文章目录 theory specific examples: Construct the optimal solution python: theory 记住,矩阵子链 链内各个矩阵相乘的结果矩阵的规模可以仅从该子链的第一个矩阵
文章目录
- theory
- specific examples:
- Construct the optimal solution
- python:
theory




记住,矩阵子链链内各个矩阵相乘的结果矩阵的规模可以仅从该子链的第一个矩阵
的行数
和最后一个矩阵
的列数
有关
即,结果矩阵的规模为
这是理解中为什么是
的基础
m[2,2]相当于单个矩阵构成的矩阵链(k=i=2),行数为,列数为
,则,规格为
specific examples:
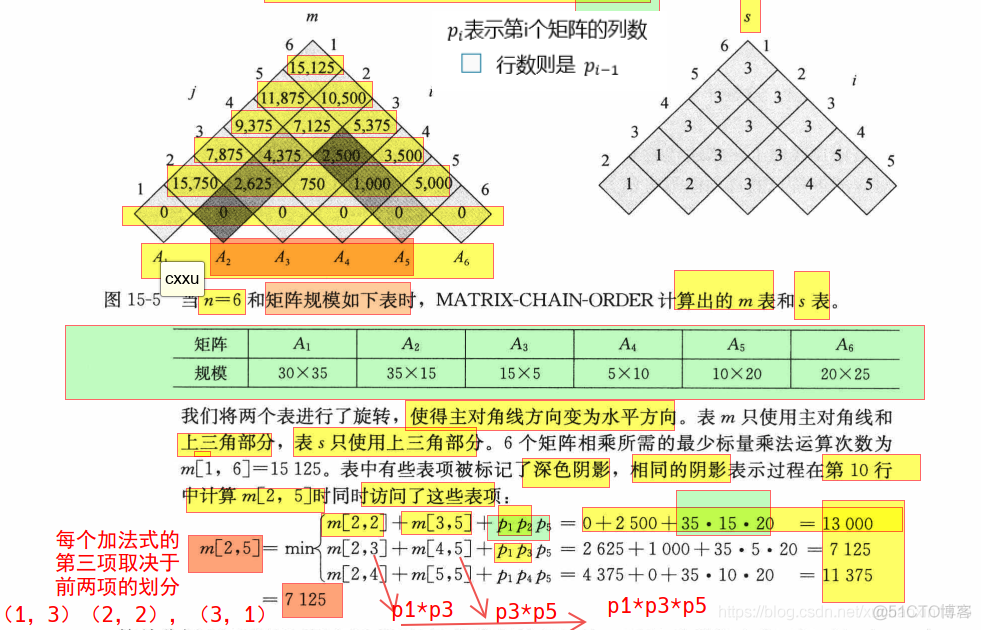
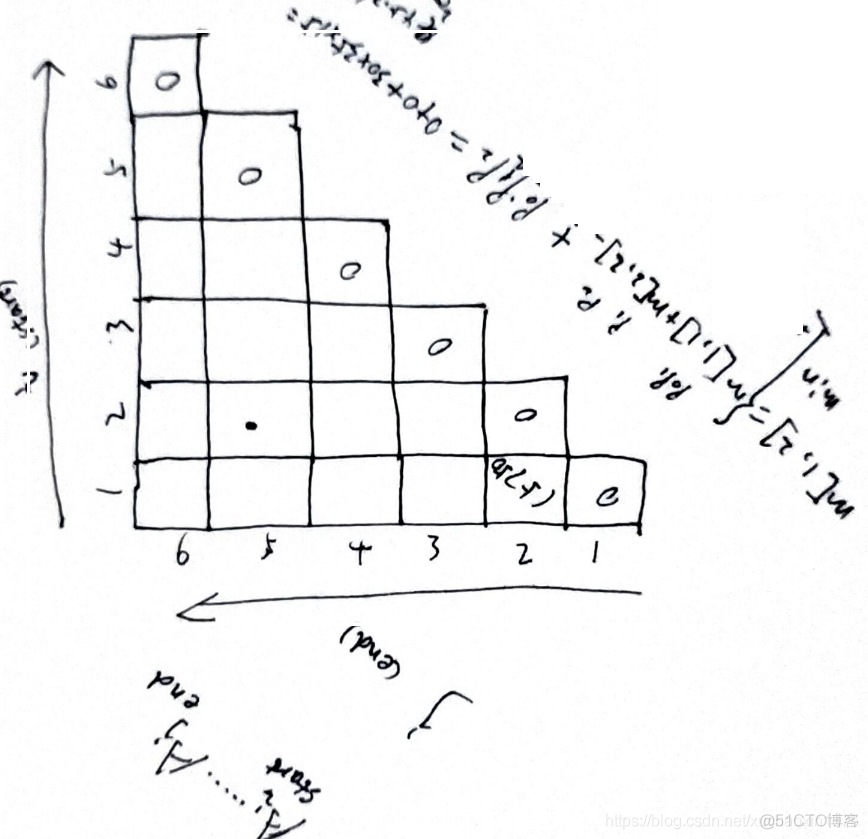
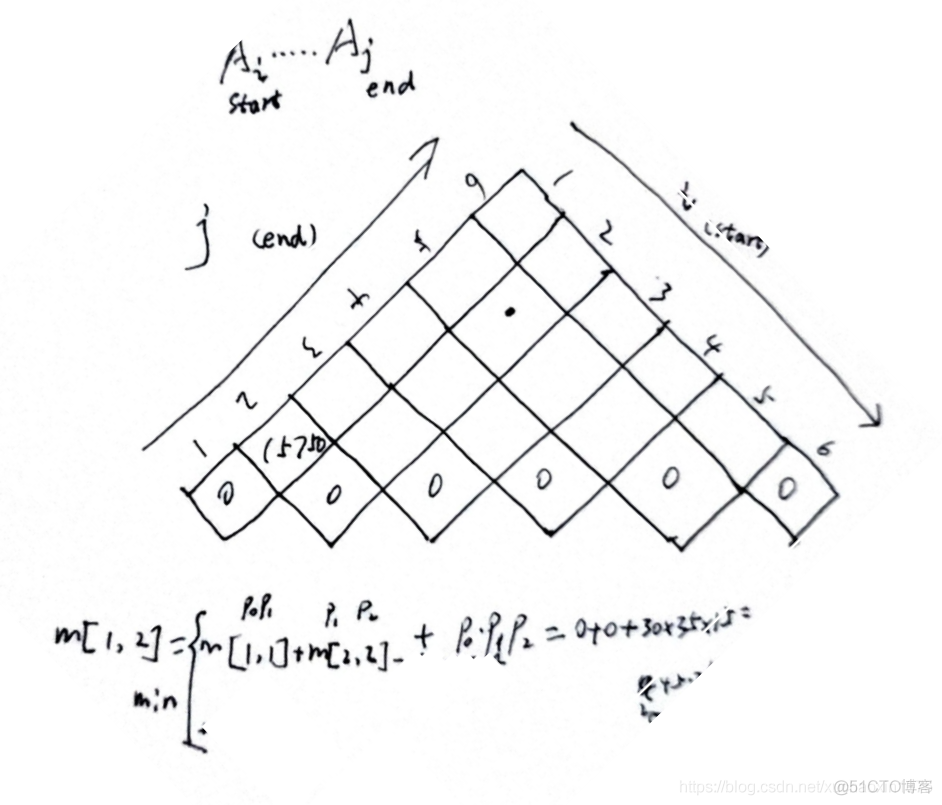

Construct the optimal solution
the parentheses solution: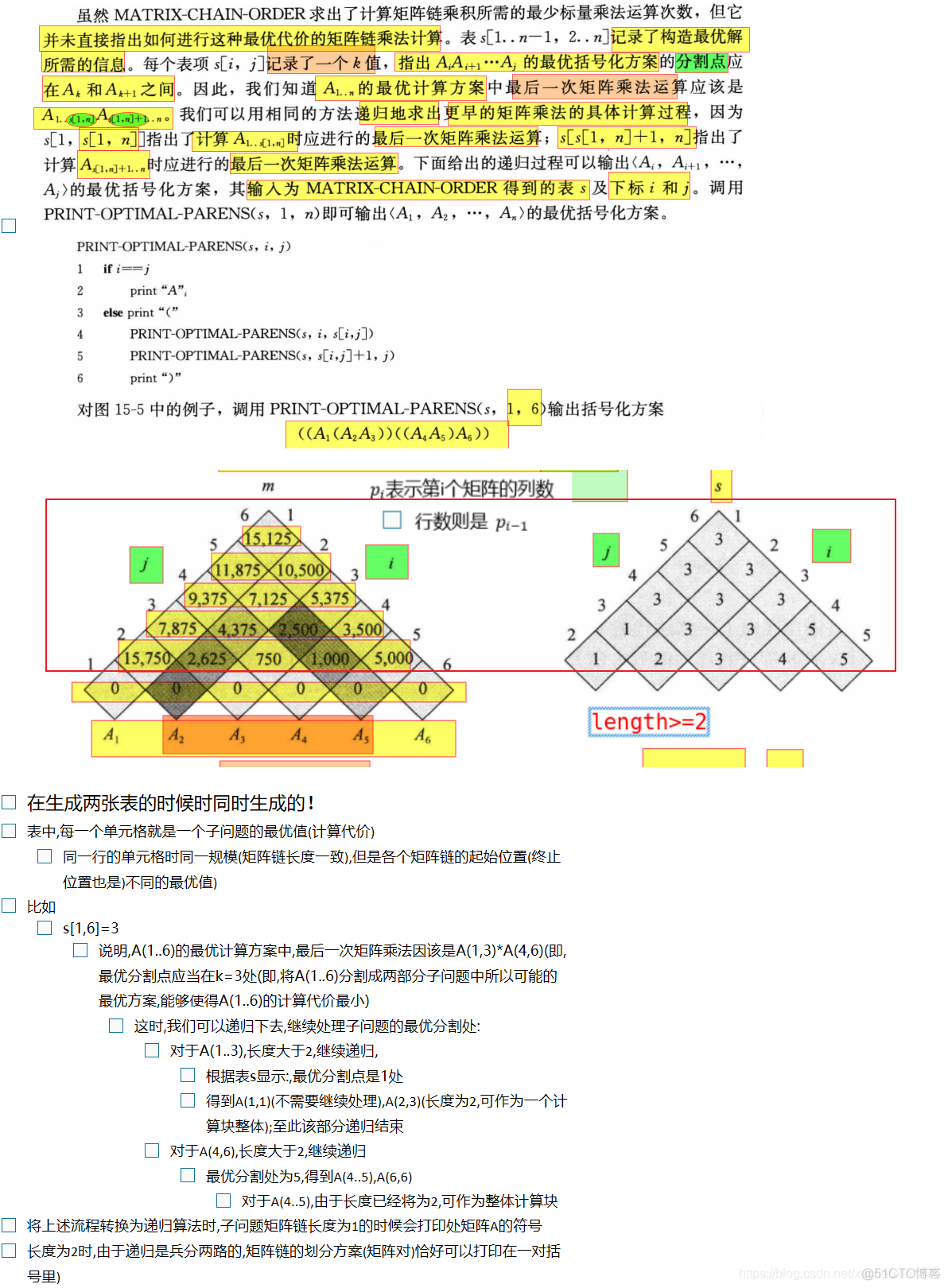
python:
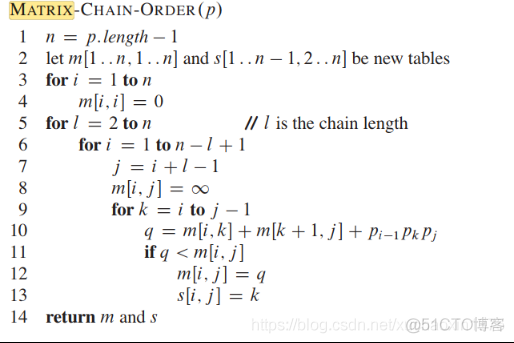
import mathdef matrix_chain_order(list_p):
"""[summary]
Args:
list_p ([type]): [description]
Returns:
[type]: [description]
"""
n = len(list_p)-1
''' we could think that the table_min_costs contains the optimal cost values of the different subproblem(sub_matrix chain) scales
(from bottom to top to solve the problem)
'''
# the table to save the lowest costs to multiple the matrix chain
table_min_costs = [[0 for i in range(0, n+1)]
for j in range(0, n+1)] # (n+1)*(n+1)
