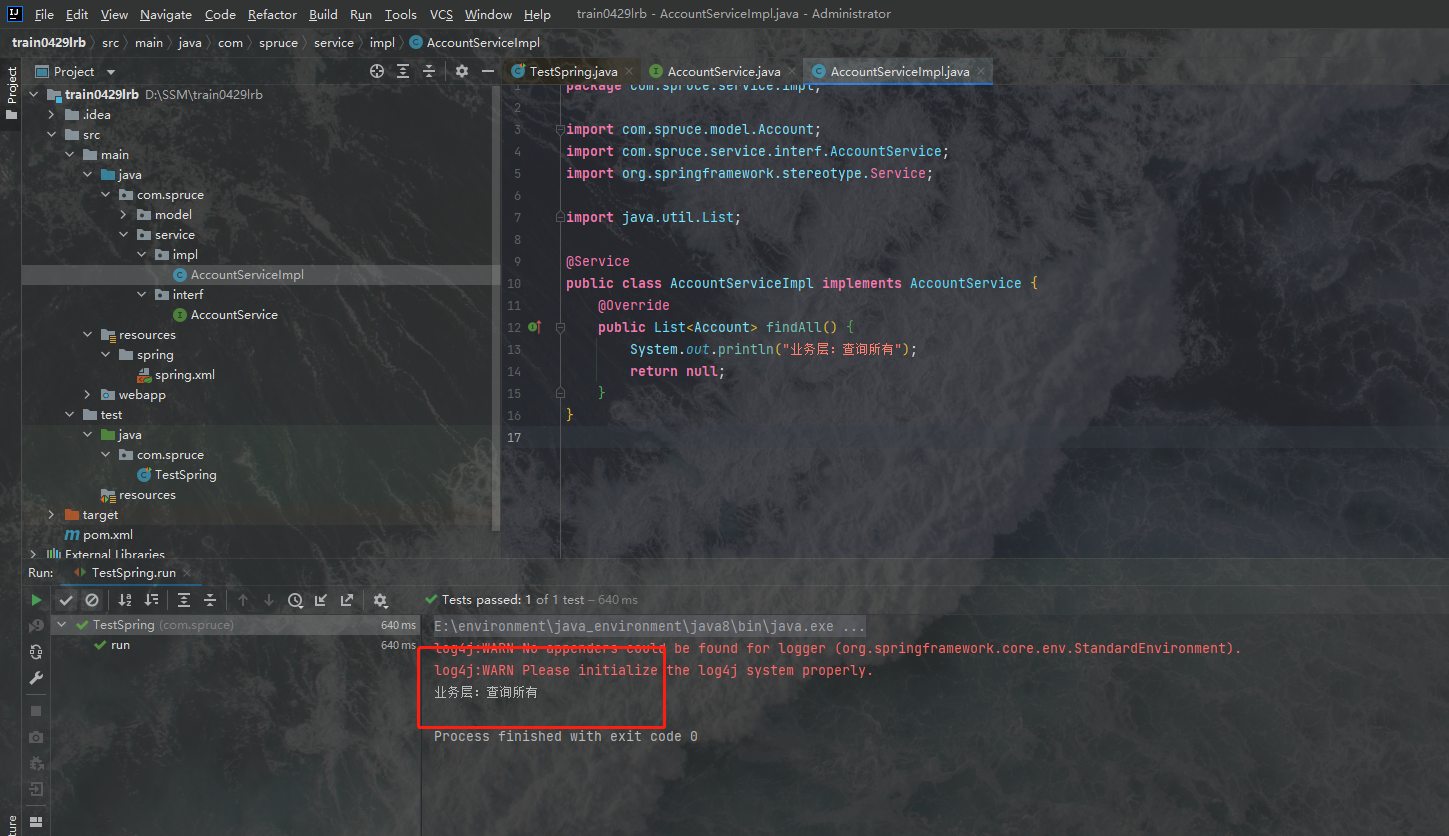
我们书写的假方法运行成功了,这说明类的对象被成功创建了,Spring层搭建成功!
2.7.Spring MVC框架的导入以及controller层的创建接下来我们开始创建controller层以及导入Spring MVC框架,Spring MVC支持的controller层主要也是使用IOC进行解耦,并且主要功能是实现请求的收发以及页面跳转的,整个项目的逻辑归他控制因此我们叫它控制层,接下来我们首先要配置Spring MVC。
1.Spring MVC框架的导入关于Spring MVC框架的导入我们可以直接看我之前写的这篇笔记:Spring MVC复习 —— 搭建Spring MVC项目 - 云杉木屋 - 自由互联 (cnblogs.com),在这里我们也重复的做一下。
首先我们将webapp中的web.xml配置信息换一下,我们换成这个:
<web-app version="3.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
</web-app>
然后我们在里边插入如下配置信息,配置我们的各种需要的工具:
<!--在web.xml中配置Spring提供的过滤器类 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--不拦截所有是html的页面请求-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.html</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--配置前端控制器,对浏览器发送的请求进行统一处理-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!--加载springmvc.xml配置文件的位置和名称,配置的是Spring配置-->
<init-param>
<!--contextConfigLocation:上下文配置路径,固定值-->
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!--classpath:类路径,值得是Java和resources文件夹-->
<!--springmvc.xml:指的是配置文件的名称:需要配置springmvc.xml,在下面-->
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--配置启动加载-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--开启项目时打开的页面-->
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>/index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
配置好之后的代码是这样的(直接把下面的代码完全粘贴在web.xml中也行):
<web-app version="3.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<!--在web.xml中配置Spring提供的过滤器类 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>encodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!--不拦截所有是html的页面请求-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>default</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.html</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--配置前端控制器,对浏览器发送的请求进行统一处理-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!--加载springmvc.xml配置文件的位置和名称,配置的是Spring配置-->
<init-param>
<!--contextConfigLocation:上下文配置路径,固定值-->
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!--classpath:类路径,值得是Java和resources文件夹-->
<!--springmvc.xml:指的是配置文件的名称:需要配置springmvc.xml,在下面-->
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--配置启动加载-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!--开启项目时打开的页面-->
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>/index.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
配置好之后我们会发现有个地方标红:
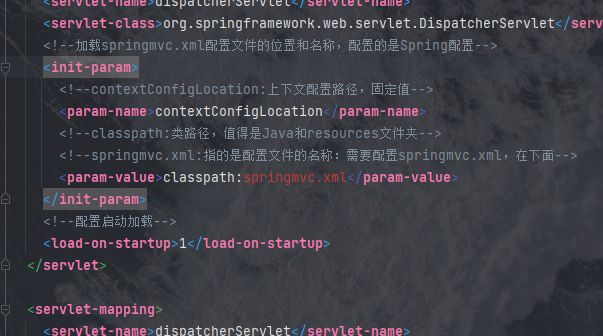
这是springmvc.xml文件的引用路径,加入这个配置信息意在监听Spring MVC的配置文件,以便于将Spring MVC整合进项目,现在我们还没有创建这个配置文件,因此它标红了,现在我们创建它,我们在resource目录下创建一个新的目录,明明为springMVC,然后在其下边创建springmvc.xml配置文件:
我们直接将下面的配置信息粘贴进去:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置spring创建容器时要扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package=""/>
<!--处理映射器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"/>
<!--处理器适配器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter"/>
<!--配置视图解析器-->
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="1"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<property name="templateEngine" ref="templateEngine"/>
</bean>
<!-- templateEngine -->
<bean id="templateEngine" class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver" ref="templateResolver"/>
</bean>
<bean id="templateResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/html/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".html" />
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置spring开启注解mvc的支持 默认就是开启的 ,要想让其他组件(不包含映射器、适配器、处理器)生效就必须需要配置了-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
</beans>
其中这里有一个和Spring配置文件中一样的标签<context:component-scan base-package=""/>,我们在此同样要书写我们的com.spruce路径:
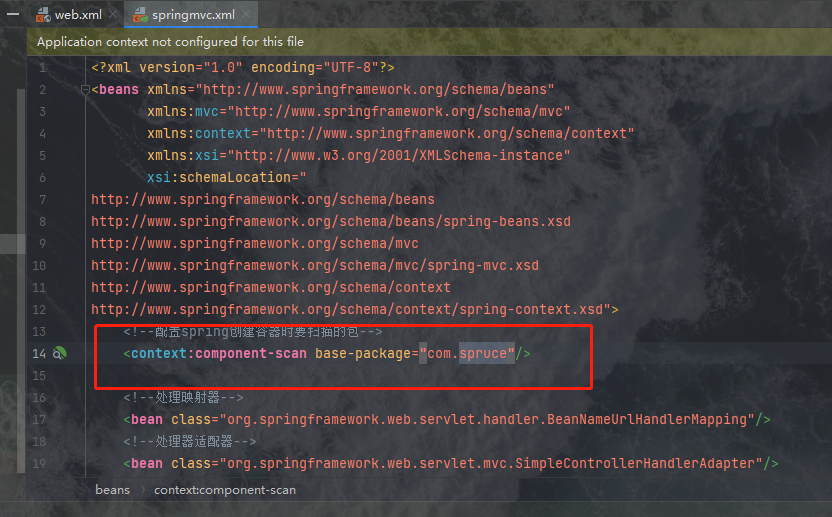
