Tip:红色字体为简要部分 《[arm驱动]linux异步通知与异步IO》 涉及内核驱动函数二个,内核结构体一个,分析了内核驱动函数二个;可参考的相关应用程序模板或内核驱动模板二个, 可参
Tip:红色字体为简要部分
《[arm驱动]linux异步通知与异步IO》涉及内核驱动函数二个,内核结构体一个,分析了内核驱动函数二个;可参考的相关应用程序模板或内核驱动模板二个,可参考的相关应用程序模板或内核驱动三个
描述:设备文件IO访问:阻塞与非阻塞io访问,poll函数提供较好的解决设备访问的机制,但是如果有了异步通知整套机制就更加完整了
一、阻塞 I/O,非阻塞IO,异步I/O
1、阻塞 I/O :挂起进程一直等待设备可访问后再访问
2、非阻塞IO:进程进行对设备访问一次,不可访问时,继续执行下一条指令
3、异步I/O:非常类似于硬件上“中断”的概念(硬件去call软件,内核去call应用程序);信号是在软件层次上对中断机制的一种模拟;
a)原理:信号是异步的,一个进程不必通过任何操作来等待信号的到达;事实上:进程也不知道信号到底什么时候到达;“一个进程收到一个异步通知信号"与"处理器收到一个中断请求"原理是一样的;
4、异步I/O通知队列(async_queue):内核通过“内核异步通知的程序 fasync()函数”将设备文件fd描述符加入异步通知队列(内核异步通知的链表)。当fd有I/O操作发生时内核通过kill_fasync()释放(产生) SIGIO 信号,从而达到主动通知注册过SIG_IO信号的应用程序。
5、异步通知对象:首先它是设备文件,其次要注册过fasync()函的文件;异步通知对象不是不是普通文件(不是随便的/tmp/text.txt),因为普通文件没有在内核中实现fasync()函数和kill_fasync()
二、异步通讯应用程序部分
模板一)设备文件的异步通知应用程序
voidinput_handler(intnum){//信号处理函数
}
//打开目标设备
fd = open("设备文件路径如/dev/xxx", O_RDWR);
//设置好目标设备的SIGIO信号处理程序;等待内核kill_fasync()释放 SIGIO 信号
signal(SIGIO,input_handler);
//使当前进程变成文件的主人,这样才能使文件中的信号发到当前进程
fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid());
//获得当前fd的flag值
oflags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
/*设置设备文件描述符号fd的FASYNC异步通知标志,
即给fd添加异步通知模式,fasync()函数将fd加入异步IO通知队列*/
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, oflags | FASYNC);
图示一、异步通知工作过程图
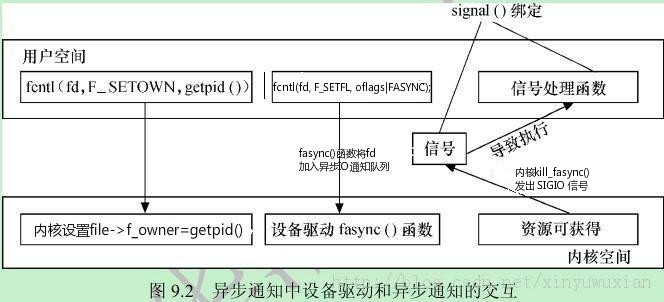
实例一)以标准输入输出设备异步通知
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
#define MAX_LEN 100
voidinput_handler(intnum)
{
chardata[MAX_LEN];
intlen;
len = read(STDIN_FILENO, &data, MAX_LEN);
data[len] = 0;
printf("input available :%s\n", data);
}
voidsetFdAsync(intfd){
intoflags;
//当前进程变成文件的主人
fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid());
//本程序中fd = STDIN_FILENO标准输入设备设备文件描述符号;普通文件内核中没有实现FASYNC,不能使用异步通知
oflags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);//
//FASYNC在glibc 的fcntl.h文件中可以看到这样的定义 #define FASYNC O_ASYNC
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, oflags | FASYNC);
}
voidmain(){
intfd = STDIN_FILENO;//STDIN_FILENO输入输出设备描述符号,一般是键盘
signal(SIGIO,input_handler);//设置好目标设备的SIGIO信号处理程序;等待内核kill_fasync()释放 SIGIO 信号
setFdAsync(fd);
while(1);
}
运行结果:
efgwrfgregr
input available :efgwrfgregr
sfsdf
input available :sfsdf
//本程序电脑上运行时,由于系统对STDIN_FILENO有特殊保护,while里面的程序运行了两次,进程就被系统挂机休眠,此时cpu消耗为0;
//但我在arm开发板上的linux2.6内核运行时,while正常,进程不被挂起,估计是没键盘的原因...,也待解
三、驱动程序部分
驱动程序:一项数据结构和两个函数
结构体一)一项数据结构----- fasync_struct结构体
内核源码一)fasync_struct结构体内核源码
struct fasync_struct {
int magic;//启用设备文件镜像,监听文件是否变化(这个说法我猜的)
int fa_fd;//文件描述符
struct fasync_struct *fa_next; /* 异步通知单链表 */
