the reference : https://www.ruanx.net/kmp/ to understand the algorithm,it make sense to use your pen to draw different cases of the kmp matcher process. code the auxiliary function to do prepare calculate the information of the
the reference :
https://www.ruanx.net/kmp/
to understand the algorithm,it make sense to use your pen to draw different cases of the kmp matcher process.
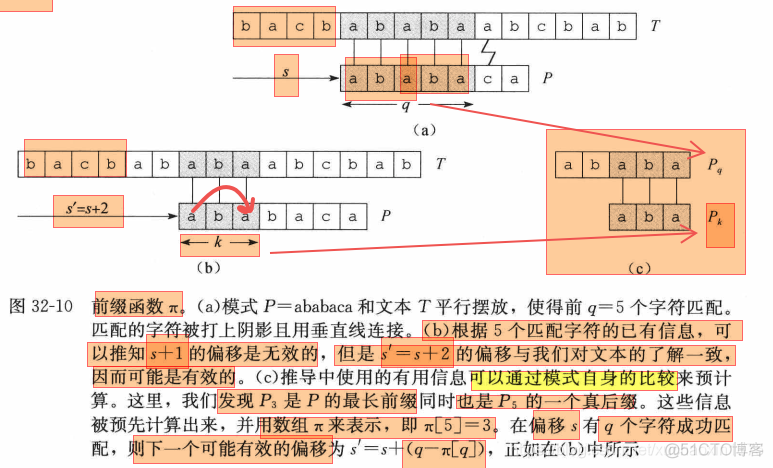


