目录
- 前言
- 游戏规则
- Three.js
- 整个程序的结构
- 实现
- html文件引入three.js引擎
- 页面结构
- 场景
- 相机
- 几何体
- 光源
- 渲染
- 添加第二块
- 跳块
- 鼠标按下状态
- 鼠标松开弹起状态
- 落在哪里
- 结尾
前言
跳一跳是微信小程序的一个小游戏。长按屏幕让小人蓄力跳跃,进行游玩。按照小人跳跃盒子的数量,以及特殊盒子加分项计算得分。
游戏地址:不会搞(所以没放)git地址:gitee.com/fwjzzz/Jump
游戏规则
十分简单:长按鼠标蓄力、放手,方块就会从一个盒子跳到另一个盒子。然而就是这个小动作,让你一旦开始就魔性地停不下来。
Three.js
Three.js 是一款运行在浏览器中的 3D 引擎,你可以用它创建各种三维场景,包括了摄影机、光影、材质等各种对象。
- 创建一个场景
- 设置光源
- 创建相机,设置相机位置和相机镜头的朝向
- 创建3D渲染器,使用渲染器把创建的场景渲染出来
整个程序的结构
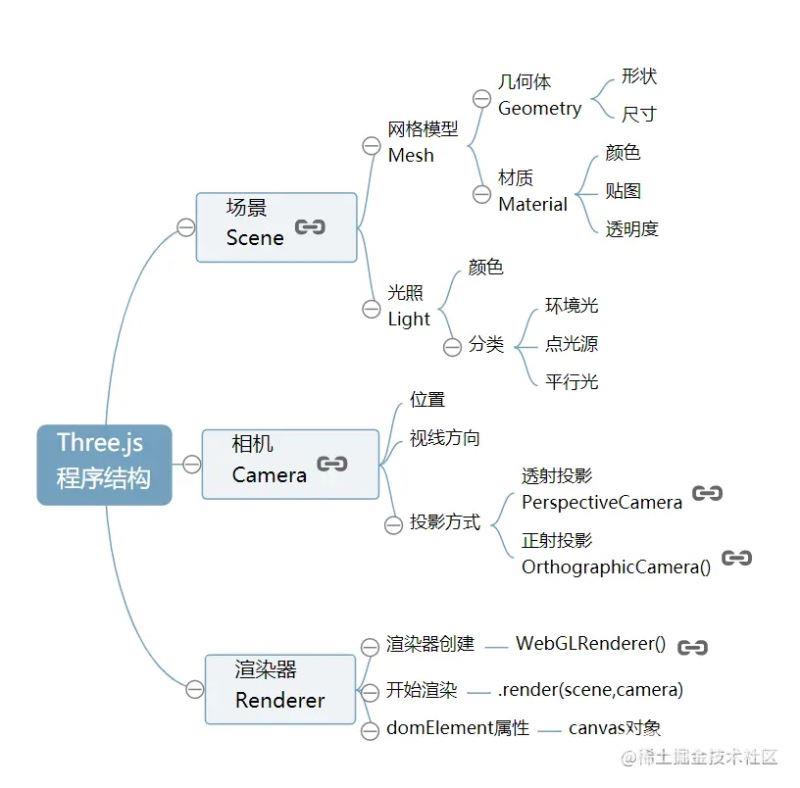
实现
html文件引入three.js引擎
<script src="/js/three.min.js"></script>
页面结构
<div class="mask">
<div class="content">
<div class="score-container">
<p class="title">本次得分</p>
<h1 class="score">0</h1>
</div>
<button class="restart">
重新开始
</button>
</div>
</div>
<div class="info">
<audio loop="loop" autoplay controls src="https://m801.music.126.net/20220413225245/3060206bc37e3226b7f45fa1
49b0fb2b/jdymusic/obj/wo3DlMOGwrbDjj7DisKw/13866197954/e351/984c/1f8b/f6d3165d6b04dc78ec0d3c273ce02ff2.mp3">
</audio>
<div class="gaming-score">
得分:<span class="current-score">0</span>
</div>
</div>

场景
let scene=new THREE.Scene(); //创建一个场景
相机
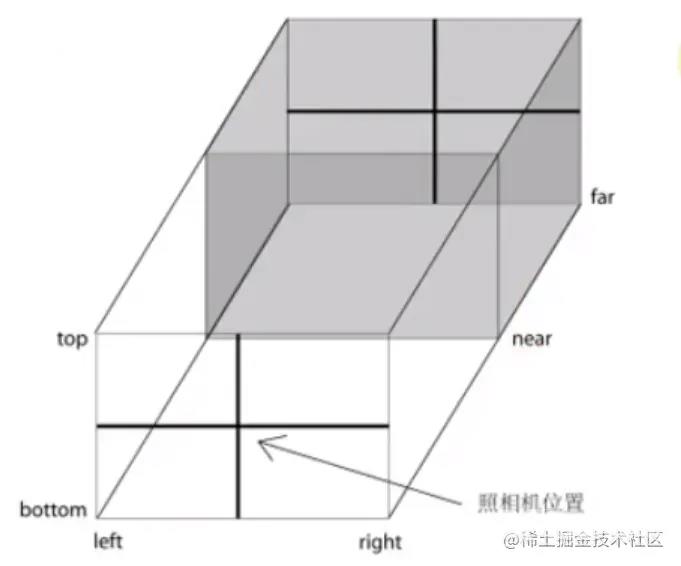
常用的相机有两种:
- 透视相机PerspectiveCamera
符合人心理习惯,近大远小。
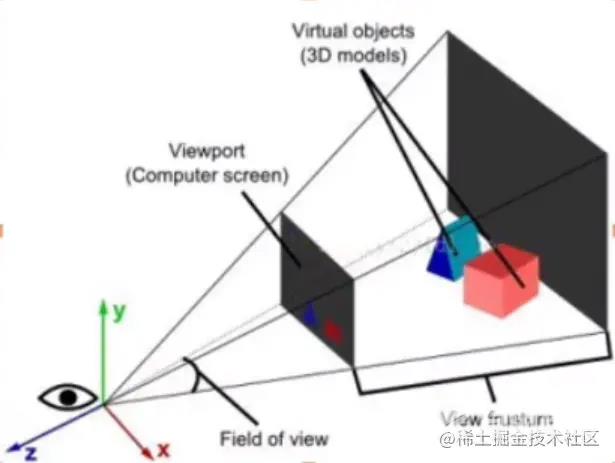
- 正视相机OrthographicCamera
远处和近处一样大
