1 简介 本文针对一些 CEC 数值优化基准函数和混合可再生能源系统 (HRES) 工程问题,对称为气味代理优化 (SAO) 的新元启发式算法进行了广泛研究。 SAO 实现了气味代理和蒸发气味分子的对
1 简介
本文针对一些 CEC 数值优化基准函数和混合可再生能源系统 (HRES) 工程问题,对称为气味代理优化 (SAO) 的新元启发式算法进行了广泛研究。 SAO 实现了气味代理和蒸发气味分子的对象之间的关系。这些关系被建模为三种独立的模式,称为嗅探模式、尾随模式和随机模式。当气味分子从气味源向代理扩散时,嗅探模式模拟代理的气味感知能力。尾随模式模拟代理跟踪气味分子的一部分直到其来源被识别的能力。然而,随机模式是代理用来避免陷入局部最小值的一种策略。对 37 个常用的 CEC 基准函数和 HRES 工程问题进行了测试,并将结果与其他 6 种元启发式方法进行了比较。实验结果表明,SAO 可以在 76% 的基准函数中找到全局最优值。同样,统计结果表明,与基准算法相比,SAO 也获得了最具成本效益的 HRES 设计。
2 部分代码
%__________________________________________% myCost = @YourCostFunction
% dim = number of your variables
% Max_Iter = maximum number of generations
% nMole = number of search agents
% lb=[lb1,lb2,...,lbn] where lbn is the lower bound of variable n
% ub=[ub1,ub2,...,ubn] where ubn is the upper bound of variable n
% If all the variables have equal lower bound you can just
% define lb and ub as two single number numbers
% To run SAO: [Best_score,Best_mole,Convergence]=SAO(nMole,Max_Iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
%__________________________________________
clear all
close all
clc
format long
nMole=50; % Number of search agents