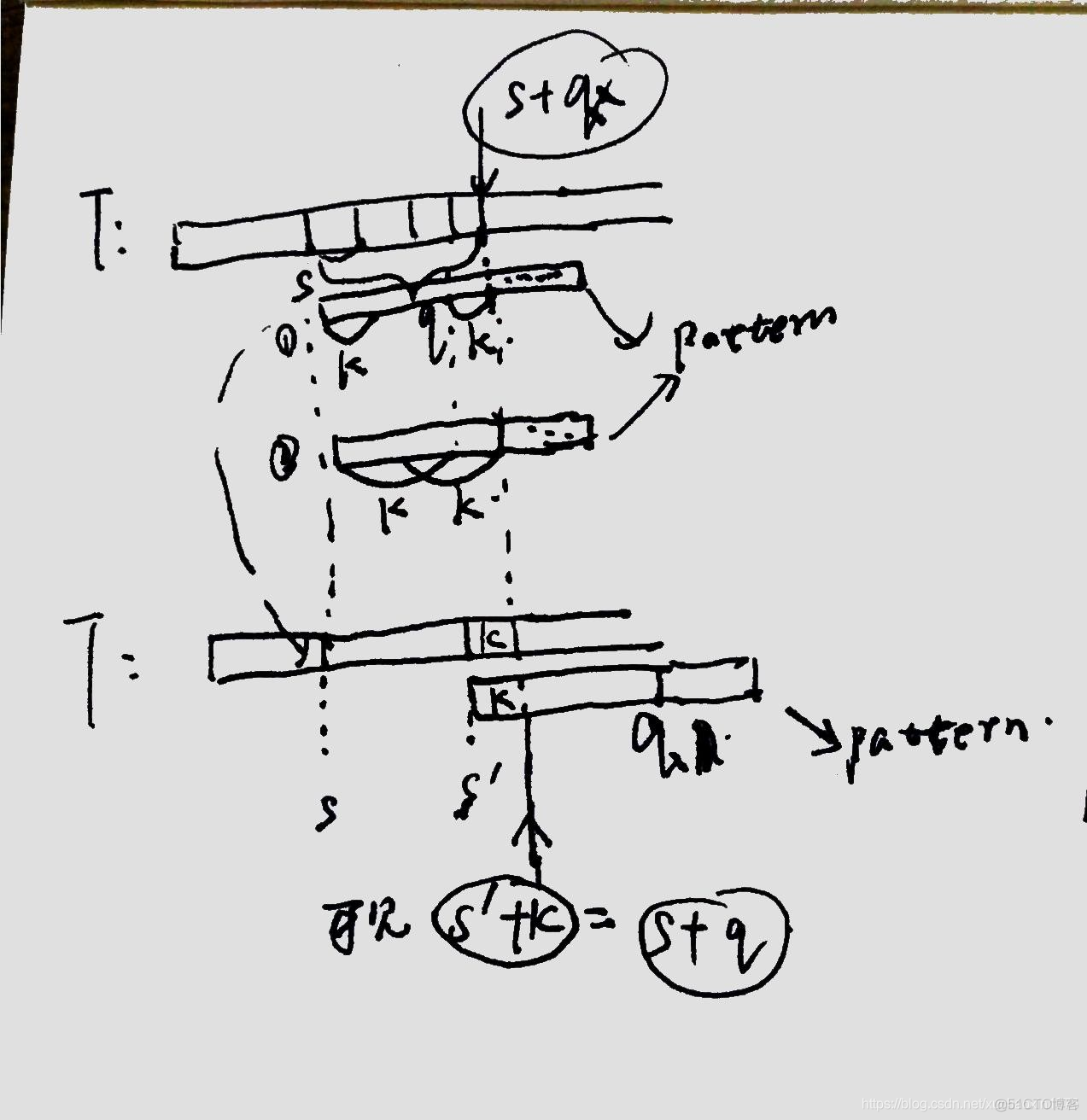
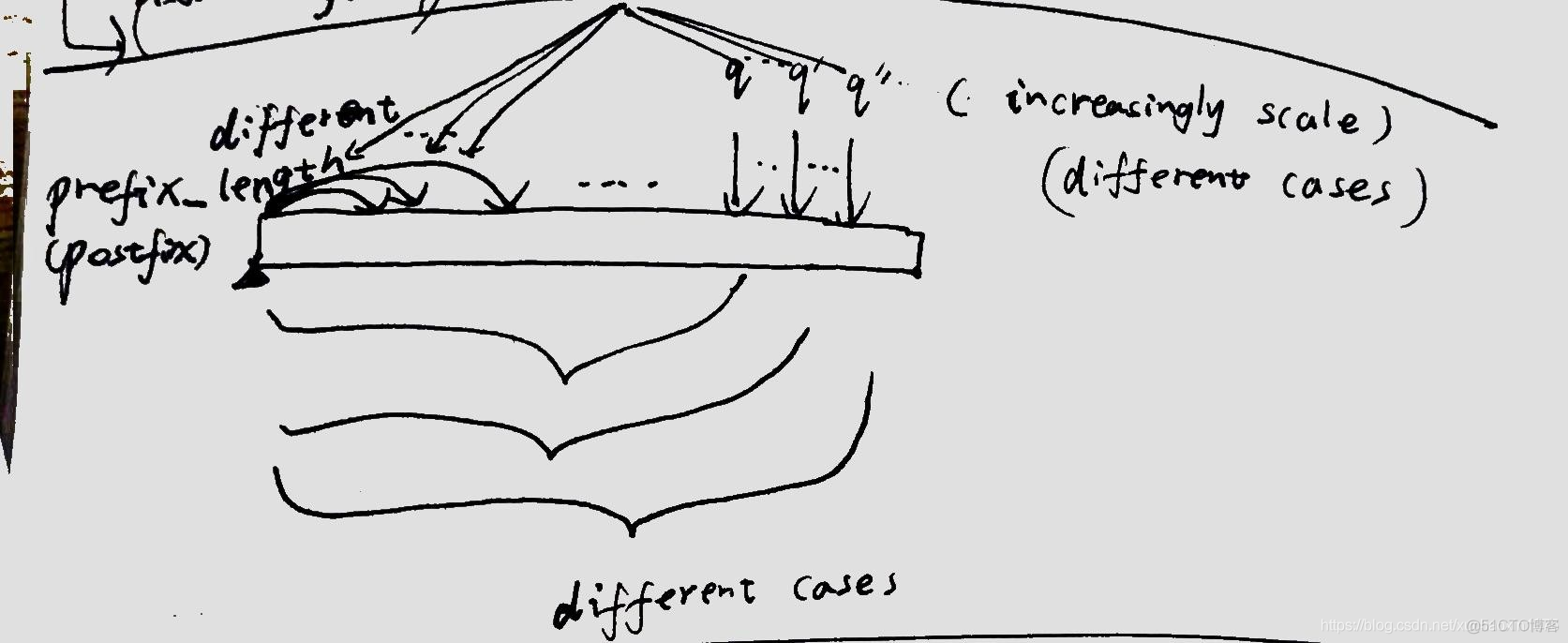

code
the auxiliary function to do prepare calculate the information of the pattern
def pre_calculate_next_list(pattern):"""get the offset(the elements of the returned list could use as the index of next character of the pattern to match ) after mismatched correspondingly
the list is calculated by the pattern independently!