这里根据你的工作空间具体命名确定,只是我的工作空间名称为com.spruce,这里才这样填的。之后Spring MVC就相当于引入了,我们还要搭建相关的层以及目录结构对其进行测试。
2.搭建相关目录结构在springmvc.xml中有这样一个标签:
<bean id="templateResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring4.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/html/" /> <!--页面跳转时,路径的前缀,可以理解为我们的页面必须放在的目录的名字-->
<property name="suffix" value=".html" /> <!--页面跳转时,路径的后缀,也就是规定了我们页面文件的类型-->
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/> <!--我们页面使用到的前端规范,现在都用h5了,所以我们在这里也用h5-->
</bean>
这里边规定的东西是我们项目中的页面信息,在Spring MVC中页面跳转实际上使用到了一个字符串拼接的方式,controller层中的方法返回一个字符,然后根据这里的配置信息进行拼接,然后根据拼接好的字符串进行定位,所以第二三行中都是页面跳转时用到的信息标签,其中第二行是路径的前缀,它意味着我们的controller层中的方法返回了一个字符串之后,在字符串拼接的时候会首先在它前边加上/html/,而第三行中的则是后缀,它意味着会在该字符串的最后加上.html,举个例子,就是说我们的controller层中返回了一个“suc”,我们就会得到一个这样的字符串“/html/suc.html”,这个字符串意味着以webapp目录为起点的绝对定位下的html目录下的suc.html文件。
根据这个信息,我们首先要在webapp目录下创建一个叫html的文件来保存我们的html文件:
同时web.xml中还配置了欢迎页面:
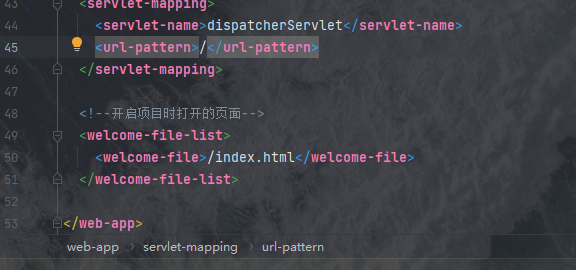
其路径是以webapp为起点的绝对路径:/index.html,我们的项目中没有这个文件,只有一个index.jsp,jsp文件现在已经不常用了,因此我们把它换成index.html文件,并在里边书写上如下的代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>主页</title>
</head>
<body>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>入门程序</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>入门</h3><a href="/SSMDemo/hello" >入门程序</a>
</body>
</html>
</body>
</html>
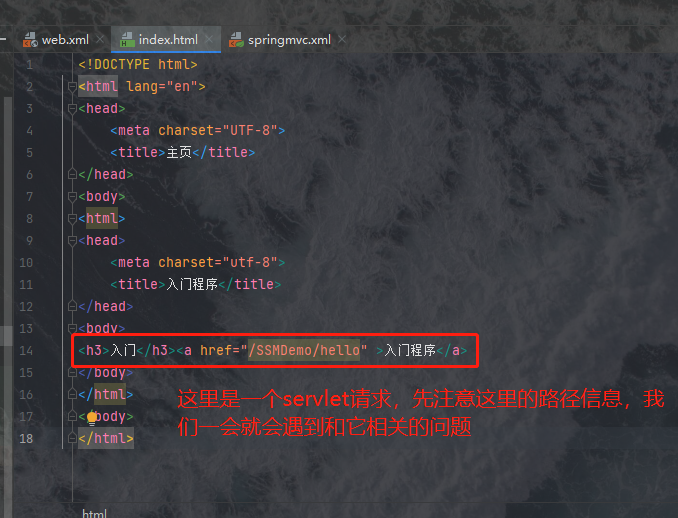
之后我们的页面相关事项基本就处理好了,我们接下来书写controller层。
3.controller层及相关文件配置我们首先要在com.spruce下面创建一个名为controller的包:
然后我们在这个包里创建我们相关的controller类就行了,我们现在新建一个名为AccountController的类,如图所示:
之后我们将Spring MVC整合到Spring中去,方法为将如下代码粘贴到web.xml文件中去:
<!--配置Spring的监听器-->
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--配置加载类路径的配置文件-->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
粘贴好之后如图所示:
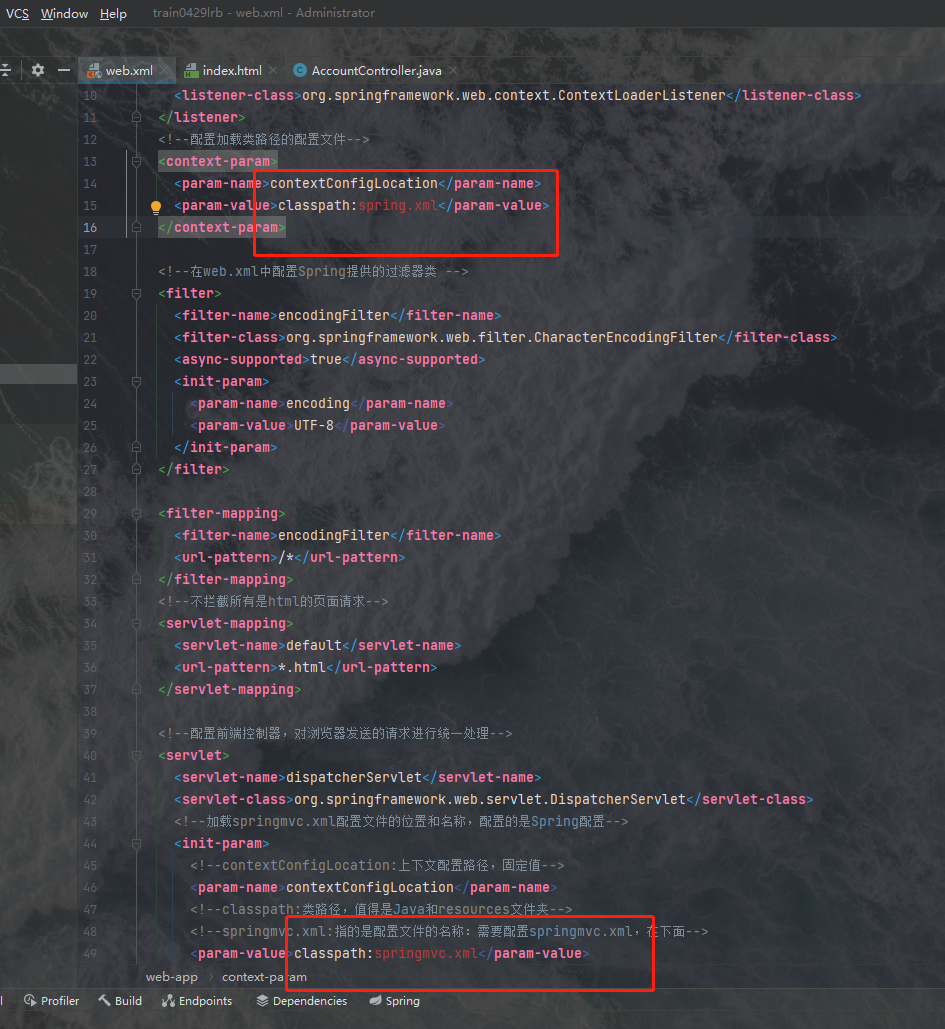
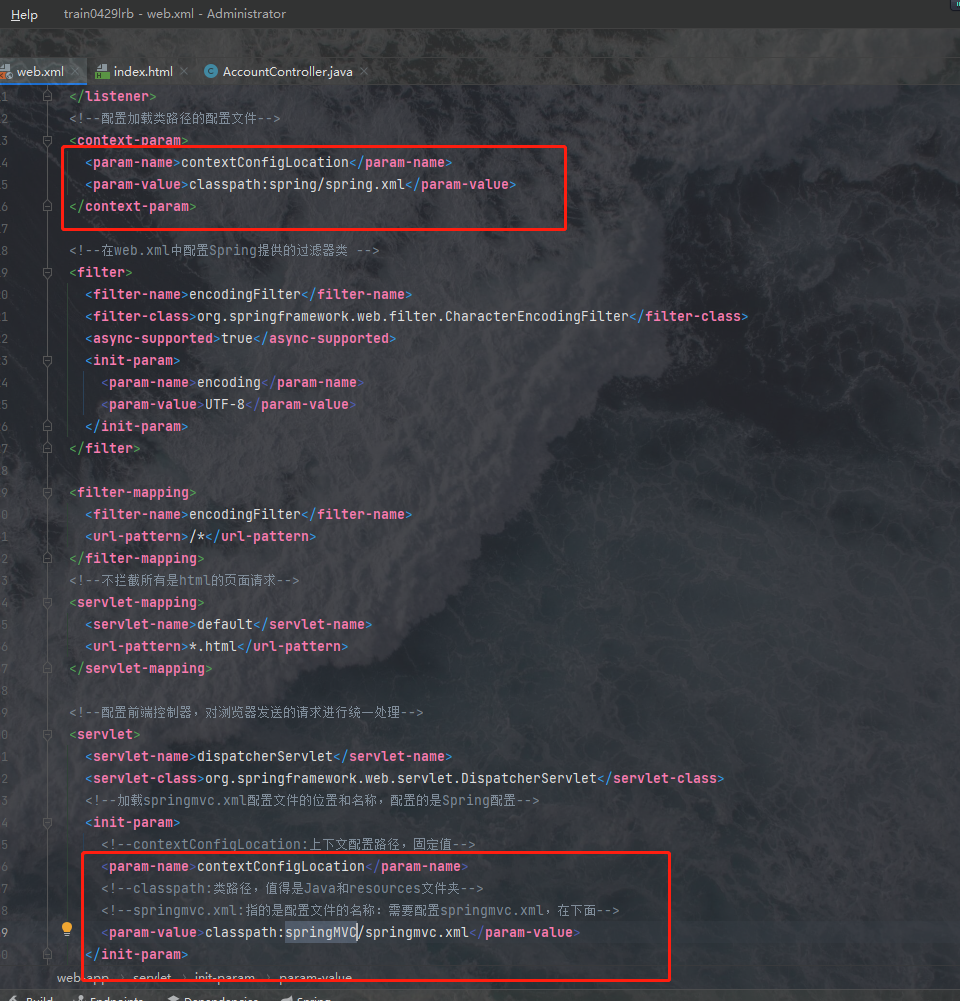
两个报错的地方是因为路径不对,我们改一下路径即可:
之后我们在AccountController中粘贴如下的代码:
package com.spruce.controller;
import com.spruce.service.interf.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/account")
public class AccountController {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
/**
* 处理超链接发送出来的请求
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(path = "/hello")
public String sayHello(Model model){
System.out.println("入门方法执行了2...");
// 向模型中添加属性msg与值,可以在html页面中取出并渲染
model.addAttribute("msg","hello,SpringMVC");
// 配置了视图解析器后,写法
return "suc";
}
}
其中我们在代码的 的上边加入了一个注解@Autowired,这个注解的意思是依赖注入,也就是让spring为其生成一个对象,我们就无需自己生成对象了,在之后我们就可以直接调用这个对象的方法了,这个对象是AccountService接口类型的,在生成对象的时候,Spring会根据Service的接口及实现方式生产一个新对象,新对象是使用多态的方式(实际上二者结构完全一致,因此并没有明显体现多态的含义)生成了一个接口类型的对象,我们只需调用这个对象,就可以规范的使用我们之前定义的方法。我们必须完成上边的整合步骤之后,才能使用这个依赖注入的功能。
的上边加入了一个注解@Autowired,这个注解的意思是依赖注入,也就是让spring为其生成一个对象,我们就无需自己生成对象了,在之后我们就可以直接调用这个对象的方法了,这个对象是AccountService接口类型的,在生成对象的时候,Spring会根据Service的接口及实现方式生产一个新对象,新对象是使用多态的方式(实际上二者结构完全一致,因此并没有明显体现多态的含义)生成了一个接口类型的对象,我们只需调用这个对象,就可以规范的使用我们之前定义的方法。我们必须完成上边的整合步骤之后,才能使用这个依赖注入的功能。
上边我们整合配置的目的在于:在controller中能成功的调用service对象中的方法。方法原理是: 在web.xml中配置ContextLoaderListener监听器,该监听器默认加载WEB-INF目录下的applicationContext.xml的配置文件,我们修改全局的路径变量: ,进而让加载的文件变成我们的目标文件,这样一来,在项目启动的时候,就去加载spring.xml的配置文件了,而我们的spring就可以直接在这里使用了。
,进而让加载的文件变成我们的目标文件,这样一来,在项目启动的时候,就去加载spring.xml的配置文件了,而我们的spring就可以直接在这里使用了。
在上面的controller代码中,类上边的@Controller代表该类被Spring托管来产生对象,这个对象的调用则是被Spring MVC申请的,这个对象的调用将使用反射的方式在我们进行Servlet请求的时候隐性的被调用,而@RequestMapping("/account")则是其Servlet请求路径,这是一级路径,里边的方法上的注解@RequestMapping(path = "/hello")是二级路径,它们用来进行精确寻址。而这个方法的返回值"suc",在Spring MVC中被默认解析为一个路径,也就是上边我们提到的文件路径,它返回之后将被拼接成一个完整的路径,用于寻找页面视图。我们在上边配置的是html目录下的html类型文件,因此为了让这个返回有地方可去,我们在html目录下创建一个suc.html,并书写如下代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>成功页面</title>
</head>
<body>
你好,我是成功页面!