//filp是进程通过PCB中的文件描述符表找到该fd所指向的文件指针;在fopen流操作中使用file结构体指针它的优点是带有I/O缓存
struct file *fa_file;
//struct file表示该进程打开的文件,其中有一个owner属性,用来表示打开设备文件的进程
};
两个函数
内核部分函数一)fasync_helper处理设备文件异步通知的标志(O_ASYNC或FASYNC),将fd加入异步通知队列函数
fasync_helper(int fd, struct file * filp, int on, struct fasync_struct * * fapp);
内核源码二)fasync_helper内核源码分析
//第一次因为on = MODE = oflag | FASYNC,on!=0所以执行if (on)对struct fasync_struct **fapp进行初始化,
//当程序释放设备使用myfasync_drv_fasync(-1, file, 0),就执行goto out释放中断
int fasync_helper(int fd, struct file * filp, int on, struct fasync_struct **fapp)
{
struct fasync_struct *fa, **fp;
struct fasync_struct *new = NULL;
int result = 0;
if (on) {//第一次分配fapp空间
new = kmem_cache_alloc(fasync_cache, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!new)
return -ENOMEM;
}
write_lock_irq(&fasync_lock);
for (fp = fapp; (fa = *fp) != NULL; fp = &fa->fa_next) {//第一次初始化fapp
if (fa->fa_file == filp) {
if(on) {
fa->fa_fd = fd;
kmem_cache_free(fasync_cache, new);
} else {
*fp = fa->fa_next;
kmem_cache_free(fasync_cache, fa);
result = 1;
}
goto out;
}
}
if (on) {
new->magic = FASYNC_MAGIC;
new->fa_file = filp;
new->fa_fd = fd;
new->fa_next = *fapp;
*fapp = new;
result = 1;
}
out:
write_unlock_irq(&fasync_lock);
return result;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(fasync_helper);
释放信号函数
内核部分函数二)kill_fasync(struct fasync_struct * * fp, int sig, int band)
参数:sig就是我们要发送的信号;band(带宽),一般都是使用POLL_IN,表示设备可读,如果设备可写,使用POLL_OUT
内核源码三)释放(产生)异步读信号函数
void __kill_fasync(struct fasync_struct *fa, int sig, int band)
{
while (fa) {
struct fown_struct * fown;
//如果设备文件镜像不存在如设备文件不存在(被删除或改名)或取消了注册FASYNC;镜像映射失败跳出kill_fasync,不产生信号
if (fa->magic != FASYNC_MAGIC) {
printk(KERN_ERR "kill_fasync: bad magic number in "
"fasync_struct!\n");
return;
}
fown = &fa->fa_file->f_owner;
/* Don't send SIGURG to processes which have not set a
queued signum: SIGURG has its own default signalling
mechanism. */
if (!(sig == SIGURG && fown->signum == 0))
send_sigio(fown, fa->fa_fd, band);
fa = fa->fa_next;
}
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(__kill_fasync);
模板二)信号的异步通知机制模板
struct VirtualDisk{
struct cdev cdev;
//...其他全局变量....
struct fasync_struct *async_queue;//异步结构体指针
};
/*异步读信号*/
static int myfasync_drv_fasync(int fd, struct file *file, int mode){
struct VirtualDisk *devp = file->private_data; /*获得设备结构体指针*/
//....................
return fasync_helper(fd, file, mode, &devp->async_queue);
}
static ssize_t myfasync_drv_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t * ppos){
struct VirtualDisk *devp = file->private_data; /*获得设备结构体指针*/
//...............