let camera=new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75,window.innerWidth/window.innerHeight,1,1000); //创建一个透视相机 4个参数(视觉范围,宽高比例,近距离,远距离) camera.position.z=10; camera.position.y=3; camera.position.x=8; //相机的xyz场景方向
几何体
使用CubeGeometry创建一个立方几何体,使用MeshLambertMaterial材质用来配置立方体渲染看上去暗淡不光亮的表面,该材质会对场景中的光源产生反应,这个材质可以配置一些其他属性如:颜色等。
let geometry=new THREE.CubeGeometry(4,2,4);
//创建一个几何体对象 (宽,高,深度)
let material=new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xbebebe});
//创建了一个可以用于立方体的材质,对象包含了颜色、透明度等属性,
let cube=new THREE.Mesh(geometry,material);
//结合在一起
cube.position.x=16;
scene.add(cube);
//添加到场景中
光源
场景Scene主要是由几何体模型和光Light构成,在实际开发过程中,大多数三维场景往往需要设置光源,通过不同的光源对模型模拟生活中的光照效果,尤其是为了提高Threejs的渲染效果更需要设置好光源,就像摄影师拍照要打灯一样。
let directionalLight=new THREE.DirectionalLight(0xffffff,1.1); //平行光 (颜色,强度) directionalLight.position.set(3,10,5); //平行光位置 scene.add(directionalLight); //在场景中加入平行光 let light=new THREE.AmbientLight(0xffffff,0.4); //光的材质 scene.add(light); //把光添加到场景
渲染
直接通过WebGL渲染器WebGLRenderer的.setSize()方法设置渲染尺寸为浏览器body区域宽高度。
let renderer=new THREE.WebGLRenderer({antialias:true});
//创建一个渲染器 (让边缘动画没有锯齿感)
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight);
// 画布宽高
renderer.setClearColor(0x282828);
//修改画布颜色
renderer.render(scene,camera);
//渲染场景相机 (后续更新也是这里)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