</body>
</html>
之后关于controller层的东西就基本上创建好了,我们为该项目配置上Tomcat服务器,然后进行测试。
4.配置Tomcat服务器首先我们点击这里:
我们点击第一个选项:
之后就会弹出一个这样的框:
点击加号:
我们选择Tomcat下的local:
之后就会进入如下界面:
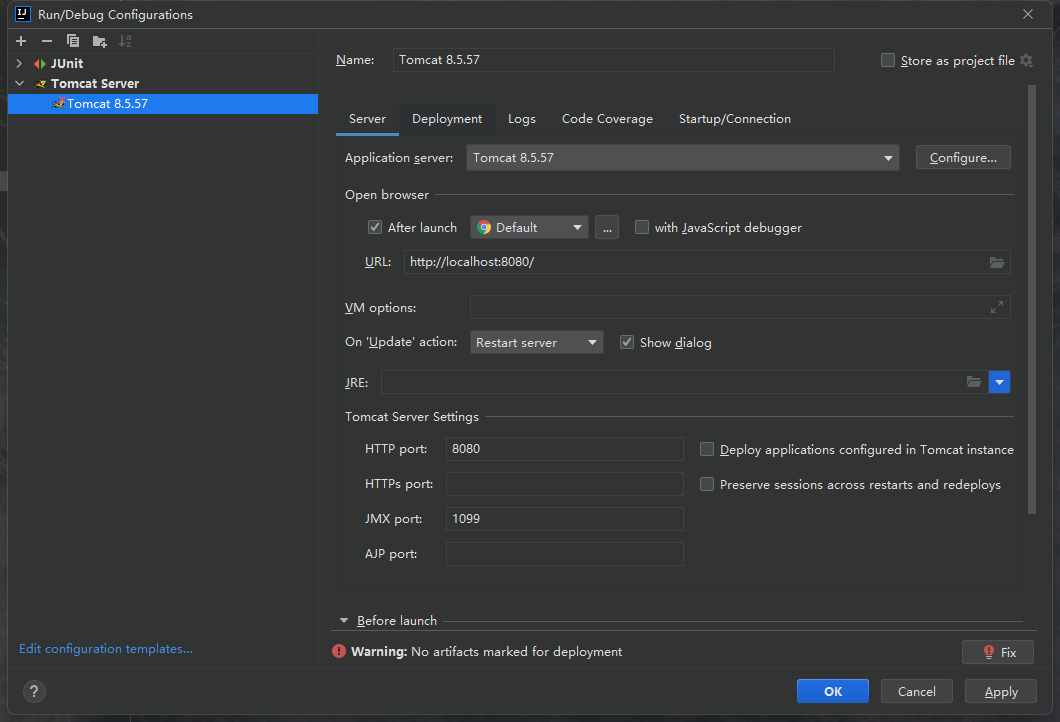
点击Deployment按钮之后,我们就会进入下面的选项:
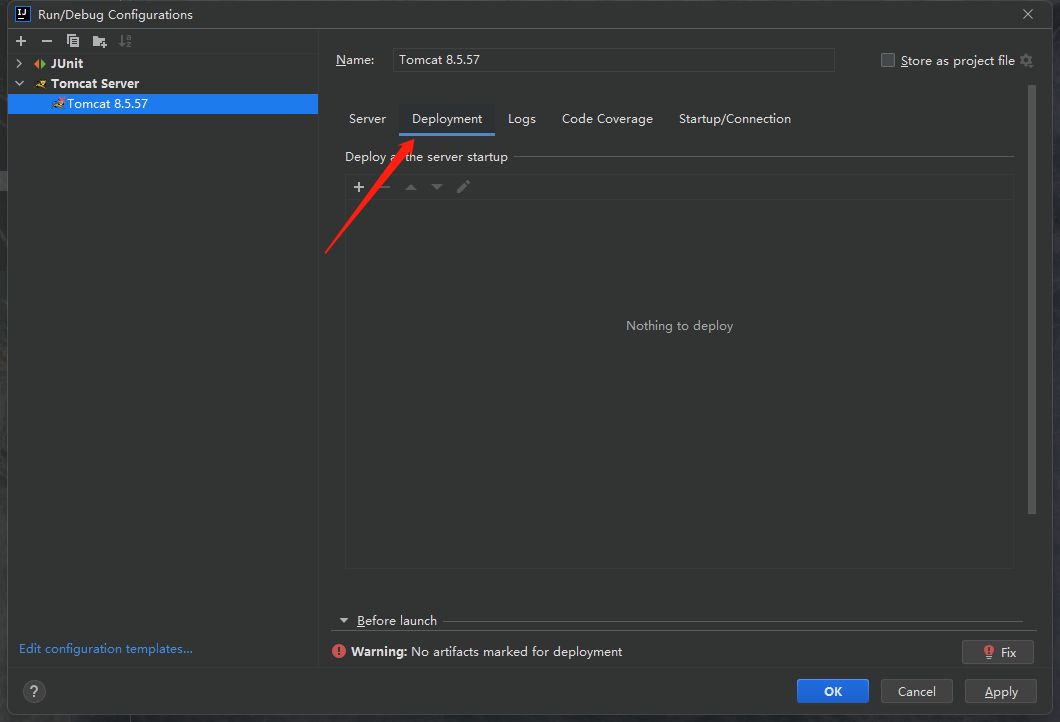
点击下图中箭头指向的加号:
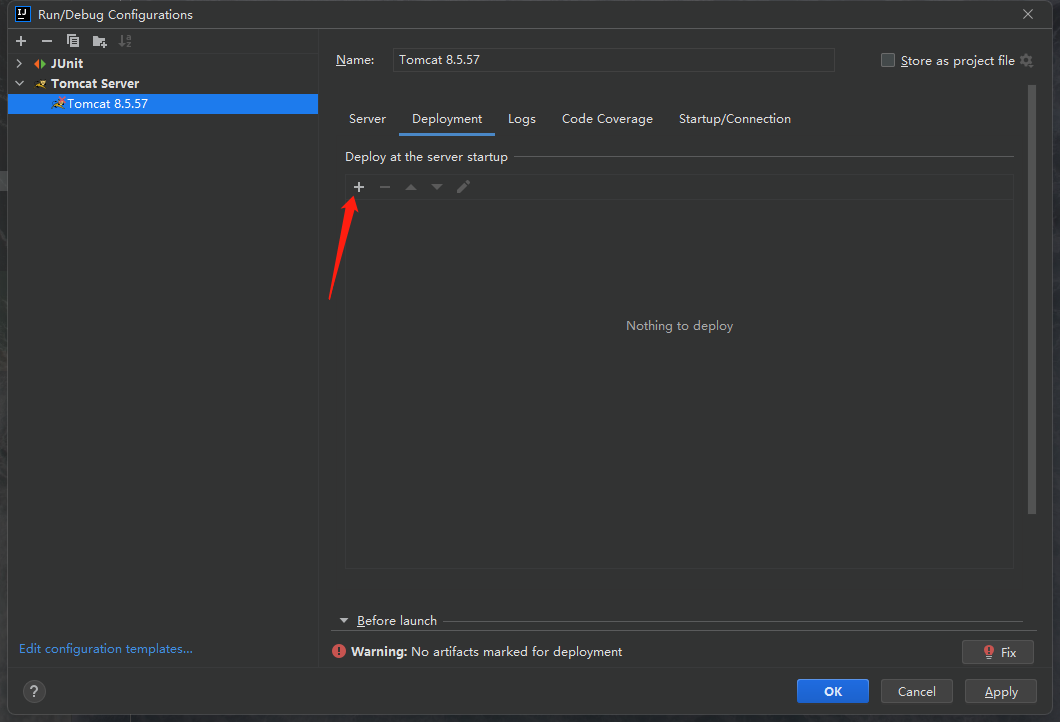
点击第一个选项:
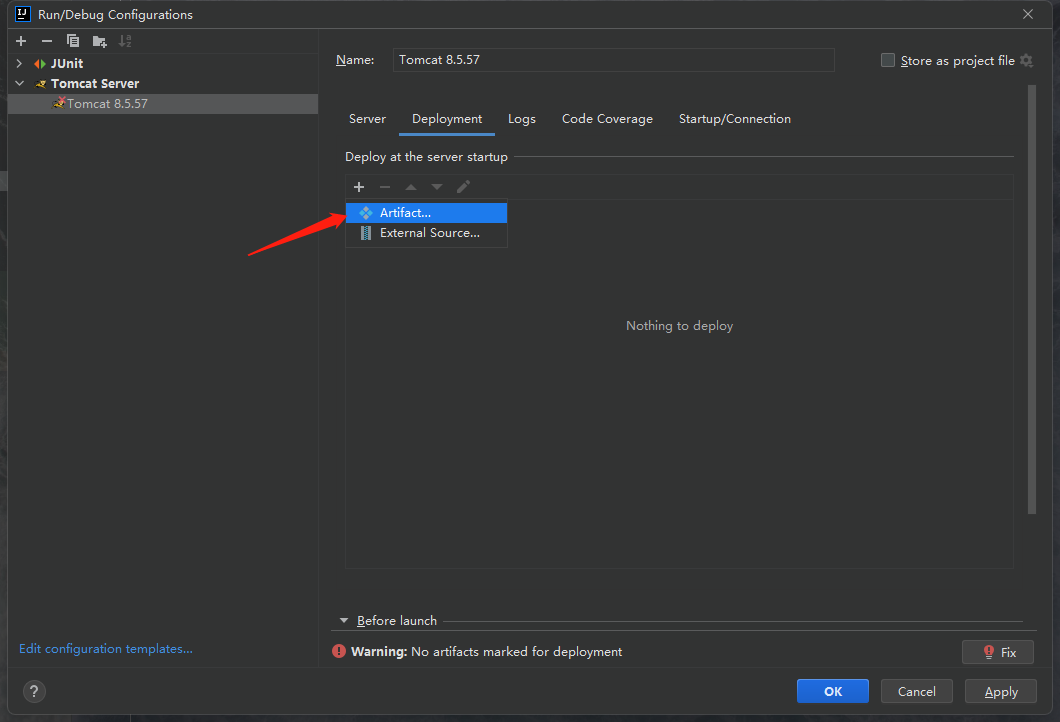
选择第二个选项:
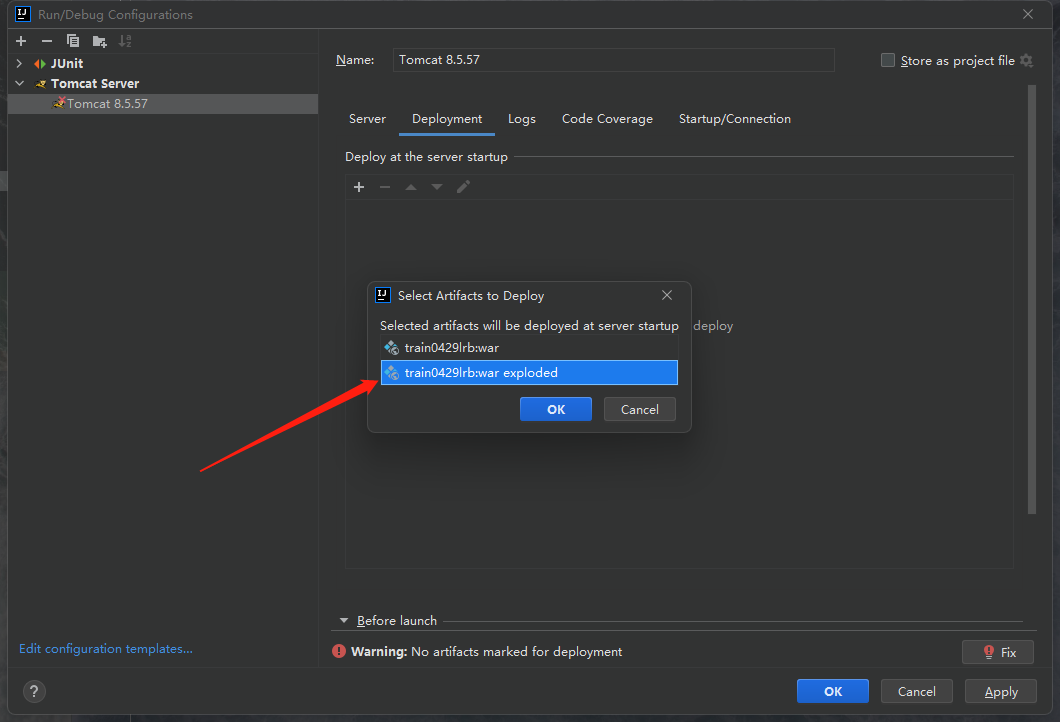
报错就会消失并出现如下的栏目:
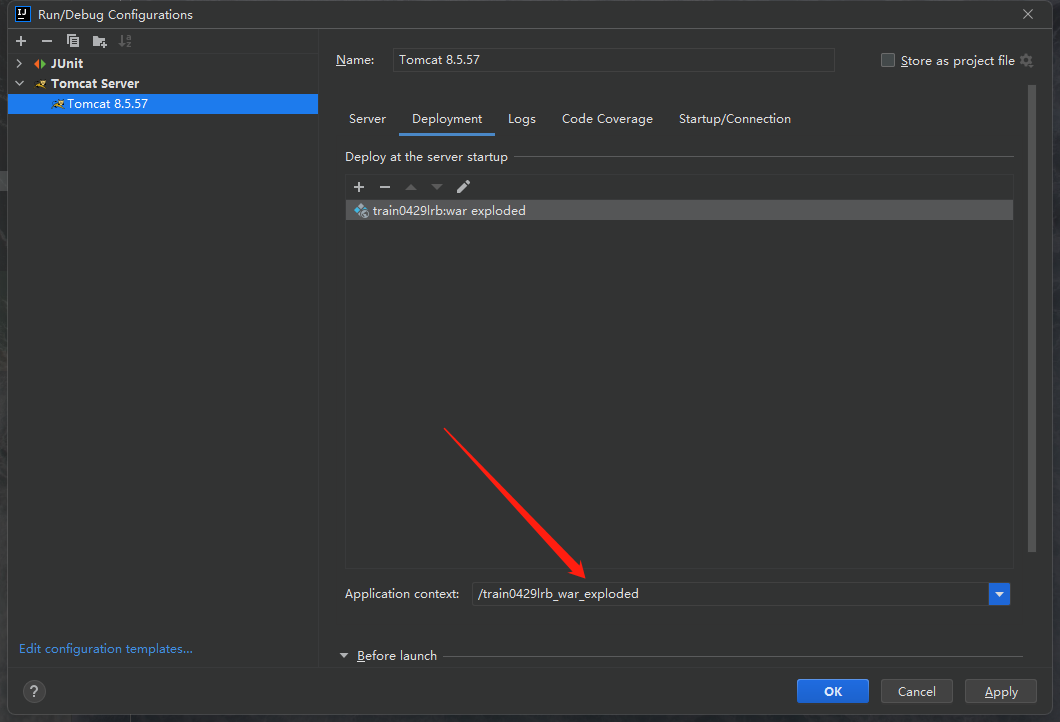
我们发现新出现的栏目中是一串字符,内容是我们的项目名称_war_exploded,我们删除掉_war_exploded部分,让这里的内容变成我们的项目名称:
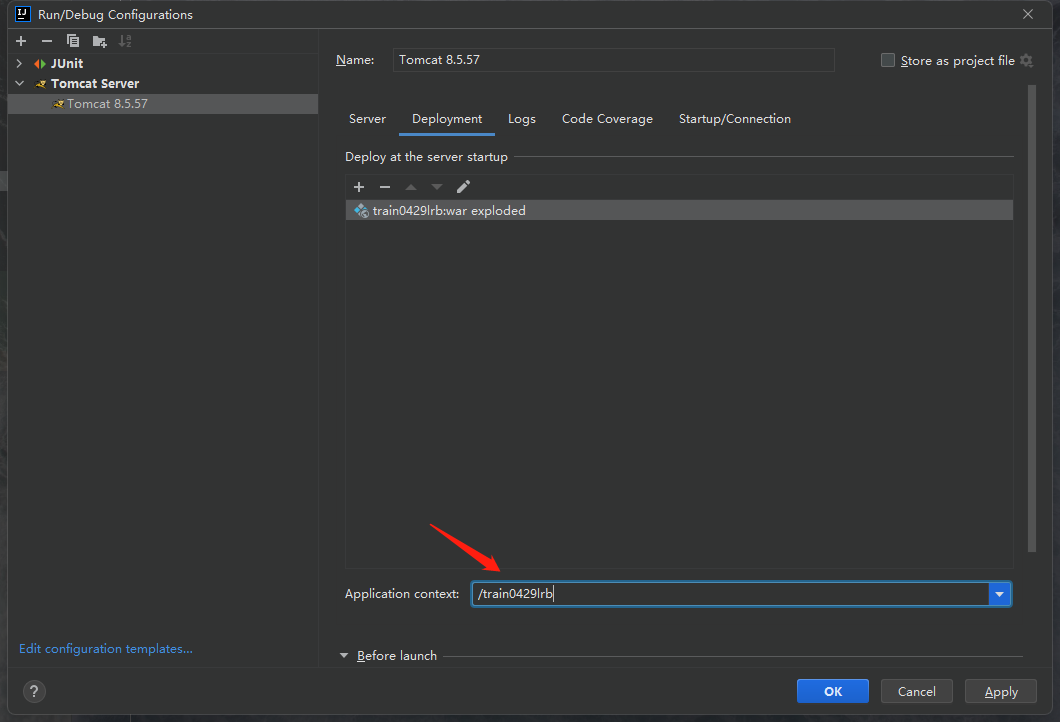
然后点击Apply->OK之后就好了。
我们直接点击绿色箭头让Tomcat运行起来:
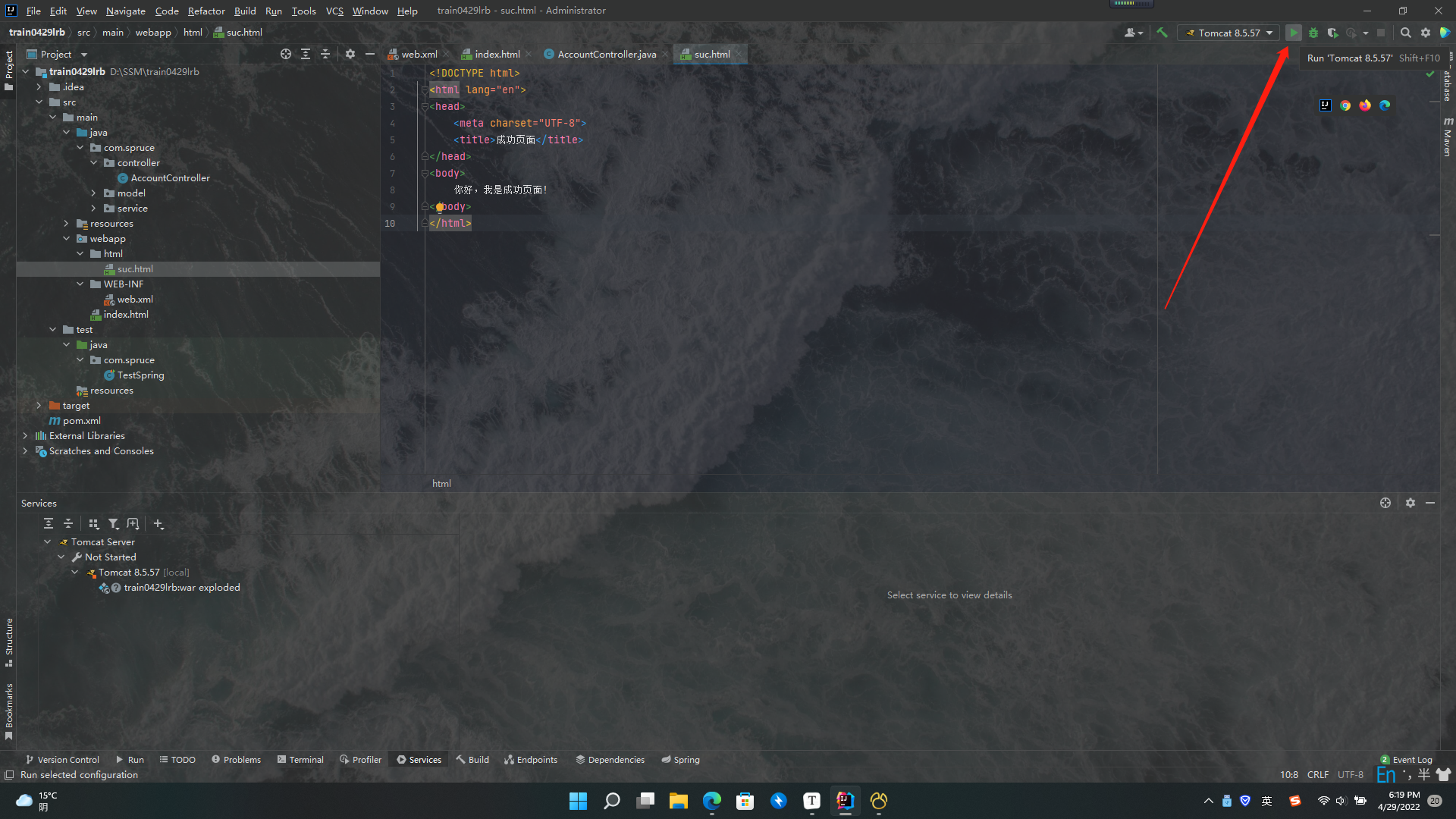
我们首先就会进入之前配置好的index.html页面,如下:

之后我们点击入门程序,进行跳转,根据上面我们书写的代码,我们知道点击这个连接会触发我们写好的servlet程序,并进行寻址,找到account/hello并执行,这个代码在controller层,这个代码会让我们跳转到html/suc.html,我们点点看:
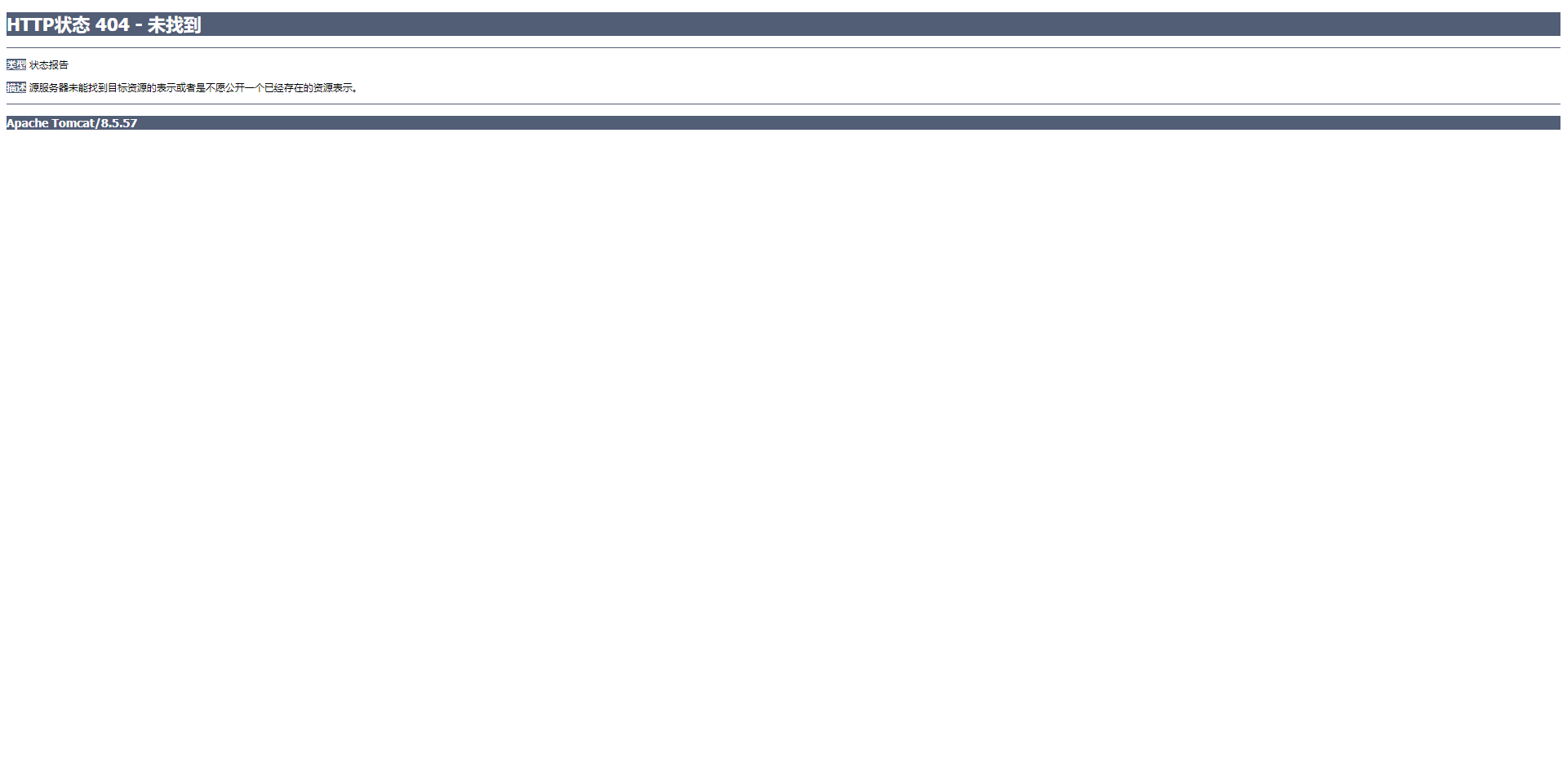
拉垮了,不行,这是为什么?404错误意思是url路径错误,还记得我们在上面的步骤中,就是在书写index.html页面的代码中做了一个提示吗,问题就出在那里,我们的请求路径没写对,现在我把那个代码拿到这里来看:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>主页</title>
</head>
<body>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>入门程序</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>入门</h3><a href="/SSMDemo/hello" >入门程序</a>
</body>
</html>
</body>
</html>