Args:
pattern (str): pattern string
Returns:
list: the elements are the offset after mismatched you could match from where to continue of the pattern in each cases;
you can use the number of matched characters-1 as index to query the length of the longest common sequence prefix and postfix,or the elements of the returned list could use as the index of next character of the pattern to match with the string to speed up the matching process
"""
len_list = len(pattern)
# attention,the length value is based on the true(strict) substring,it does not include the string itself
next_list = []
next_list.append(0) # the first value(next_list[0]) is initialize as 0(the first length element value means the number of the matched char is only 1;similarly,the second value of the next_list is mean that the matched character is 2,...)
# the the adding char index of to calculate the next scale of the longest common substring prefix and postfix
# the_adding_char_index indicated the scale increasingly(it also means that the last matched character's successor to be tested)
the_adding_char_index = 1
# the length which has been calculated (the now_lengths will be the element of the next_list)
now_length = 0
# meanwhile the now_length could as the index to judge the_adding_char_index character wheather matched the new prefix
#the length counting from character pattern[0] always!it may be longer or shorter depend on the different cases(namely,different the_adding_char_index cases)
# the process involves three scale values:the current scale lenght value to calculate:now_length(the judging value),now_length-1(the known length value);
# the while loop will calculate the seconde value of the next_list(and other more later length values)
while the_adding_char_index < len_list:
""" the lucky case:the prefix is the same after add a character
judge the new character to be wheather it could be add to the new scale prefix
we must know that althouth there are different scales(cases),but all prefix have the same begining characters"""
# attention,the first character of pattern is pattern[0]
# the pattern[the_adding_char_index] is from the second character of the pattern
if pattern[now_length] == pattern[the_adding_char_index]: # matched!
now_length += 1
the_adding_char_index += 1
# this new scale is calculated! it could be recorded into the next_list
next_list.append(now_length)
# mismatched:
else:
#in the case, the now_length is >= 1(because we intent to visit the next_list[now_length-1])
# else,then execute the last 'else' branch case
if now_length: # to iterate the length value
# use the last scale calculated length value (little smaller the the currently scale now_length) to calculate the next length value(larger scale)
# this is the essential part of the kmp algorithm
# use the now_length-1(the known length value) to calculate the current calculating scale
# this method transform the case to case lucky one(just the scale become smaller) to solve
now_length = next_list[now_length-1] # the now_length>=0
else:
# explictly set the length value as 0 in this case
next_list.append(0)
the_adding_char_index += 1
return next_list
kmp(string,pattern)
def kmp(string, pattern):s = 0 # offset
# the position will continuosly to match(as the specified index of the pattern str)
postion_to_continue = 0
next_list = pre_calculate_next_list(pattern)
while s < len(string):
# matched!
# if two charactor are identical ,step the index (s and pos)
# the same to the brute force (naive)method
if string[s] == pattern[postion_to_continue]:
s += 1
postion_to_continue += 1
elif postion_to_continue: # mismatched!(postion_to_continue>=1)
# accroding the next_list to locate the charactor where to match continuosly
# postion_to_continue-1>=0
# the next_list count from 0,so,if we want to visit the first element of the next_list, we use next_list[0];
postion_to_continue = next_list[postion_to_continue-1]
else:
s += 1 # keep the postion_to_continue no change
# judge if a substring is matched completely,then print the position (count from 1) of
# the string
if postion_to_continue == len(pattern):
print(s-postion_to_continue+1)
postion_to_continue = next_list[postion_to_continue-1]
string = "teababaca_aaaeeaae"
# pattern = "ea"
pattern1 = "eea"
# pattern="aacaa"
# pattern="aadabaadaadaa"
# pattern = "acbabaca"
pattern2 = "ababaca"
# print(pre_calculate_next_list(pattern1))
# print(kmp())
kmp(string, pattern1)
kmp(string,pattern2)