//产生异步读信号SIGIO
if(devp->async_queue)kill_fasync(&devp->async_queue, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
return 0;
}
static int myfasync_drv_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
/*当设备关闭时,需要将fasync_struct从异步队列中删除/*
myfasync_drv_fasync(-1, file, 0);
return 0;
}
实例二)驱动程序完整实例:
//“myfasync_drv”,"myfasync_","myfasync_drv"
#include <linux/module.h>//模块所需的大量符号和函数定义
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>//文件系统相关的函数和头文件
#include <linux/init.h> //指定初始化和清除函数
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h> //cdev结构的头文件包含<linux/kdev_t.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/mm.h>
//#include <linux/sched.h>//包含驱动程序使用的大部分内核API的定义,包括睡眠函数以及各种变量声明
#include <asm/uaccess.h>//在内核和用户空间中移动数据的函数
#include <asm/irq.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#include <asm/arch/regs-gpio.h>
#include <asm/hardware.h>
#define VIRTUALDISK_SIZE 0x1000//4k
#define MEM_CLEAR 0x1
#define VIRTUALDISK_MAJOR 250
int VirtualDisk_major = VIRTUALDISK_MAJOR;
struct fasync_struct *async_queue;//异步结构体指针
struct VirtualDisk{
struct cdev cdev;//详细看cdev机制
unsigned char mem[VIRTUALDISK_SIZE ];
long count; /*记录设备目前被多少设备打开*/
};
static struct class *myfasync_class;
static struct class_device *myfasync_class_dev;
struct VirtualDisk *VirtualDiskp;
static int myfasync_drv_fasync(int fd, struct file *file, int mode){
printk("myfasync_drv_fasync %d\n", fd);
return fasync_helper(fd, file, mode, &async_queue);
}
static int myfasync_drv_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("myfasync_drv open\n");
file->private_data = VirtualDiskp;
VirtualDiskp->count++; /*增加设备打开次数*/
return 0;
}
static int myfasync_drv_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("myfasync_drv release\n");
VirtualDiskp->count--; /*减少设备打开次数*/
myfasync_drv_fasync(-1, file, 0);//当设备关闭时,需要将fasync_struct从异步队列中删除
return 0;
}
/*seek文件定位函数:seek()函数对文件定位的起始地址可以是文件开头(SEEK_SET,0)、当前位置(SEEK_CUR,1)、文件尾(SEEK_END,2)*/
static loff_t myfasync_drv_llseek(struct file *file, loff_t offset, int origin){
loff_t ret = 0;/*返回的位置偏移*/
switch (origin)
{
case SEEK_SET: /*相对文件开始位置偏移*/
if (offset < 0)/*offset不合法*/
{
ret = - EINVAL; /*无效的指针*/
break;
}
if ((unsigned int)offset > VIRTUALDISK_SIZE)/*偏移大于设备内存*/
{
ret = - EINVAL; /*无效的指针*/
break;
}
file->f_pos = (unsigned int)offset; /*更新文件指针位置*/
ret = file->f_pos;/*返回的位置偏移*/
break;
case SEEK_CUR: /*相对文件当前位置偏移*/
if ((file->f_pos + offset) > VIRTUALDISK_SIZE)/*偏移大于设备内存*/
{
ret = - EINVAL;/*无效的指针*/
break;
}
if ((file->f_pos + offset) < 0)/*指针不合法*/
{
ret = - EINVAL;/*无效的指针*/
break;
}
file->f_pos += offset;/*更新文件指针位置*/
ret = file->f_pos;/*返回的位置偏移*/
break;
default:
ret = - EINVAL;/*无效的指针*/
break;
}
return ret;
}
/*设备控制函数:ioctl()函数接受的MEM_CLEAR命令,这个命令将全局内存的有效数据长度清零,对于设备不支持的命令,ioctl()函数应该返回-EINVAL*/
static int myfasync_drv_ioctl(struct inode *inode, struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg){
struct VirtualDisk *devp = file->private_data;/*获得设备结构体指针*/
switch (cmd)
{
case MEM_CLEAR:/*设备内存清零*/
memset(devp->mem, 0, VIRTUALDISK_SIZE);
printk(KERN_INFO "VirtualDisk is set to zero\n");
break;
default:
return - EINVAL;
}
return 0;
}
/*读函数:读写函数主要是让设备结构体的mem[]数组与用户空间交互数据,并随着访问字节数变更返回用户的文件读写偏移位置*/
static ssize_t myfasync_drv_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