//把当前渲染的画布放到body里面
let x=8;
function render() {
//递归
x-=0.1;
camera.position.x=x;
renderer.render(scene,camera);
//更新重新渲染
if(x>=-8){
//满足当前条件
requestAnimationFrame(render)
//循环渲染
}
}
目前为止实现了一个雏形

添加第二块
_createCube() {
let geometry = new THREE.CubeGeometry(this.config.cubeWidth, this.config.cubeHeight, this.config.cubeDeep);
//创建一个几何体对象 (宽,高,深度)
let material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: this.config.cubeColor
});
//材质,对象包含了颜色、透明度等属性,
let cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material); //合并在一起
if (this.cubes.length) {
//从第二块开始随机左右方向出现
cube.position.x = this.cubes[this.cubes.length - 1].position.x;
cube.position.y = this.cubes[this.cubes.length - 1].position.y;
cube.position.z = this.cubes[this.cubes.length - 1].position.z;
this.cubeStat.nextDir = Math.random() > 0.5 ? "left" : "right"; //要不左边要不右边
if (this.cubeStat.nextDir == "left") {
//左边改变x轴否则y轴
cube.position.x = cube.position.x - Math.round(Math.random() * 4 + 6);
} else {
cube.position.z = cube.position.z - Math.round(Math.random() * 4 + 6);
}
}
this.cubes.push(cube); //统一添加块
if (this.cubes.length > 5) {
//页面最多看到5个块
this.scene.remove(this.cubes.shift()); //超过就移除
}
this.scene.add(cube); //添加到场景中
if (this.cubes.length > 1) {
//更新镜头位置
this._updateCameraPros();
}
};
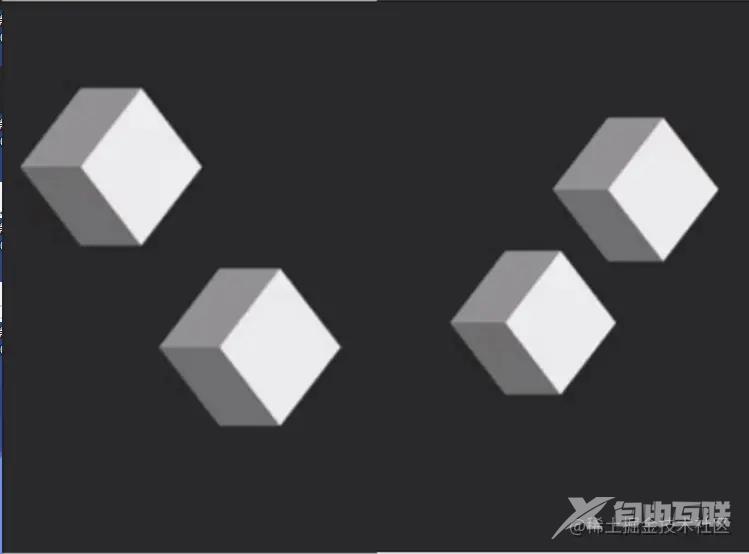
