编译原理初衷 想把编译这里做成一个新的系列,主要跟我的课程有关,但是与作业没有关系。 只讲 词法分析 和 文法分析 。因为大部分高校集中学这里,根据给编译的课时来看,讲到
想把编译这里做成一个新的系列,主要跟我的课程有关,但是与作业没有关系。
只讲词法分析和文法分析。因为大部分高校集中学这里,根据给编译的课时来看,讲到后面的也只是一笔带过。
这个系列有 讲解,笔记,源代码,习题,可以看作一个速成的小课程。
概论(必会基础名词含义)
编译过程六个阶段: 词法分析,语法分析,语义分析,中间代码生成,代码优化,目标代码生成。
两个附加阶段:表格管理(在前),出错处理(在后)。
我下面列到的所有名词的含义以及描述一定要弄清楚
不理解的直接百度:编译原理+词 就好,会有很多更优秀的博文解释
我的目的是为了使这门课变得简单易懂,虽然是一个速成课,但是你也需要了解一些基础的知识
符号串:由字母表组成的任何有穷序列
文法: 用 G 表示, 本质为四元组(由四个部分组成的东西):VN(非终结符集)、V T(终结符集)、P(产生式)、S(起始符)
四种类型的文法:0 1 2 3 型文法
推导: 最左(右)推导,指对于一个推导序列中的每一直接推导,被替换的总是当前符号串中的最左 (右)非终结符号
闭包: Σ+ =Σ* - ε,*代表有空串,+代表没空串,在图中理解更好
句型:既可以是终结符也可以是非终结符,可以为空串
句子:句子是不包含非终结符的句型
语言:用 L(G)表示,语言是文法G一切句子的集合
文法和语言(语法树)

实验二(基于预测分析法的语法分析程序的构造)
1. 实验内容

2. 实验指导


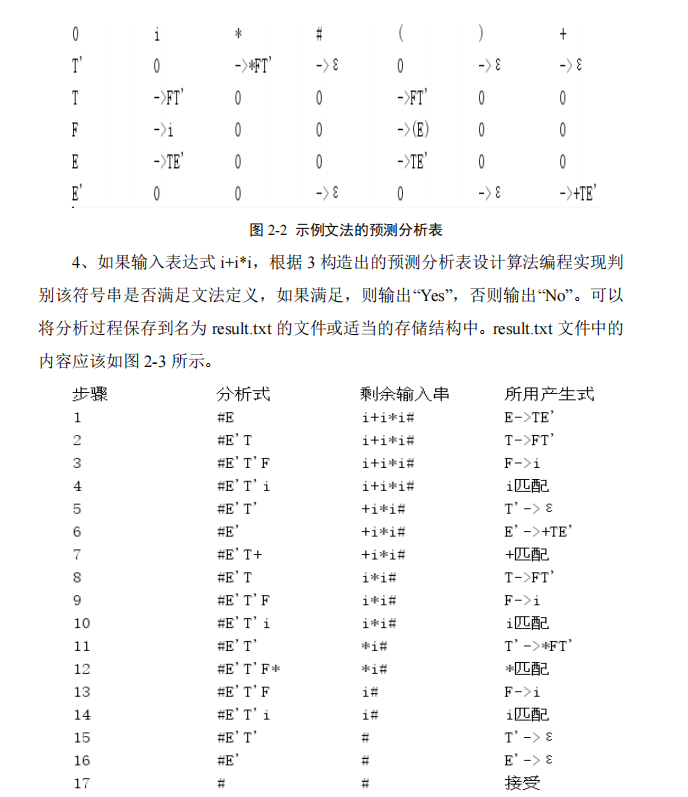
3. 代码实现
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <iomanip> 3 #include <string> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <set> 6 #include<stdlib.h> 7 #include<string.h> 8 #define maxsize 100 9 10 using namespace std; 11 12 struct node { // 产生式的数据结构 13 char left; 14 string right; 15 }; 16 17 class Base { 18 protected: 19 int T; // 产生式的个数 20 node production[maxsize]; // 产生式集 21 22 set<char> firstSet[maxsize]; // First集 23 set<char> followSet[maxsize]; // Follow集 24 vector<char> terminalNoEmpty; // 去$(空)的终结符 25 vector<char> terminal; // 终结符 26 vector<char> nonterminal; // 非终结符 27 28 bool isNonterminal(char c); 29 int getIndex(char target); // 获得target在终结符集合中的下标 30 int getNIndex(char target); // 获得target在非终结符集合中的下标 31 void getFirst(char target); // 得到First(target) 32 void getFollow(char target); // 得到Follow(target) 33 34 public: 35 Base() {}; 36 37 void inputAndSolve(); // 处理和求出First和Follow集 38 void displayFirstAndFollow(); // 输出First和Follow集 39 40 }; 41 42 bool Base::isNonterminal(char c) { // 判断c是否为非终结符 43 if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') 44 return true; 45 return false; 46 } 47 int Base::getNIndex(char target) { // 获得target在非终结符集合中的下标 48 for (int i = 0; i<nonterminal.size(); i++) { 49 if (target == nonterminal[i]) 50 return i; 51 } 52 return -1; 53 } 54 int Base::getIndex(char target) { // 获得target在终结符集合中的下标 55 for (int i = 0; i<terminalNoEmpty.size(); i++) { 56 if (target == terminalNoEmpty[i]) 57 return i; 58 } 59 return -1; 60 } 61 62 void Base::getFirst(char target) { // 求FIRST(target) 63 int isEmpty = 0; 64 int targetIndex = getNIndex(target); //找出非终结符下标 65 for (int i = 0; i < T; i++) { //遍历每一个产生式 66 if (production[i].left == target) { // 匹配产生式左部 67 if (!isNonterminal(production[i].right[0])) { // 对于终结符,直接加入first 68 firstSet[targetIndex].insert(production[i].right[0]); //将终结符存储 (第1) 69 } 70 else { 71 char Yj = production[i].right[0]; 72 getFirst(Yj);// Yj是非终结符,递归 先求出FIRST(Yj) 73 74 set<char>::iterator it; 75 int YjIndex = getNIndex(Yj); //找出该非终结符下标 76 for (it = firstSet[YjIndex].begin(); it != firstSet[YjIndex].end(); it++) { 77 if (*it == '$') { // 遍历查看FIRST(Yj)中是否含有'$'(能产生空) 78 isEmpty = 1; 79 firstSet[getNIndex(target)].insert('$'); 80 } 81 else 82 firstSet[targetIndex].insert(*it); //将FIRST(Yj)中的非$就加入FIRST(X) 83 } 84 } 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 89 void Base::getFollow(char target) { // 求FOLLOW(target) 90 int targetIndex = getNIndex(target); 91 for (int i = 0; i < T; i++) { //每个产生式 92 int index = -1; 93 int len = production[i].right.length(); 94 for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) { // 寻找target在产生式中的位置index 95 if (production[i].right[j] == target) { 96 index = j; //横向坐标 97 break; 98 } 99 } 100 if (index != -1 && index < len - 1) { // 找到target在产生式中的位置index 说明后面有东西 101 // 存在A->αBβ, 将FIRST(β)中除了空$之外的所有放入FOLLOW(B)中 102 // 这里B对应target, β对应nxt 103 char nxt = production[i].right[index + 1]; //提取后面符号 104 if (!isNonterminal(nxt)) { // β是终结符 FIRST(β)=β,直接插入β 105 followSet[targetIndex].insert(nxt); 106 } 107 else { // β是非终结符 108 int hasEmpty = 0; 109 set<char>::iterator it; 110 int nxtIndex = getNIndex(nxt); // 插入FIRST(β)中除了空$之外的所有 找非终结符位置 111 for (it = firstSet[nxtIndex].begin(); it != firstSet[nxtIndex].end(); it++) { 112 if (*it == '$') 113 hasEmpty = 1; 114 else 115 followSet[targetIndex].insert(*it); 116 } 117 118 if (hasEmpty && production[i].left != target) { // 存在A->αBβ且FIRST(β)->$ 119 // FOLLOW(A)放在FOLLOW(B)中 120 getFollow(production[i].left); 121 set<char>::iterator it; 122 char tmp = production[i].left; 123 int tmpIndex = getNIndex(tmp); 124 for (it = followSet[tmpIndex].begin(); it != followSet[tmpIndex].end(); it++) 125 followSet[targetIndex].insert(*it); 126 } 127 } 128 } 129 else if (index != -1 && index == len - 1 && target != production[i].left) { // 说明后面无 存在A->αB ,FOLLOW(A)放在FOLLOW(B)中 130 getFollow(production[i].left); 131 set<char>::iterator it; 132 char tmp = production[i].left; 133 int tmpIndex = getNIndex(tmp); 134 for (it = followSet[tmpIndex].begin(); it != followSet[tmpIndex].end(); it++) 135 followSet[targetIndex].insert(*it); 136 } 137 } 138 } 139 140 void Base::inputAndSolve() { // 处理和求出First和Follow集 141 string s; 142 int i=0; 143 cout << "输入的产生式的个数:" << endl; 144 cin >> T; 145 cout << "输入的产生式:" << endl; 146 for (int index = 0; index < T; index++) { // 处理每一个产生式 147 cin >> s; 148 production[index].left = s[0]; // 产生式的左部 149 for ( i = 3; i < s.length(); i++) // 产生式的右部 150 production[index].right += s[i]; 151 152 for (i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { // 存储所有终结符和非终结符 153 if (i == 1 || i == 2) 154 continue; // 跳过产生符号-> 155 if (isNonterminal(s[i])) { //插入一个非终结符 156 int flag = 0; // 是否找到该字符 (有了就不压入栈了) 157 for (int j = 0; j < nonterminal.size(); j++) { 