F_name='F4'; % Selecte Benchmark Function
Max_Iter=200; % Maximum numbef of iterations
run=1;
% Load Function Details
[lb,ub,dim,myCost]=Select_Function(F_name);
for k=1:run
[Best_score,Best_mole,Convergence]=SAO(nMole,Max_Iter,lb,ub,dim,myCost);
Best_score(k,:)=Best_score;
end
Best=min(Best_score)
% Worst=max(Best_score)
% Average=mean(Best_score)
% STD=std(Best_score)
figure('Position',[500 500 660 290])
%Draw objective space
subplot(1,2,2);
semilogy(Convergence,'Color','r','linewidth',2)
title('Objective space')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best score obtained so far');
axis tight
grid on
box on
legend('SAO')
%Draw function in hyperspace
subplot(1,2,1);
func_plot(F_name);
title('Parameter space')
xlabel('x_1');
ylabel('x_2');
zlabel([F_name,'( x_i , x_j )'])
3 仿真结果
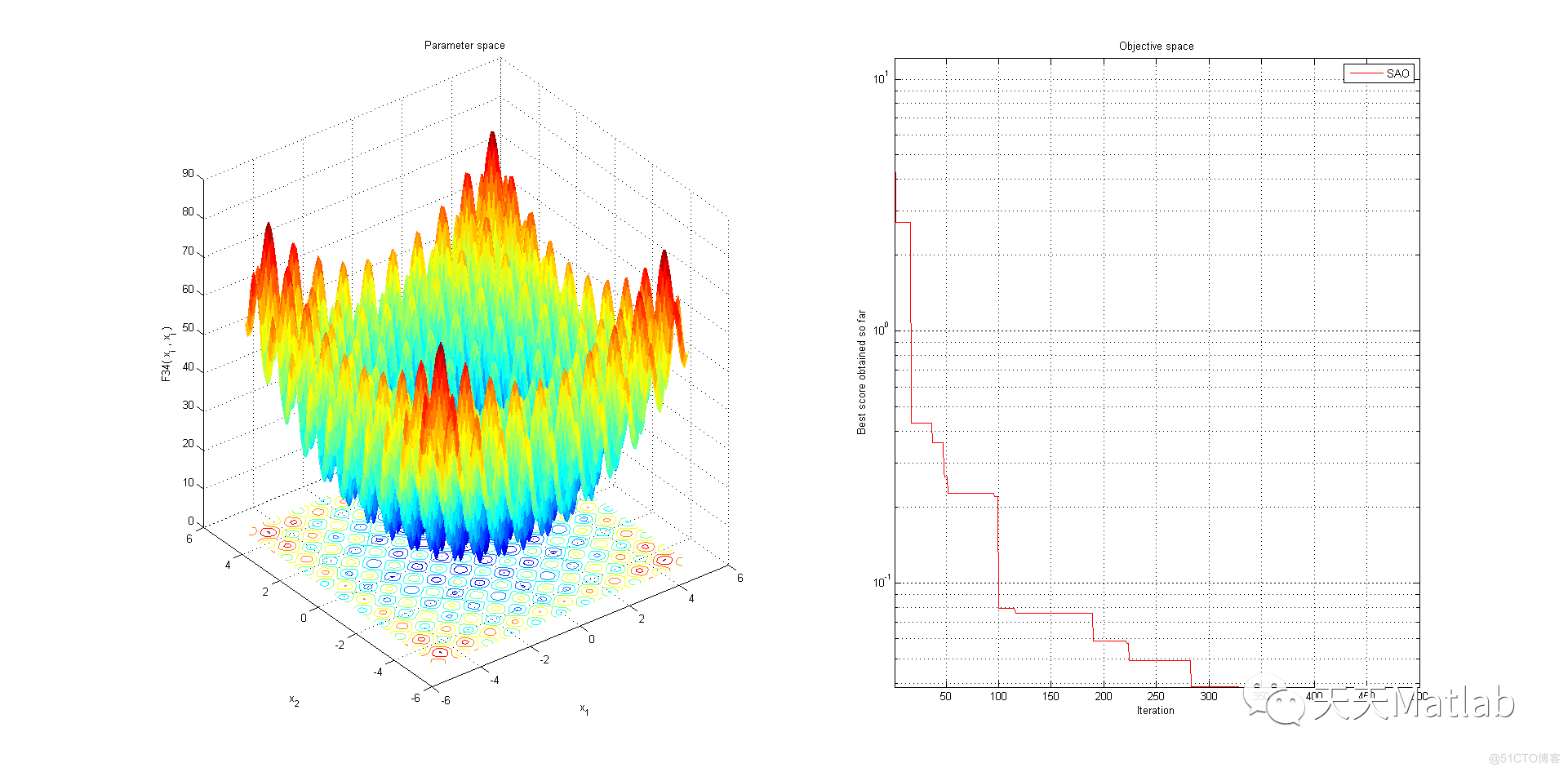
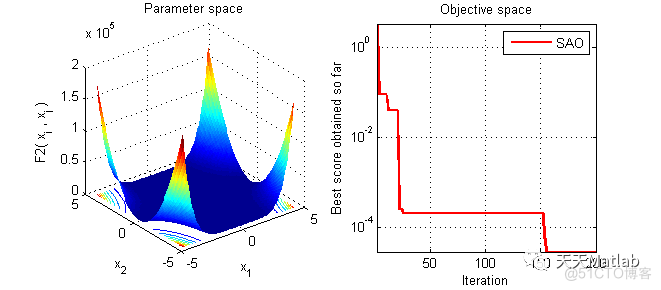
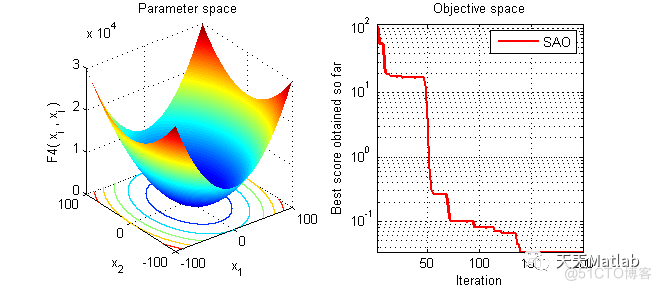
4 参考文献
[1] Salawudeen, A. T. , et al. "A Novel Smell Agent Optimization (SAO): An extensive CEC study and engineering application." Knowledge-Based Systems 4(2021):107486.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。