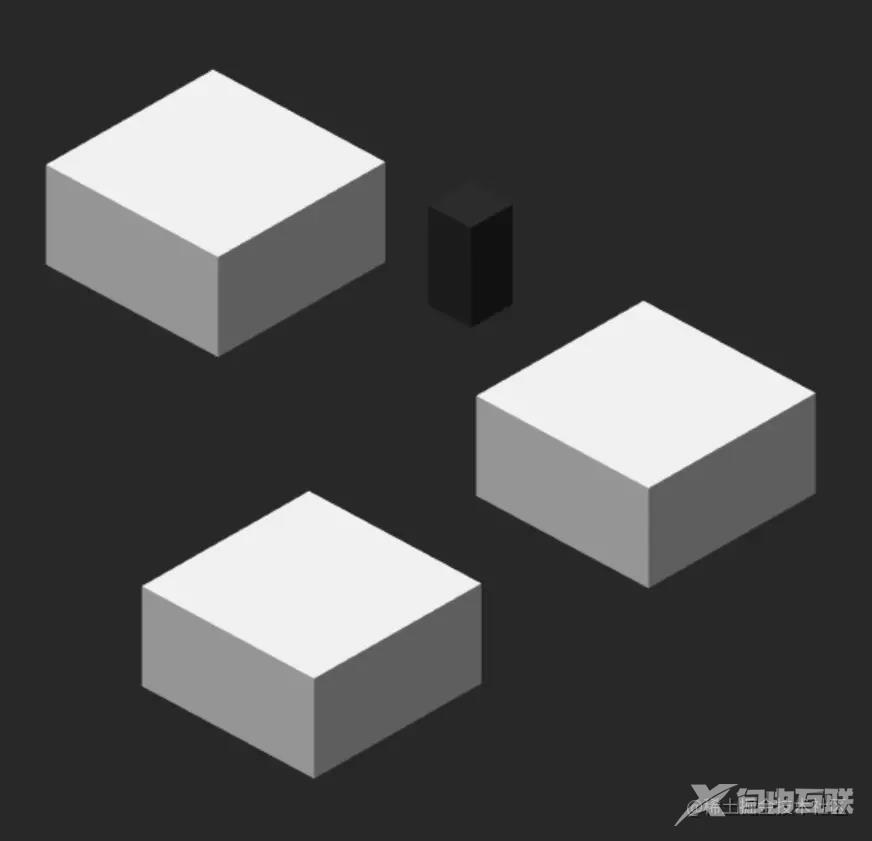
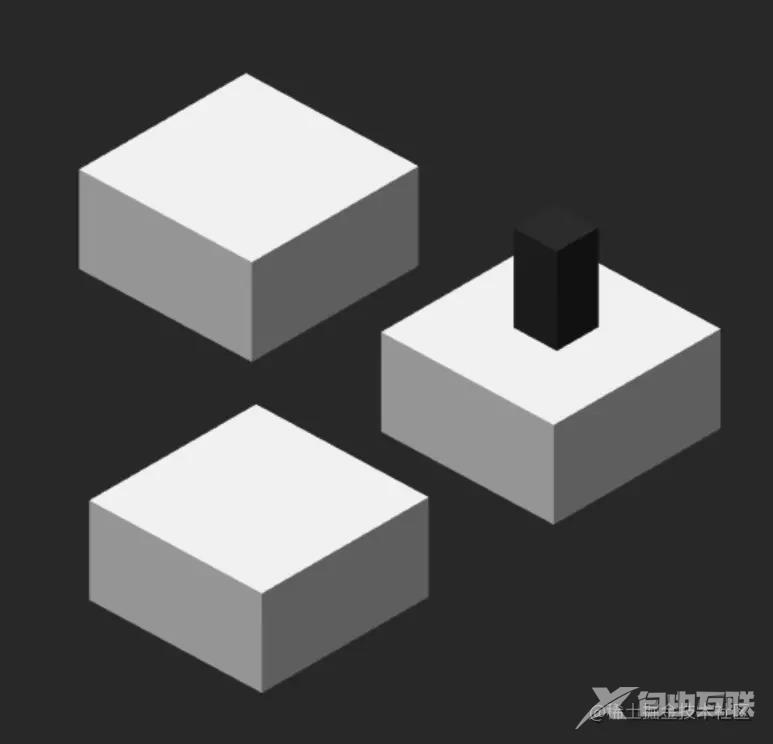
定义一个方块数组,判断从第二块开始向左右两边随机出现。this.cubeStat.nextDir = Math.random() > 0.5 ? "left" : "right" 如上图:(这是由两张图组成的)
跳块

_createJumper() {
let geometry = new THREE.CubeGeometry(this.config.jumperWidth, this.config.jumperHeight, this.config
.jumperDeep); // (宽,高,深度)
let material = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({
color: this.config.jumperColor
}); //材质,颜色、透明度
this.jumper = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material); //合并在一起
this.jumper.position.y = 1; //显示跳块
geometry.translate(0, 1, 0); //平移
this.scene.add(this.jumper); //添加到场景中
}
使用Geometry几何体对象有一系列的顶点属性和方法,通过.scale()、.translate()、.rotateX()等方法可以对几何体本身进行缩放、平移、旋转等几何变换。注意本质上都是改变结合体顶点位置坐标数据。
鼠标按下状态
this.jumperStat = {
//鼠标按下速度
ready: false,
xSpeed: 0,
ySpeed: 0
};
_handleMouseDown() {
if (!this.jumperStat.ready && this.jumper.scale.y > 0.02) {
this.jumper.scale.y -= 0.01; //压缩块
this.jumperStat.xSpeed += 0.004;
this.jumperStat.ySpeed += 0.008;
this._render();
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
this._handleMouseDown()
})
}
};
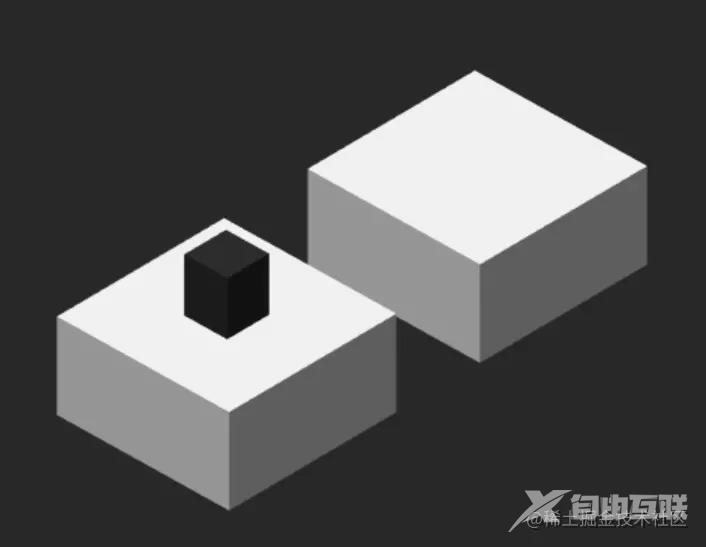
鼠标松开弹起状态
人生不就是这样吗?只要你跳对了位置,就能够“逆袭”!
//鼠标松开谈起状态
_handleMouseUp() {
this.jumperStat.ready = true;
if (this.jumper.position.y >= 1) {