# the table_save_partition save the the optimal partition point:make the multiplication cost lowest each scale cases
table_save_partition = [
[0 for i in range(0, n+1)] for j in range(0, n+1)] # (n)*(n)
''' the length of the sub_matrix chain is 1 cases could be centralized process:assign them as 0 in the table_min_costs '''
for i in range(1, n+1):
table_min_costs[i][i] = 0
''' the essential part of the algorithm: '''
# length is the chain length(traverse the all kinds of sub matrix chains cases(length>1))
for length in range(2, n+1):
''' each specific length cases have different partition schemes:
traverse all these divide cases:'''
for start_i in range(1, n-length+2): # the start_i is the index of each sub_matrix chain
# make the j-i+1==l(namely ,the length of sub_matrix chain)
end_i = start_i+length-1
# initial the costs as infinite value:
table_min_costs[start_i][end_i] = math.inf
"""
# focus on the each sepecified sub_matrix chain
# the following loop will test(run) j-i times:to find the optimal split point:
# the index to_opt_partition is the index of the optimal split point(the matrix to_opt_partition matrix will be belong to the former subproble(sub_matrix chain))
"""
for to_opt_partition in range(start_i, end_i):
''' the to_opt_partition >=start_i>=1 '''
to_lowest_cost = table_min_costs[start_i][to_opt_partition] + table_min_costs[to_opt_partition+1][end_i] + \
list_p[start_i-1]*list_p[to_opt_partition]*list_p[end_i]
if to_lowest_cost < table_min_costs[start_i][end_i]:
table_min_costs[start_i][end_i] = to_lowest_cost
table_save_partition[start_i][end_i] = to_opt_partition
return table_min_costs, table_save_partition
def print_optimal_parentheses(s, i, j):
"""
matrix_index=1
Args:
s ([list]): [table_save_partition(optimal)]
i ([int]): [start_i index of the subproblem]
j ([int]): [end_i index of the subproblem]
"""
""" the simplest case (the sub_matrix chain length is 1)
the case as the recursive exit:"""
if i == j:
print("A"+str(i), end="")
else:
print("(", end="")
print_optimal_parentheses(s, i, s[i][j])
print_optimal_parentheses(s, s[i][j]+1, j)
print(")", end="")
def test(list_p):
table_min_costs, table_save_partition = matrix_chain_order(list_p)
print_optimal_parentheses(table_save_partition, 1, len(list_p)-1)
list_p = [30, 35, 15, 5, 10, 20, 25]
test(list_p)