unsigned long p = *ppos; /*记录文件指针偏移位置*/
unsigned int countt = count;/*记录需要读取的字节数*/
int ret = 0; /*返回值*/
struct VirtualDisk *devp = file->private_data; /*获得设备结构体指针*/
printk("myfasync_drv read\n");
/*分析和获取有效的读长度*/
if (p >= VIRTUALDISK_SIZE ) /*要读取的偏移大于设备的内存空间*/
return 0;/*读取地址错误*/
if (countt > VIRTUALDISK_SIZE - p)/*要读取的字节大于设备的内存空间*/
countt = VIRTUALDISK_SIZE - p;/*将要读取的字节数设为剩余的字节数*/
/*内核空间->用户空间交换数据*/
if (copy_to_user(buf, (void*)(devp->mem + p), countt))
{
ret = - EFAULT;
}
else
{
*ppos += countt;
ret = countt;
printk("read %d bytes(s) is %ld\n", countt, p);
}
printk("bytes(s) is %s\n", devp->mem);
return ret;
}
/*
file 是文件指针,count 是请求的传输数据长度,buff 参数是指向用户空间的缓冲区,这个缓冲区或者保存要写入的数据,或者是一个存放新读入数据的空缓冲区,该地址在内核空间不能直接读写,ppos 是一个指针指向一个"long offset type"对象, 它指出用户正在存取的文件位置. 返回值是一个"signed size type。写的位置相对于文件开头的偏移。
*/
static ssize_t myfasync_drv_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t * ppos)
{
unsigned long p = *ppos; /*记录文件指针偏移位置*/
int ret = 0; /*返回值*/
unsigned int countt = count;/*记录需要写入的字节数*/
struct VirtualDisk *devp = file->private_data; /*获得设备结构体指针*/
printk("myfasync_drv write\n");
/*分析和获取有效的写长度*/
if (p >= VIRTUALDISK_SIZE )/*要写入的偏移大于设备的内存空间*/
return 0;/*写入地址错误*/
if (countt > VIRTUALDISK_SIZE - p)/*要写入的字节大于设备的内存空间*/
countt = VIRTUALDISK_SIZE - p;/*将要写入的字节数设为剩余的字节数*/
/*用户空间->内核空间*/
if (copy_from_user(devp->mem + p, buf, countt))
ret = - EFAULT;
else
{
*ppos += countt;/*增加偏移位置*/
ret = countt;/*返回实际的写入字节数*/
printk("written %u bytes(s) from%lu, buffer is %s\n", countt, p, devp->mem);
}
if(async_queue){
kill_fasync(&async_queue, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
printk("write kill_fasync\n");
}
return ret;
}
static struct file_operations myfasync_drv_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE, /* 这是一个宏,推向编译模块时自动创建的__this_module变量 */
.open = myfasync_drv_open,
.read = myfasync_drv_read,
.write = myfasync_drv_write,
.release = myfasync_drv_release,
.llseek = myfasync_drv_llseek,
.ioctl = myfasync_drv_ioctl,
.fasync = myfasync_drv_fasync,
};
/*将 cdev 结构嵌入一个你自己的设备特定的结构,你应当初始化你已经分配的结构使用以上函数,有一个其他的 struct cdev 成员你需要初始化. 象 file_operations 结构,struct cdev 有一个拥有者成员,应当设置为 THIS_MODULE,一旦 cdev 结构建立, 最后的步骤是把它告诉内核, 调用:
cdev_add(&dev->cdev, devno, 1);*/
static void VirtualDisk_setup_cdev(struct VirtualDisk *dev, int minorIndex){
int err;
int devno = MKDEV(VirtualDisk_major, minorIndex);
cdev_init(&dev->cdev, &myfasync_drv_fops);
dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
err = cdev_add(&dev->cdev, devno, 1);
if(err){
printk("error %d cdev file added\n", err);
}
}
static int myfasync_drv_init(void)
{
int result;
dev_t devno = MKDEV(VirtualDisk_major, 0);
if(VirtualDisk_major){
result = register_chrdev_region(devno, 1, "myfasync_drv");
}else{
result = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, 1, "myfasync_drv");
VirtualDisk_major = MAJOR(devno);
}
if(result < 0 ){
return result;
}
VirtualDiskp = kmalloc(sizeof(struct VirtualDisk), GFP_KERNEL);
if(!VirtualDiskp){
result = -ENOMEM;
goto fail_malloc;
}
memset(VirtualDiskp, 0, sizeof(struct VirtualDisk));
VirtualDisk_setup_cdev(VirtualDiskp, 0);
myfasync_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "myfasync_drv");
if (IS_ERR(myfasync_class))
return PTR_ERR(myfasync_class);
myfasync_class_dev = class_device_create(myfasync_class, NULL, MKDEV(VirtualDisk_major, 0), NULL, "myfasync_drv"); /* /dev/xyz */