if (this.jumper.scale.y < 1) {
this.jumper.scale.y += 0.1; //压缩状态小于1就+
}
if (this.cubeStat.nextDir == "left") {
//挑起盒子落在哪里
this.jumper.position.x -= this.jumperStat.xSpeed;
} else {
this.jumper.position.z -= this.jumperStat.xSpeed;
}
this.jumper.position.y += this.jumperStat.ySpeed;
this.jumperStat.ySpeed -= 0.01; //上升落下状态
this._render();
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
//循环执行
this._handleMouseUp();
})
} else {
//落下状态
this.jumperStat.ready = false;
this.jumperStat.xSpeed = 0;
this.jumperStat.ySpeed = 0;
this.jumper.position.y = 1;
this.jumper.scale.y = 1;
this._checkInCube(); //检测落在哪里
if (this.falledStat.location == 1) {
//下落后等于1,+分数
this.score++;
this._createCube();
this._updateCamera();
if (this.successCallback) {
//否则失败
this.successCallback(this.score);
}
} else {
this._falling()
}
}
};
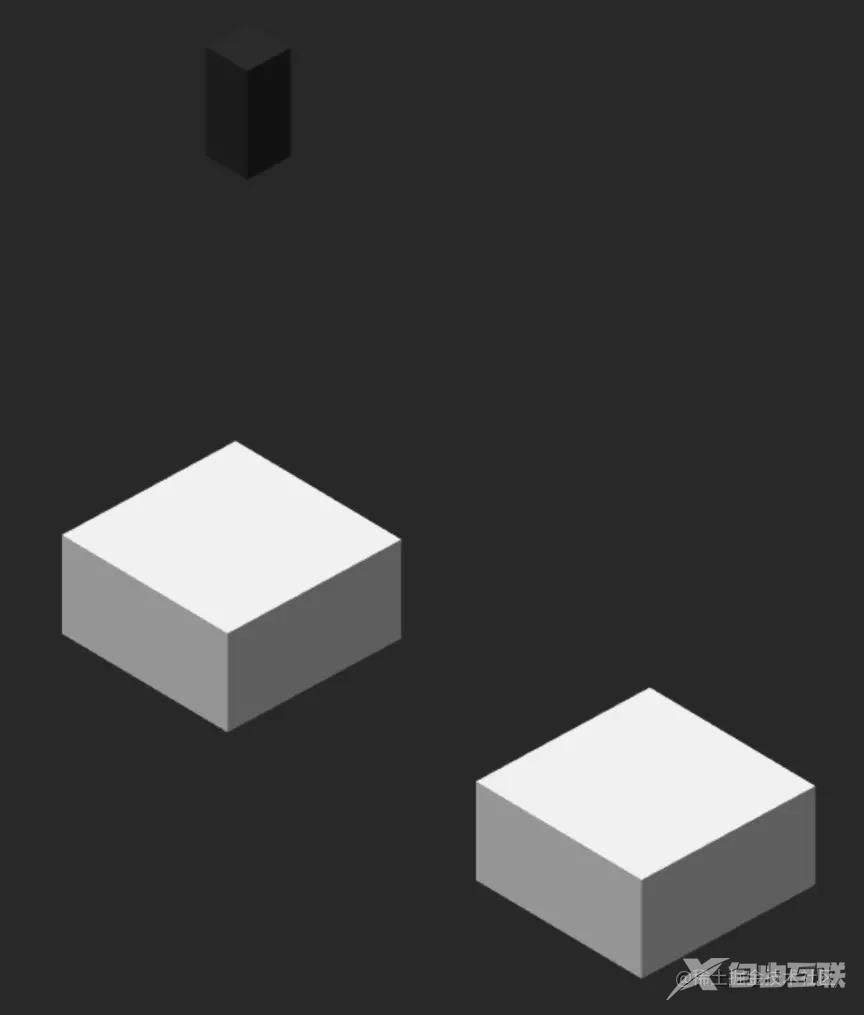
落在哪里
学会控制速度感是非常奇妙的事情。当你慢下来了,学会控制速度。因为在每一个过程当中,都有你生命中值得停下来浏览、欣赏、感受的事物。在我们的认知中,总觉得越快,拥有的时间就越多,效率就越高,生产力就提高。其实并不是。如果你的头脑常常处在思维高速运转的状态,一定会感觉繁忙且毫无头绪;如果你总是担心着未来或者挂念过去,就无法专注在当下所做的事,也一定感到时间不够用,效率大大降低。
this.falledStat = {
location: -1, //落在哪里 当前块块上
distance: 0, //距离是否倒下
};
this.fallingStat = {
//有没有落到点
end: false,
speed: 0.2
}
//检测落在哪里
//-1 -10从当前盒子掉落
//1 下一个盒子上 10从下一个盒子上掉落
//0没有落在盒子上
_checkInCube() {
let distanceCur, distanceNext;
//当前盒子距离 下一个盒子距离
