感觉web框架gin和asp.net core对http消息处理和中间件的实现用法差不多,很优雅的aop切面操作,查了下资料也手动实现一个简单的中间件,加深下原理的理解,可以对一个外部函数进行切面
感觉web框架gin和asp.net core对http消息处理和中间件的实现用法差不多,很优雅的aop切面操作,查了下资料也手动实现一个简单的中间件,加深下原理的理解,可以对一个外部函数进行切面操作,测试就直接使用tcp简单的测试了
1.context.go
注册的中间件需要队列保存,中间件参数需要传入注册的中间信息用来进行嵌套,用Context来进行封装
每次Next()用来中间件的嵌套及运行,不在代码中间/不写就是同级中间件运行(代码中for循环部分),不同顺序
Abort()用来中断后面中间件的运行
Content后面用来tcp测试,做下统一的消息处理用的
代码如下:
package aop
import (
"log"
"math"
)
const MaxIndex = math.MaxInt8 / 2
type Content struct {
Code string
Msg string
}
type Context struct {
currentIndex int8
handleChans []func(*Context)
}
func newContext(size int) *Context {
return &Context{
currentIndex: -1,
handleChans: make([]func(*Context), 0, size),
}
}
func (c *Context) appendHandle(handle func(*Context)) {
c.handleChans = append(c.handleChans, handle)
}
func (c *Context) Next() {
if c.currentIndex < MaxIndex {
c.currentIndex++ //中间件嵌套
length := int8(len(c.handleChans))
for ; c.currentIndex < length; c.currentIndex++ { //同级中间件运行
if !c.isAbort() {
c.handleChans[c.currentIndex](c)
} else {
return
}
}
}
}
func (c *Context) Abort() {
c.currentIndex = MaxIndex
log.Printf("handle was aborted...")
}
func (c *Context) isAbort() bool {
return c.currentIndex == MaxIndex
}
func (c *Context) reset() {
c.currentIndex = -1
c.handleChans = c.handleChans[:0]
}
2.engine.go
通过Use()用来将中间件注册到Context中,所以Engine保存Context,同时需要将外部的需要aop处理的函数加入到中间件队列最后面
代码如下:
package aop
type Engine struct {
funcHandle func()
context *Context
}
func NewEngine(funcHandle func()) Engine {
return Engine{
funcHandle: funcHandle,
context: newContext(10),
}
}
func (e *Engine) Use(handle func(*Context)) {
e.context.appendHandle(handle)
}
func (e *Engine) Run() {
e.context.appendHandle(func(*Context) { e.funcHandle() })
if len(e.context.handleChans) > 0 {
e.context.Next()
}
e.context.reset()
}
3.测试代码,用法
服务端:server.go
package main
import (
"bufio"
"encoding/json"
aop "gobase/aop/core"
"log"
"net"
)
func main() {
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":8080")
log.Printf("server listening on :%s", listener.Addr())
if err != nil {
log.Printf("server listen tcp err:%v", err)
panic(err)
}
defer listener.Close()
for {
conn, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
log.Printf("connection tcp accept err:%v", err)
panic(err)
}
go func() {
content := &aop.Content{Code: "ok", Msg: ""}
aopEngine := aop.NewEngine(func() { handle(conn, content) })
aopEngine.Use(func(ctx *aop.Context) {
log.Printf("method one starting...")
content.Msg += "method one run->"
ctx.Next()
log.Printf("method one ending...")
})
aopEngine.Use(func(ctx *aop.Context) {
log.Printf("method two starting...")
content.Msg += "method two run->"
ctx.Next()
log.Printf("method two ending...")
})
aopEngine.Use(func(ctx *aop.Context) {
log.Printf("method three starting...")
content.Msg += "method three run->"
log.Printf("method three ending...")
//ctx.Next()
})
aopEngine.Use(func(ctx *aop.Context) {
log.Printf("method four starting...")
//ctx.Abort()
// ctx.Content.Code = "err"
content.Msg += "method four run->"
log.Printf("method four ending...")
})
aopEngine.Run()
}()
}
}
func handle(conn net.Conn, content *aop.Content) error {
defer conn.Close()
log.Printf("handle starting...")
writer := bufio.NewWriter(conn)
content.Msg += "hello world!"
bytes, _ := json.Marshal(*content)
n, err := writer.Write(bytes)
writer.Flush()
if err != nil {
log.Printf("write string err:%v", err)
return err
}
log.Printf("handle ending...,write bytes len :%v", n)
return nil
}
客户端:client.go
package main
import (
"bufio"
"encoding/json"
aop "gobase/aop/core"
"log"
"net"
)
func main() {
conn, err := net.Dial("tcp", ":8080")
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
defer conn.Close()
reader := bufio.NewReader(conn)
var contentBytes []byte
bytes := make([]byte, 8)
for {
n, _ := reader.Read(bytes)
if n == 0 {
break
}
contentBytes = append(contentBytes, bytes[:n]...)
}
content := &aop.Content{}
err = json.Unmarshal(contentBytes, content)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("json err:%v", err)
}
log.Printf("result:%+v", content)
}
4.测试结果:
服务端:
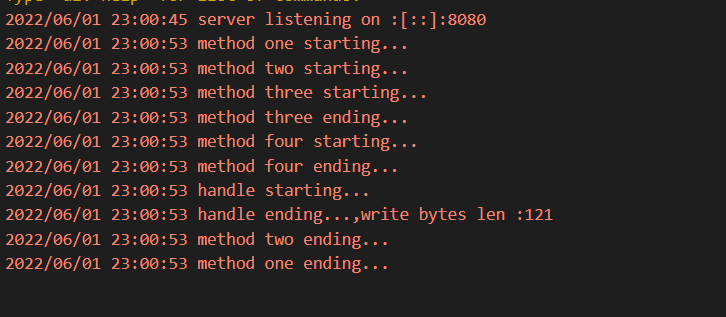
客户端:

