1 简介 自动车型识别系统是从人们对车辆分型的标准出发,对进出站点的各种车辆进行信息(即有关车辆类型的各种参数)采集,然后利用这些信息对车辆进行自动分型(即车型判别),为自动管
1 简介
自动车型识别系统是从人们对车辆分型的标准出发,对进出站点的各种车辆进行信息(即有关车辆类型的各种参数)采集,然后利用这些信息对车辆进行自动分型(即车型判别),为自动管理提供依据,为集中管理信息统计提供有关数据。该系统运用图像处理、图像分析和模式识别技术实现车辆类型的自动识别,具有投资少、适应性强、安装维护方便等优点。 小波分析是二十世纪八十年代发展起来的一门新的数学分支,由于它具有良好的性质,在信号处理和图像处理等许多领域得到了广泛的应用。 本文主要探讨了利用小波变换和分形维数在图像处理中的应用实现自动车型识别系统的开发。将算法用Matlab进行仿真试验,证明效果良好。
2 部分代码
function B=boundaries(BW,conn,dir)%BOUNDARIES Trace object boundaries.
%B=BOUNDARIES(BW) traces the exterior boundaries of objects in the binary
%image BW.B is a p_by_1 cell array,where p is the number of objects in the
%image.Each cell contains a Q_by_2 matrix,each row of which contains the
%row and column coordinates of a boundary pixel.Q is the number of boundary
%pixels for the corresponding object.Object boundaries are traced in the
%clockwise direction.
%
%B=BOUNDARIES(BW,CONN) specifies the connectivity to use when tracing
%boundaries.CONN may be either 8 or 4.The default value for CONN is 8.
%
%
%B=BOUNDARIES(BW,CONN,DIR) specifies the direction used for tracing
%boundaries.DIR should be either 'cw'(trace boundaries clockwise顺时针) or
%'ccw'(trace boundaries counterclockwise逆时针).If DIR is omitted BOUNDARIES
%traces in the clockwise direction.
if nargin<3
dir='cw';
end
if nargin<2
conn=8;
end
L=bwlabel(BW,conn);
%The number of objects is the maximum value of L.Initialize the cell array
%B so that each cell initially contains a 0_by_2 matrix.
numObjects=max(L(:));
if numObjects>0
B={zeros(0,2)};
B=repmat(B,numObjects,1);
else
B={};%只有背景
end
%Pad label matrix with zeros(用0扩展标签矩阵).This lets us write the boundary_following loop
%without worrying about going off the edge of the image.
Lp=padarray(L,[1 1],0,'both');
%Compute the linear indexing offsets to take us from a pixel to its
%neighbors.
M=size(Lp,1);
if conn==8
%Order is N NE E SE S SW W NW.
offsets=[-1,M-1,M,M+1,1,-M+1,-M,-M-1];
else
%Order is N E S W.
offsets=[-1,M,1,-M];
end
%next_search_direction_lut is a lookup tabl.Given the direction from pixel
%k to pixel k+1,what is the direction to start with when examining the
%neighborhood of pixel k+1?
if conn==8
next_search_direction_lut=[8 8 2 2 4 4 6 6];
else
next_search_direction_lut=[4 1 2 3];
end
%next_direction_lut is a lookup table查询表.Given that we just looked at neighbor
%in a given direction,which neighbor do we look at
%next?
if conn==8
next_direction_lut=[2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1];
else
next_direction_lut=[2 3 4 1];
end
%Values used for marking the starting and boundary pixels.
START=-1;
BOUNDARY=-2;
%Initialize scratch space in which to record the boundary pixels as well as
%follow the boundary.
scratch=zeros(100,1);
%Find candidate starting locations for boundaries.
[rr,cc]=find((Lp(2:end-1,:)>0)&(Lp(1:end-2,:)==0));
rr=rr+1;
for k=1:length(rr)
r=rr(k);
c=cc(k);%得到边界点的位置【r c】
if (Lp(r,c)>0)&(Lp(r-1,c)==0)&isempty(B{Lp(r,c)})
%We've found the start of the next boundary.Compute its linear
%offset,record which boundary it is,mark it,and initialize the
%counter for the number of boundary pixels.
idx=(c-1)*size(Lp,1)+r;
which=Lp(idx);
scratch(1)=idx;
Lp(idx)=START;
numpixels=1;
currentpixel=idx;
initial_departure_direction=[];
done=0;
next_search_direction=2;
while ~done
%Find the next boundary pixel.
direction=next_search_direction;
found_next_pixel=0;
for k=1:length(offsets)
neighbor=currentpixel+offsets(direction);
if Lp(neighbor)~=0
%Found the next boundary pixel.
if (Lp(currentpixel)==START)&...
isempty(initial_departure_direction)
%We are making the initial departure from the starting
%pixel.
initial_departure_direction=direction;
elseif (Lp(currentpixel)==START)&...
(initial_departure_direction==direction)
% We are about to retrace our path.
%That means we're done.
done=1;
found_next_pixel=1;
break;
end
%Take the next step along the boundary.
next_search_direction=...
next_search_direction_lut(direction);
found_next_pixel=1;
numpixels=numpixels+1;
if numpixels>size(scratch,1)
%Double the scratch space.
scratch(2*size(scratch,1))=0;
end
scratch(numpixels)=neighbor;
if Lp(neighbor)~=START
Lp(neighbor)=BOUNDARY;
end
currentpixel=neighbor;
break;
end
direction=next_direction_lut(direction);
end
if ~found_next_pixel
%If there is no next neighbor,the object must just have a
%single pixel.
numpixels=2;
scratch(2)=scratch(1);
done=1;
end
end
%Convert linear indices to row_column coordinates and save in the
%output cell array.
[row,col]=ind2sub(size(Lp),scratch(1:numpixels));
B{which}=[row-1,col-1];
end
end
if strcmp(dir,'ccw')
for k=1:length(B)
B{k}=B{k}(end:-1:1,:);
end
end
3 仿真结果
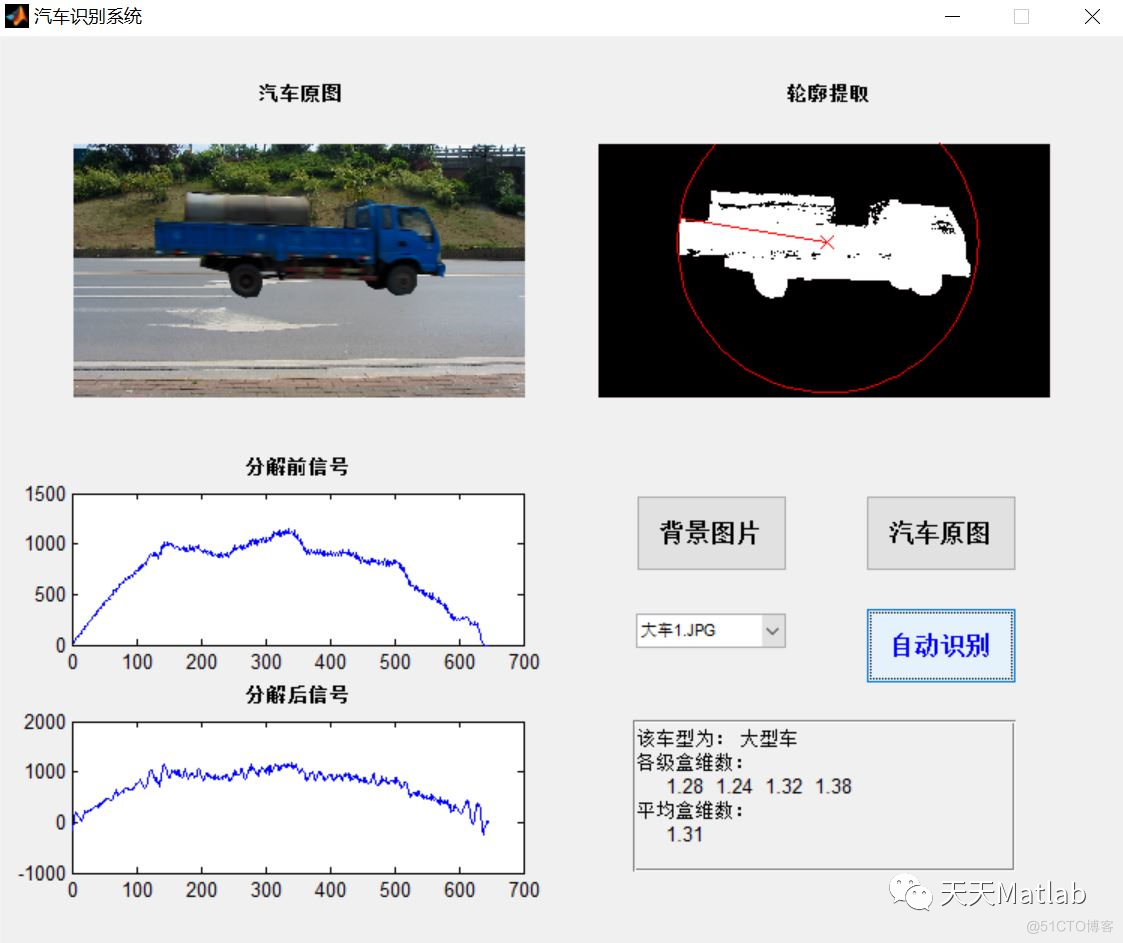

4 参考文献
[1]押成. 基于小波分析的车型识别系统[D]. 西安电子科技大学.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。