if (IS_ERR(myfasync_class_dev))
return PTR_ERR(myfasync_class_dev);
return 0;
fail_malloc:
unregister_chrdev_region(devno, 1);
return result;
}
static void myfasync_drv_exit(void)
{
cdev_del(&VirtualDiskp->cdev);
kfree(VirtualDiskp);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(VirtualDisk_major, 0), 1);
class_device_unregister(myfasync_class_dev);
class_destroy(myfasync_class);
}
module_init(myfasync_drv_init);
module_exit(myfasync_drv_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
Makefile
#myfasync_drv.c
KERN_DIR = /workspacearm/linux-2.6.2.6
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
cp myfasync_drv.ko /opt/fsmini/
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf timerlists.order
obj-m += myfasync_drv.o
实例三)驱动程序对应的测试的应用程序部分
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <signal.h>
int myfd;
int lenthe;
void input_handler(int num)
{
char data[80];
int len;
lseek(myfd, -lenthe, SEEK_CUR);//移动偏移量到写之前位置
len = read(myfd, data, lenthe);
//data[len] = '\0';
printf("myfd = %d, len = %d buffuer input available :%s\n",myfd, len, data);
}
void setFdAsync(int fd){
int oflags;
//当前进程变成文件的主人
fcntl(fd, F_SETOWN, getpid());
//本程序中fd = STDIN_FILENO标准输入设备设备文件描述符号;普通文件内核中没有实现FASYNC,不能使用异步通信
oflags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);//
//FASYNC在glibc 的fcntl.h文件中可以看到这样的定义 #define FASYNC O_ASYNC
fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, oflags | FASYNC);
}
int main(){
myfd = open("/dev/myfasync_drv", O_RDWR);//STDIN_FILENO输入输出设备描述符号,一般是键盘
printf("fd = %d,pid = %d", myfd, getpid());
signal(SIGIO,input_handler);//设置好目标设备的SIGIO信号处理程序;等待内核kill_fasync()释放 SIGIO 信号
setFdAsync(myfd);
printf("before while\n");
while(1){
char buffer[80];
lenthe = read(STDIN_FILENO, buffer, 80);
write(myfd, buffer, lenthe);
}
return 0;
}
我的Makefile
objs := $(patsubst %c, %o, $(shell ls *.c))
myarmgcc := /workspacearm/armlinuxgcc2626/bin/arm-linux-gcc
mybutton.bin:$(objs)
$(myarmgcc) -o $@ $^
cp *.bin /opt/fsmini/
%.o:%.c
$(myarmgcc) -c -o $@ $<
clean:
rm -f *.bin *.o
实验结果
# insmod myfasync_drv.ko
# ./mybutton.bin
myfasync_drv open//对应应用程序myfd = open("/dev/myfasync_drv",调用了内核驱动open函数
myfasync_drv_fasync 3//对应应用程序fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, oflags | FASYNC);调用了内核驱动的myfasync_drv_fasync()函数
//
fd = 3,pid = 793before while//while前的进程信息输出
hello//键盘输入hello
myfasync_drv write//调用驱动程序write函数
written 6 bytes(s) from0, buffer is hello//驱动程序write函数内部输出
write kill_fasync//内涵write函数中,执行kill_fasync(&async_queue, SIGIO, POLL_IN);释放SIGIO信号
myfasync_drv read//此时应用程序收到中断,应用程序执行read函数,read对应内核驱动的read
read 6 bytes(s) is 0//内核驱动read打印输出
bytes(s) is hello //内核驱动read打印输出
myfd = 3, len = 6 buffuer input available :hello//应用程序input_handler函数输出驱动的写入值
//下面是while第二次执行
it is ok
myfasync_drv write
written 9 bytes(s) from6, buffer is hello
it is ok
write kill_fasync
myfasync_drv read
read 9 bytes(s) is 6
bytes(s) is hello
it is ok
myfd = 3, len = 9 buffuer input available :it is ok
//按ctrl+c退出程序,会执行myfasync_drv_release中myfasync_drv_fasync(-1, file, 0),释放本进程的异步通知
myfasync_drv release
myfasync_drv_fasync -1
#
四、异步IO缺陷:当有多个文件发送异步通知信号给一个进程时,进程无法知道是哪个文件发送的信号,这时候“设备文件 ”还是要借助poll机制完成IO;(应用程序中使用select)
【文章转自
香港云服务器 http://www.1234xp.com 复制请保留原URL】