我们的路径是"/SSMDemo/hello",第一级目录是"SSMDemo",这是我们的项目名,我这里的代码因为是直接复制的老师给我的,这个项目名是老师的项目名所以错了。那么我们改成我们自己的“/train0429lrb/hello”就行了吗?答案还是不行,我们应该应该还记得我们在书写controller的时候还配置了一个二级路径,第一级为account,这个路径给在了类上,而hello才是给定在了方法上,这里这个跳转我们是想调用那个方法,那就应该把路径写全进行精确调用,因此路径应该是这样:“/train0429lrb/account/hello”,我们的index.html代码应该是这样:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>主页</title>
</head>
<body>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>入门程序</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>入门</h3><a href="/train0429lrb/account/hello" >入门程序</a>
</body>
</html>
</body>
</html>
我们重启项目再次测试:

跳转成功!尽管有乱码错误,但是根据我们最后书写的那个感叹号,我们可以依稀判断出,这句话就是我们在suc.html中书写的:你好,我是成功页面!,关于编码问题,我会在文章的最后进行研究,这里如果你想让效果更明显的话,可以先改成英文,这样就不会出现乱码。
现在我们来进行最后一个步骤的配置,这个步骤的配置可能比较繁琐,我们现在来配置Dao层和MyBatis框架。
1.创建数据库信息配置文件我们首先创建用来填写数据库信息的配置文件,我们可以将数据库信息直接填在xml文件中,也可以新建一个properties文件,然后将数据库信息放在这里边,在xml文件中用变量的形式来填写,两种方法均可,配置文件的方式更利于后人维护时更改,因此我们使用这种更为先进的方法,我们首先创建一个MyBatisConfig目录,然后在下面创建一个SqlMapConfig.xml文件,一个jdbc.properties文件:
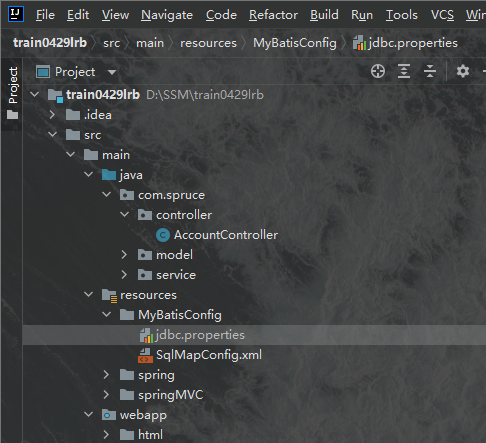
我们在jdbc.properties文件中书写下列信息:
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:你的数据库服务端口名/你的数据库名称?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false
username=你的数据库用户名
password=你的数据库用户密码
initialSize=0
maxActive=20
maxIdle=20
minIdle=1
maxWait=60000
然后我们在SqlMapConfig.xml中书写如下配置信息:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd">