158 if (nonterminal[j] == s[i]) { 159 flag = 1; 160 break; 161 } 162 } 163 if (!flag) nonterminal.push_back(s[i]); 164 } 165 else { //插入一个终结符 166 int flag = 0; 167 for (int j = 0; j < terminal.size(); j++) { 168 if (terminal[j] == s[i]) { 169 flag = 1; 170 break; 171 } 172 } 173 if (!flag) terminal.push_back(s[i]); 174 } 175 } 176 } 177 terminal.push_back('#'); 178 179 for ( i = 0; i < terminal.size(); i++) { // 存储没有$符号的终结符 180 if (terminal[i] != '$') 181 terminalNoEmpty.push_back(terminal[i]); 182 } 183 184 // 获得first集 185 for ( i = 0; i < nonterminal.size(); i++) { 186 getFirst(nonterminal[i]); 187 } 188 189 // 获得follow集 190 for ( i = 0; i < nonterminal.size(); i++) { 191 if (i == 0) // 开始符号, 先加入结束符号 192 followSet[0].insert('#'); 193 getFollow(nonterminal[i]); 194 } 195 } 196 197 void Base::displayFirstAndFollow() { // 输出First和Follow集 198 int i=0; 199 cout << "FIRST集合" << endl; 200 for (i = 0; i<nonterminal.size(); i++) { 201 cout << nonterminal[i] << ": "; 202 set<char>::iterator it; 203 for (it = firstSet[i].begin(); it != firstSet[i].end(); it++) 204 cout << *it << " "; 205 cout << endl; 206 } 207 cout << endl; 208 209 cout << "FOLLOW集合" << endl; 210 for (i = 0; i<nonterminal.size(); i++) { 211 cout << nonterminal[i] << ": "; 212 set<char>::iterator it; 213 for (it = followSet[i].begin(); it != followSet[i].end(); it++) 214 cout << *it << " "; 215 cout << endl; 216 } 217 cout << endl; 218 } 219 220 class LL1 : public Base { 221 private: 222 vector<char> analyStack; // 分析栈 223 vector<char> leftExpr; // 剩余输入串 224 int tableMap[100][100]; // 预测表 225 226 public: 227 LL1(); 228 229 void getTable(); // 生成预测表 230 void printPredictTable(); // 输出预测表 231 void analyExpression(string s); // 分析输入语句s 232 void getResult(); // 综合处理 233 }; 234 LL1::LL1() { 235 memset(tableMap, -1, sizeof(tableMap)); 236 } 237 238 void LL1::getTable() { //获得预测表 239 for (int index = 0; index < T; index++) {// 遍历产生式 对于每个产生式(编号index):A->α 240 int row = getNIndex(production[index].left); // 左部 下标 241 int emptyCount = 0; 242 char tmp = production[index].right[0]; 243 if (!isNonterminal(tmp)) { // tmp是终结符 244 if (tmp != '$') 245 tableMap[row][getIndex(tmp)] = index; 246 if (tmp == '$') 247 emptyCount++; 248 } 249 else { // tmp是非终结符 250 set<char>::iterator it; 251 int tmpIndex = getNIndex(tmp); //找非终结符下标 252 // 对FIRST(tmp)中的每个终结符号a,将i加入(A, a)中 253 for (it = firstSet[tmpIndex].begin(); it != firstSet[tmpIndex].end(); it++) { 254 tableMap[row][getIndex(*it)] = index; 255 } 256 if (firstSet[tmpIndex].count('$') != 0) // 2) 如果空$在FIRST(tmp)中,继续看α中的下一个符号 257 emptyCount++; 258 } 259 260 // 2) 如果空$在FIRST(α)中,对FOLLOW(A)中的每个终结符或结束符b,将i加入(A,b)中 261 if (emptyCount == production[index].right.size()) { // 产生式右部只有空 262 set<char>::iterator it; 