文章目录 背景 饿汉式加载单例模式在多线程环境中的问题 原因分析 synchronized同步与volatile修饰 总结 背景 在单例模式的设计中,一般会用
文章目录
- 背景
- 饿汉式加载单例模式在多线程环境中的问题
- 原因分析
- synchronized同步与volatile修饰
- 总结
背景
在单例模式的设计中,一般会用到两种方式:
立即加载 : 在类加载初始化的时候就主动创建实例;也称为饿汉式加载。
延迟加载 : 等到真正使用的时候才去创建实例,不用时不去主动创建。也称为懒汉式加载。
//立即创建对象
private static SingletonThread singletonThread = new SingletonThread ();
private SingletonThread (){}
public static SingletonThread getInstance(){
return singletonThread ;
}
//懒汉式加载
private static SingletonThread instance;
//使用用才创建对象
public static SingletonThread getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SingletonThread();
}
return instance;
}
饿汉式加载单例模式在多线程环境中的问题
/*** 懒汉式单例模式在多线程安全的问题
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-05-08
*/
public class SingletonThread {
static SingletonThread instance;
static SingletonThread getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SingletonThread();
}
return instance;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
SingletonThread singletonThread = SingletonThread.getInstance();
//打印线程获取的hash值,用来判断返回的是否是同一单例
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + singletonThread.hashCode());
}).start();
}
}
}
多次运行以上程序,会出现以下BUG,第一个线程得到的实例的hash值与其他线程的得到的hash不一致,单例模式未生效。
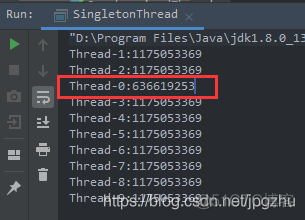
原因分析
- 饿汉式加载单例模式在单例类创建时就完成了对象的初始化,在多线程环境下,线程访问单例时对象就创建完成了,所以线程天生就是安全的。
- 而懒汉式加式模式是使用单例类时才完成对象的初始化,在多线程环境下,多个线程会同时进入到 if (instance == null) { instance = new SingletonThread();}很有可能造成创建出多个实例,违背了单例模式的初衷。
synchronized同步与volatile修饰
那怎么解决以上代码中有可能出现的多个实例的问题呢?可以添加synchronized同步锁与volatile修饰静态变量来解决(synchronized的原理可参见 java多线程:synchronized的深度理解)(volatile的原理可参见java多线程:volatile的深度理解 )
/*** 懒汉式单例模式在多线程安全的问题
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-05-08
*/
public class SingletonThread {
//使用volatile关键字防止重排序,因为 new Instance()是一个非原子操作,可能创建一个 不完整的实例
static volatile SingletonThread instance;
static SingletonThread getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
//对代码块线程同步锁,进行双重判断
synchronized (SingletonThread.class) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new SingletonThread();
}
}
//
}
return instance;
}
static void destroy() {
instance = null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int k = 0; k < 100; k++) {
System.out.println("第" + (k + 1) + "次");
Thread[] threads = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(() -> {
SingletonThread singletonThread = SingletonThread.getInstance();
//打印线程获取的hash值,用来判断返回的是否是同一单例
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + singletonThread.hashCode());
});
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threads[i].start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threads[i].join();
}
SingletonThread.destroy();
}
}
}
总结
为保证程序的执行效率 ,考虑只对部分代码块用synchronized实现同步锁,并且用volatile进行修饰静态变量,这种做法无疑是优秀的。