<!-- 自动扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.spruce" /> <!--MyBatis托管的包路径-->
<!-- 引入配置文件 -->
<bean id="propertyConfigurer"
class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
</bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${url}" />
<property name="username" value="${username}" />
<property name="password" value="${password}" />
<!-- 初始化连接大小 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="${initialSize}"></property>
<!-- 连接池最大数量 -->
<property name="maxActive" value="${maxActive}"></property>
<!-- 连接池最大空闲 -->
<property name="maxIdle" value="${maxIdle}"></property>
<!-- 连接池最小空闲 -->
<property name="minIdle" value="${minIdle}"></property>
<!-- 获取连接最大等待时间 -->
<property name="maxWait" value="${maxWait}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- spring和MyBatis完美整合,不需要mybatis的配置映射文件 -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!-- 自动扫描mapping.xml文件 -->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapping/*.xml"></property> <!--你的mapper类型的xml文件路径-->
</bean>
<!-- DAO接口所在包名,Spring会自动查找其下的类 -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.spruce.dao" /> <!--你的dao层接口路径-->
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean>
<!-- (事务管理)transaction manager, use JtaTransactionManager for global tx -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
</beans>
这是一个比较完善的MyBatis配置文件,以后我们可以直接使用它作为模板,现在我们复制进入:
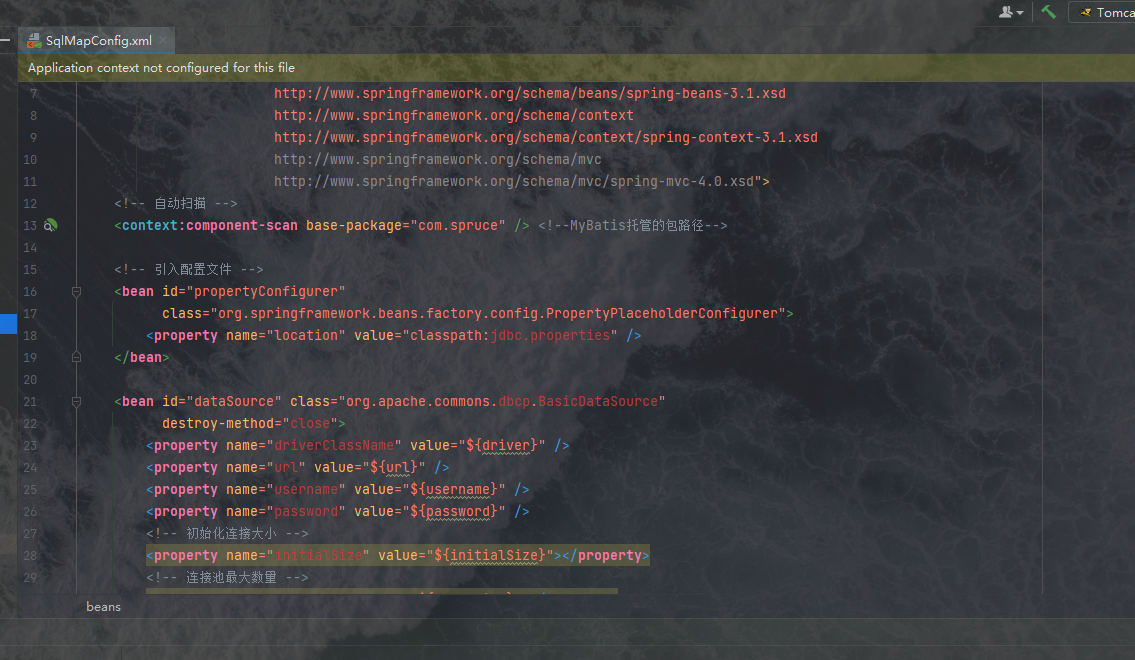
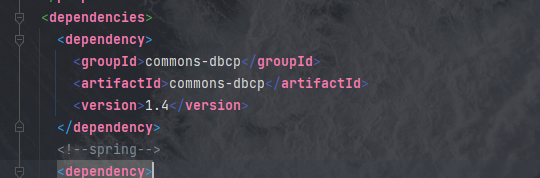
配置文件出报错是因为我们的路径有误,而下面的类找不到问题则是我们没有导入commons-dbcp.jar包,我们逐一修正这些问题,我们在pom文件的坐标依赖中加入下面的语句:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-dbcp</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-dbcp</artifactId>
<version>1.4</version>
</dependency>
之后就好了:
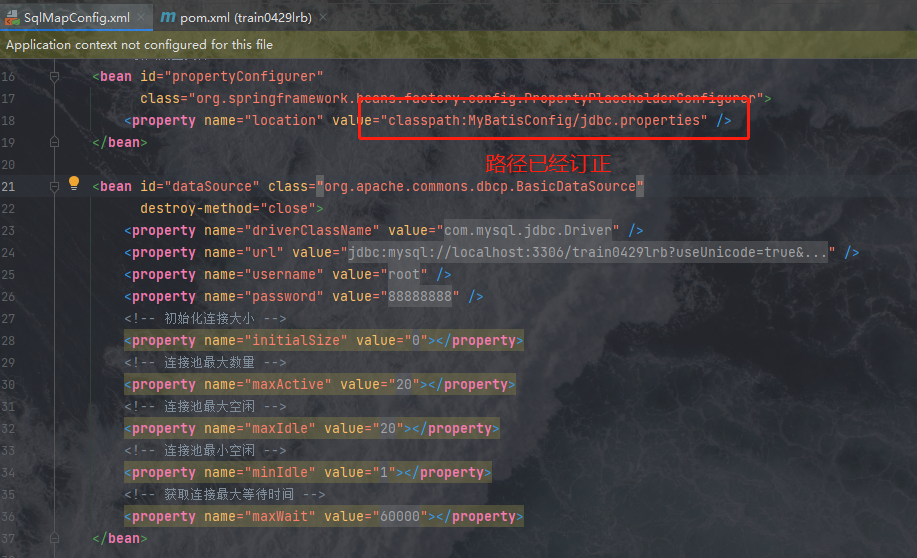
需要注意的是这个包不能导入太新的,太新的里边去掉了这个类,导致仍然报错,我们使用1.4版本就完全没问题。(这些东西已经上升到玄学的约定问题了,没有一定之规,只要不报错就能用)
最后我们还有一个检测mapper类型配置文件的位置也报错,这是因为我们还没有创建这个目录:
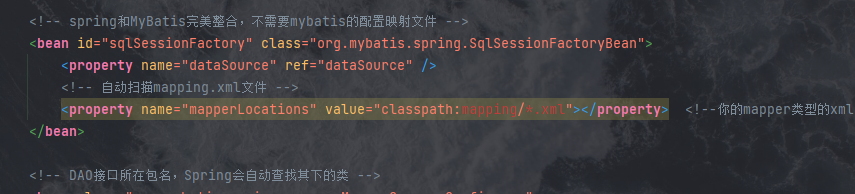
我们现在来创建这个目录:
等我们往里边创建了实现数据操作的xml配置文件之后就完全不会报错了,这个属于下个步骤的内容。
2.搭建Dao层Dao层分为两部分,一部分为Dao层接口,一部分为mapping中的实现配置文件,我们现在都没创建,我们先创建Dao层接口,我们现在com.spruce下创建一个新包:dao
然后我们在里边书写一个针对account的dao层接口类AccountDao:
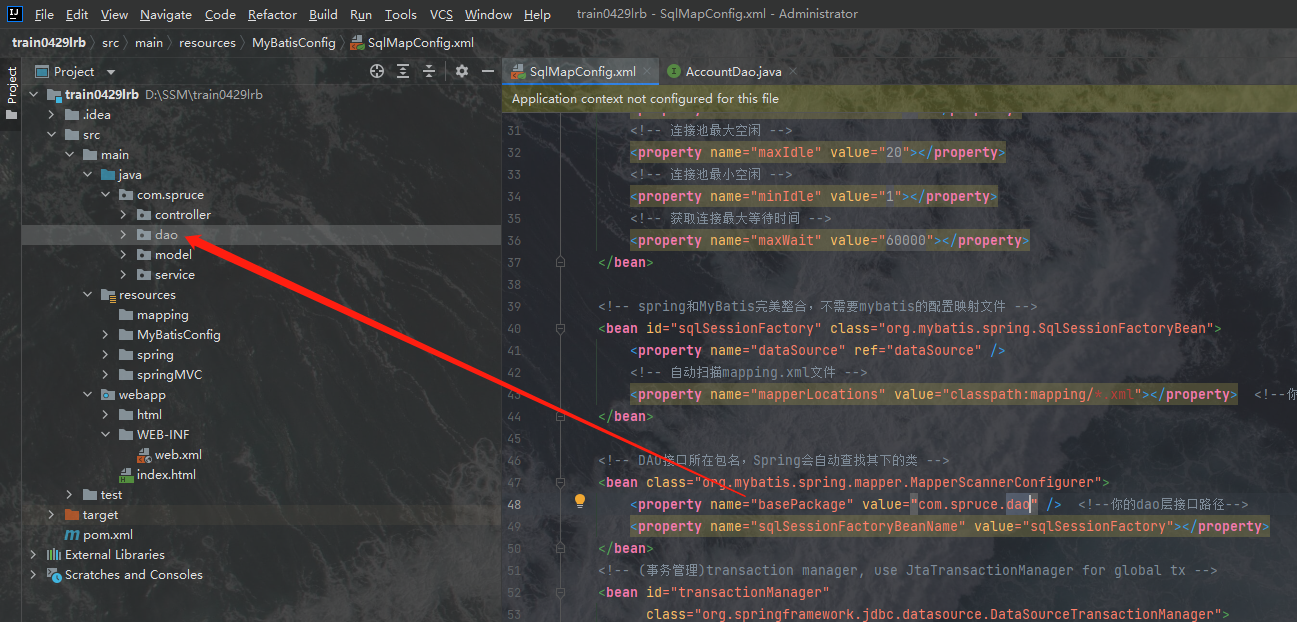
如上图所示我们创建好了Dao层的接口,需要注意的是在配置文件中,MyBatis里边也需要用到Spring对Dao层的类进行托管,这个托管的作用是使用IOC的思想生成Dao层对象时用到的。之后我们在Dao层中的接口下书写如下代码:
package com.spruce.dao;
import com.spruce.model.Account;
import java.util.List;
public interface AccountDao {
public List<Account> findAll();
}
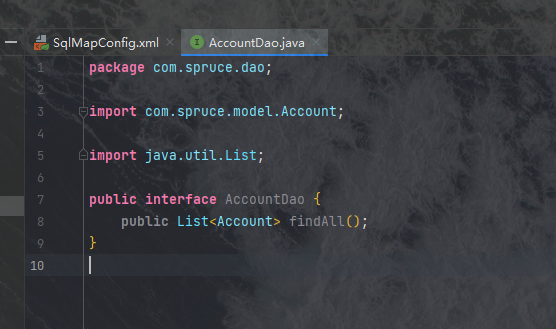
然后我们在mapping中书写一个关于Account的全览方式的实现:
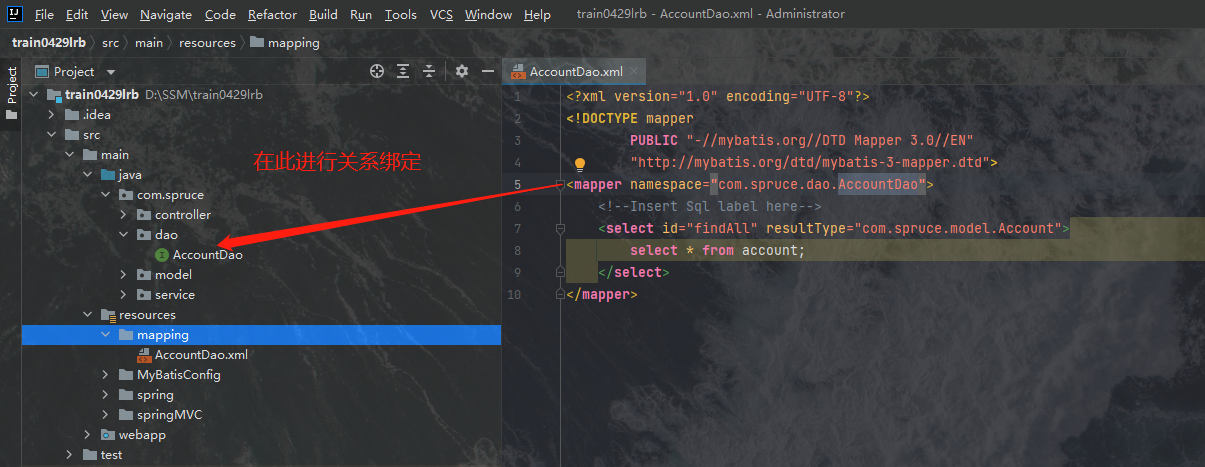
之后Dao层就创建好了,最后我们将MyBatis加入到Spring的配置文件中去,我们将将如下代码复制到web.xml文件中去:
<!-- 配置加载类路径下的applicationContext.xml配置文件 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- 配置监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
需注意的是我们如果直接将这个代码复制进去的话必定报错,这是因为我们已经配置过一个监听器了,mybatis的监听器和spring的监听器重名了,因此我们首先需要给mybatis的监听器改个名字,然后直接将它复制进去即可:
<!-- 配置加载类路径下的applicationContext.xml配置文件 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation1</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
但是,这种方式万万不行的,初学的我天真的以为这样就行了,实际上不行,我亲自尝试的结果告诉我们,这种方法是错误的,且说出来会被嘲笑,这是因为这个监听器只能监听这个contextConfigLocation名字的文件,如果这么写的话会导致整个mybatis无法使用,在创建dao层对象是,依赖注入出现问题:
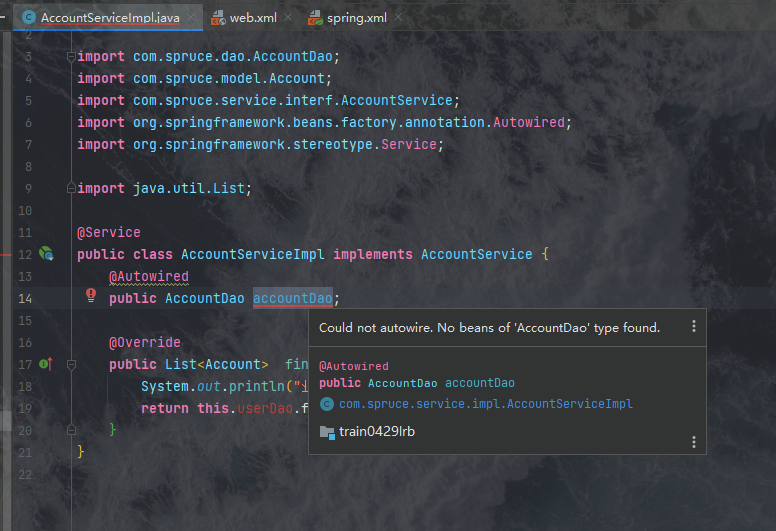
如果大家碰到这种问题那就是监听器没配置对,我们如何解决这个问题呢?我们对比之前书写的spring.xml和SqlMapConfig.xml会发现二者在开有一个标签是重复的:
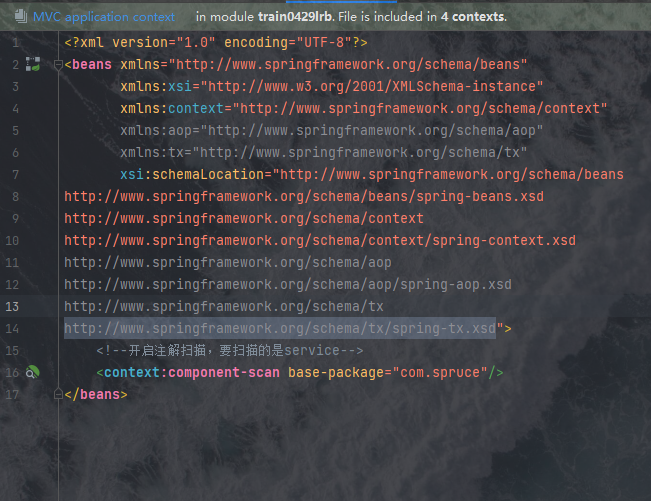
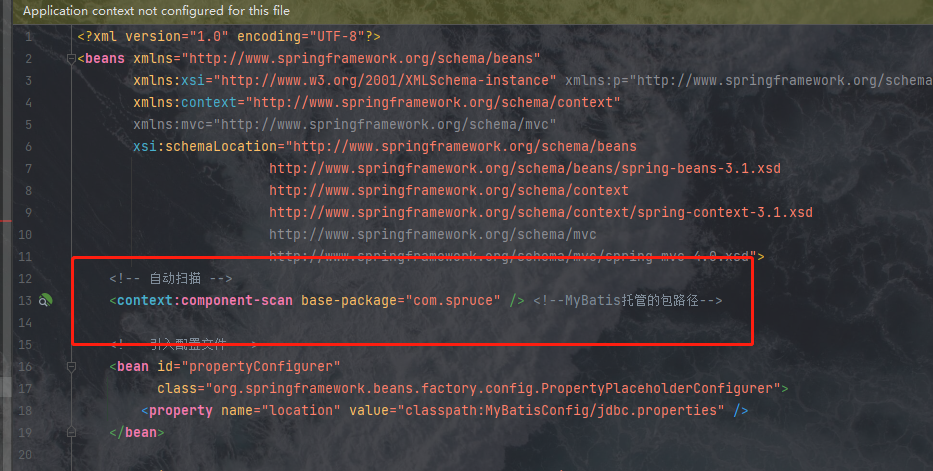
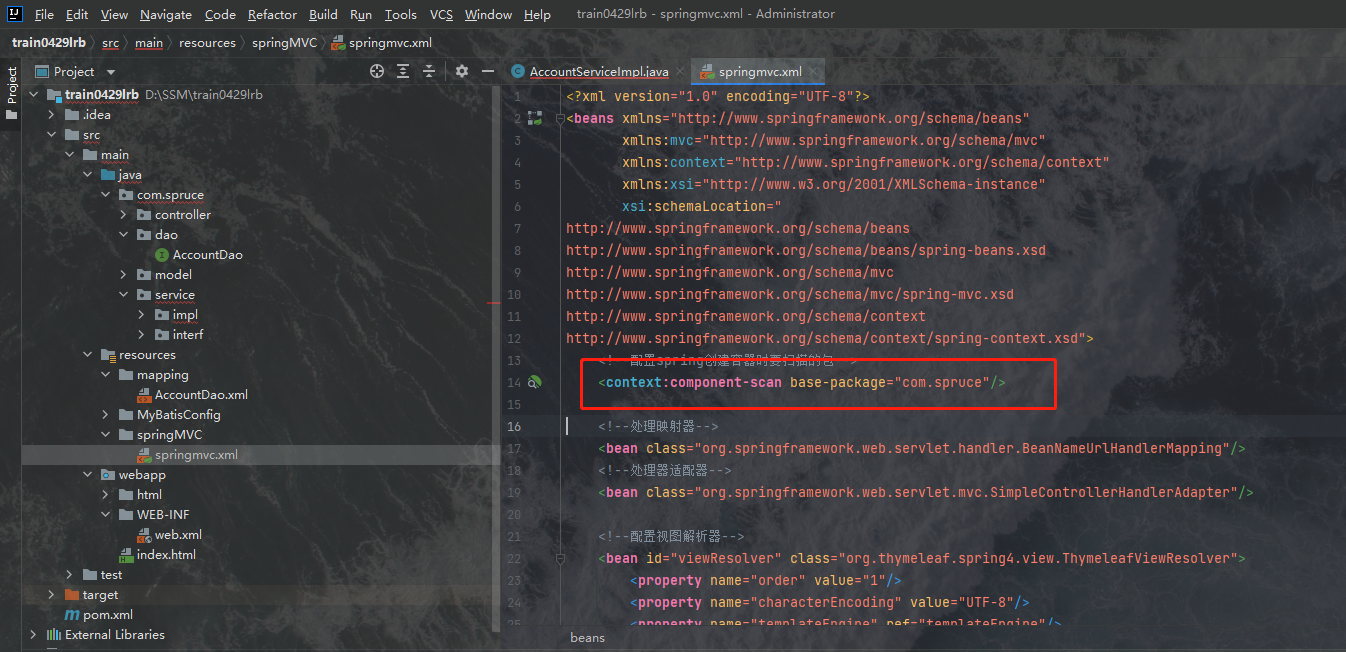
实际上,两个标签是同一个东西,就是Spring托管,因此我们完全可以将spring.xml删除掉,然后将其配置融入进mybatis的配置文件中:
然后我们惊喜的发现这里就不报错了:
因此在书写配置文件时,由于Spring的配置文件过于简单并且和其他的配置文件都是相容的,因此我们可以将Spring的配置文件书写进MyBatis的配置文件中去或者书写进Spring MVC的配置文件中去,我个人觉得书写进Spring MVC的里边更好一点。
而实际上我已经这么做了,只不过是因为我刚才不懂,才会忽略这个部分。
2.9.测试我们现在开始测试:
1.书写Service层的方法package com.spruce.service.impl;
import com.spruce.dao.AccountDao;
import com.spruce.model.Account;
import com.spruce.service.interf.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
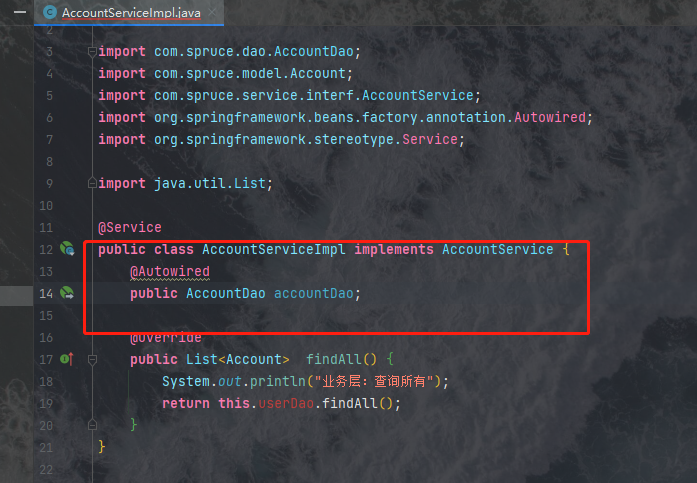