263 for (it = followSet[row].begin(); it != followSet[row].end(); it++) { 264 tableMap[row][getIndex(*it)] = index; //把左部的follow放在预测表里 265 } 266 } 267 } 268 } 269 270 void LL1::analyExpression(string s) { 271 int i=0; 272 for (i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) 273 leftExpr.push_back(s[i]); // 压栈剩余字符串 274 leftExpr.push_back('#'); //压# 275 276 analyStack.push_back('#'); 277 analyStack.push_back(nonterminal[0]); // 加入开始符号 278 279 while (analyStack.size() > 0) { // 分析栈里有值 280 //cout<<"分析栈:"; 281 string outs = ""; 282 for (i = 0; i < analyStack.size(); i++) 283 outs += analyStack[i]; 284 cout << setw(30) << outs; 285 286 //cout<<"剩余输入串:"; 287 outs = ""; 288 for (i = 0; i < leftExpr.size(); i++) 289 outs += leftExpr[i]; 290 cout << setw(30) << outs; 291 292 // 匹配 293 char char1 = analyStack.back(); 294 char char2 = leftExpr.front(); 295 if (char1 == char2 && char1 == '#') { 296 cout << setw(15) << "Accepted!" << endl; 297 return; 298 } 299 if (char1 == char2) { 300 analyStack.pop_back(); 301 leftExpr.erase(leftExpr.begin()); 302 cout << setw(15) << "匹配:" << char1 << endl; 303 } 304 else if (tableMap[getNIndex(char1)][getIndex(char2)] != -1) { // 预测表中有推倒项,可进行推导 305 int tg = tableMap[getNIndex(char1)][getIndex(char2)]; 306 analyStack.pop_back(); 307 308 if (production[tg].right != "$") { 309 for ( i = production[tg].right.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) // 注意这里是反向的压栈 310 analyStack.push_back(production[tg].right[i]); 311 } 312 313 cout << setw(15) << "推导:" << production[tg].left << "->" << production[tg].right << endl; 314 } 315 else { // 错误 316 cout << setw(15) << "error!" << endl; 317 return; 318 } 319 } 320 } 321 322 void LL1::printPredictTable() { 323 int i=0; 324 // 表头 325 for (i = 0; i < terminalNoEmpty.size(); i++) { 326 cout << setw(10) << terminalNoEmpty[i]; //空格 327 } 328 cout << endl; 329 for (i = 0; i < nonterminal.size(); i++) { 330 cout << nonterminal[i] << ": "; 331 for (int j = 0; j < terminalNoEmpty.size(); j++) { 332 if (tableMap[i][j] == -1) 333 cout << setw(10) << " "; 334 else 335 cout << setw(10) << production[tableMap[i][j]].right; 336 } 337 cout << endl; 338 } 339 cout << endl; 340 } 341 342 void LL1::getResult() { //获得结果 343 //int a = 0; 344 inputAndSolve(); 345 displayFirstAndFollow(); 346 getTable(); 347 printPredictTable(); 348 //栈匹配 349 string ss; 350 cout << "请输入符号串:" << endl; 351 cin >> ss; 352 cout <<setw(30) << "分析栈" << setw(30) << "剩余输入串" << setw(16) << "推导式" << endl; 353 analyExpression(ss); 354 355 } 356 357 358 int main() { 359 // $表示空, #表示终止 360 LL1 res; 361 res.getResult(); 362 system("pause"); 363 return 0; 364 } 365 366 /* 367 E->TA 368 A->+TA 369 A->$ 370 T->FB 371 B->*FB 372 B->$ 373 F->i 374 F->(E) 375 */ 376 // i+i*i
4. 测试结果