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
public AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public List<Account> findAll() {
System.out.println("业务层:查询所有");
return this.accountDao.findAll();
}
}
package com.spruce.controller;
import com.spruce.model.Account;
import com.spruce.service.interf.AccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.util.List;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(path = "/account")
public class AccountController {
@Autowired
private AccountService accountService;
/**
* 处理超链接发送出来的请求
* @param model
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(path = "/hello")
public String sayHello(Model model){
System.out.println("入门方法执行了2...");
List<Account> accounts = accountService.findAll();
for (Account account: accounts) {
System.out.println(account.toString());
}
// 向模型中添加属性msg与值,可以在html页面中取出并渲染
model.addAttribute("msg","hello,SpringMVC");
// 配置了视图解析器后,写法
return "suc";
}
}
根据逻辑,我们调用这个方法会使得控制台中输出我们的查询结果,我们运行尝试:
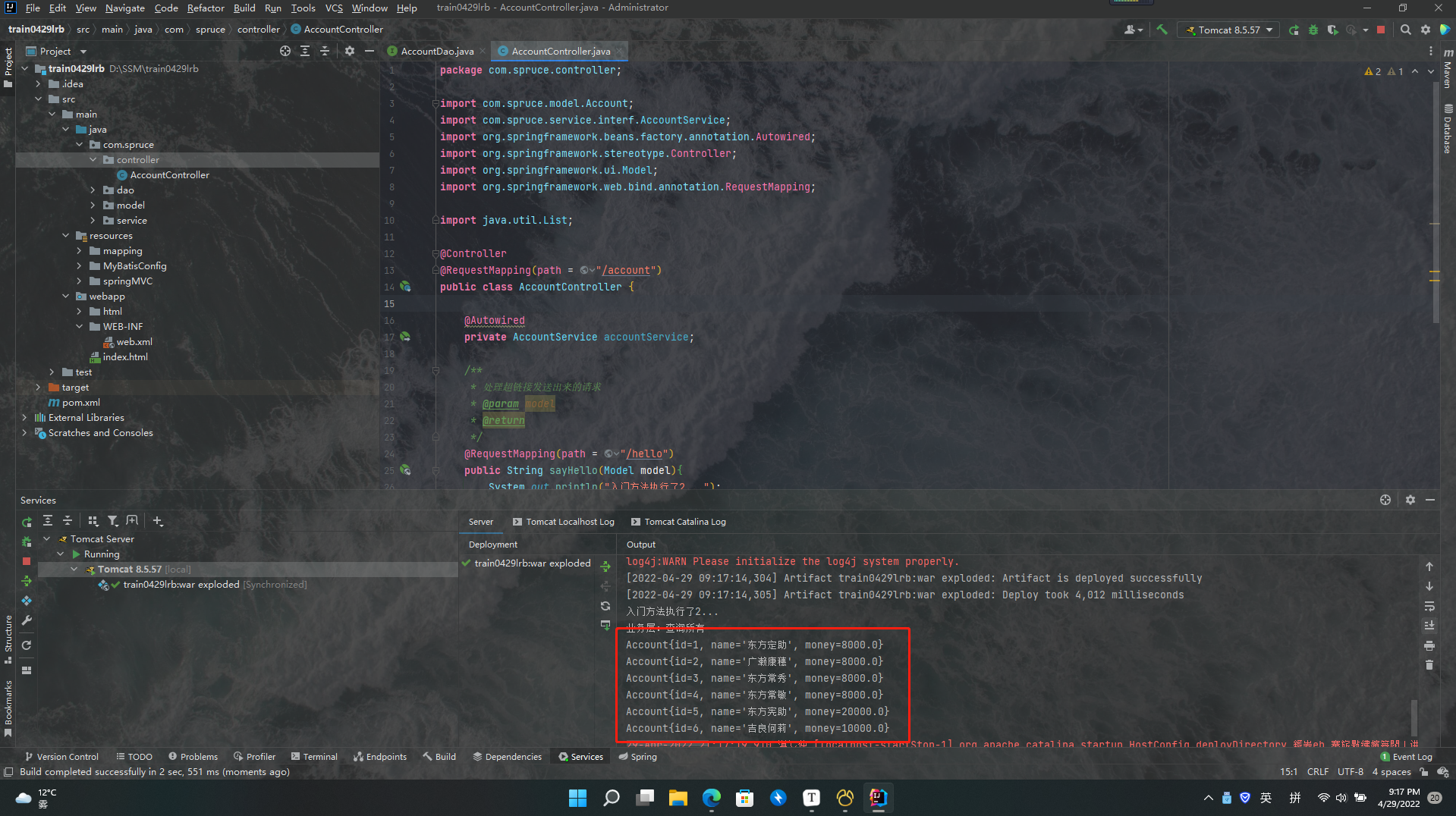
执行成功!太感动了!我们整体上在controller层和service层使用了依赖注入,这两个地方的依赖注入都是依托的spring的IOC容器,整个项目的依赖注入都没问题说明我们的SSM项目已经整合成功,赛高泥嗨铁鸭子哒!!!!!!!
在SSM项目整合成功之后我们就可以愉快的使用它进行开发了,使用SSM开发是一种非常简单的事情,我们只需创建两个接口然后写crud就行了,难一点的顶多是设置个懒加载,连接个LayUI,不过都无所谓了,都是简单的使用工具吗,而创建SSM项目却是一件让人血压飙升的事情,即使创建完成了,我也仍然是不太懂,还有更多的知识在等着我。
附录:关于编码的问题,我最终解决了,详情见下面的链接针对本项目的编码问题解决。