let should = (this.config.jumperWidth + this.config.cubeWidth) / 2;
//
if (this.cubeStat.nextDir == "left") {
//往左走了
distanceCur = Math.abs(this.jumper.position.x - this.cubes[this.cubes.length - 2].position.x);
distanceNext = Math.abs(this.jumper.position.x - this.cubes[this.cubes.length - 1].position.x);
} else {
//往右走了
distanceCur = Math.abs(this.jumper.position.z - this.cubes[this.cubes.length - 2].position.z);
distanceNext = Math.abs(this.jumper.position.z - this.cubes[this.cubes.length - 1].position.z);
}
if (distanceCur < should) {
//落在当前块
this.falledStat.distance = distanceCur;
this.falledStat.location = distanceCur < this.config.cubeWidth / 2 ? -1 : -10;
} else if (distanceNext < should) {
//落在下一个块上
this.falledStat.distance = distanceNext;
this.falledStat.location = distanceNext < this.config.cubeWidth / 2 ? 1 : 10;
} else {
//落在中间
this.falledStat.location = 0;
}
};
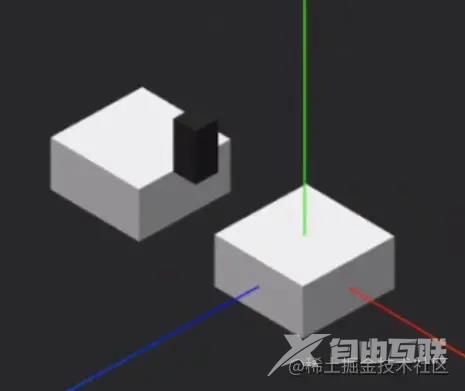
落到方块上,停上一会儿,放松自己,亦会有十分的额外奖励。人生路上,匆匆忙忙赶路的时候,不要忘了适度休息调整,你会有意外地收获,命运的魔方会给你别致的惊喜。人生很短,何须急着走完。
//下落过程
_falling() {
if (this.falledStat.location == 10) {
//从下一个盒子落下
if (this.cubeStat.nextDir == "left") {
//判断左方向
if (this.jumper.position.x > this.cubes[this.cubes.length - 1].position.x) {
this._fallingRotate("leftBottom")
} else {
this._fallingRotate("leftTop")
}
} else {
//判断右方向
if (this.jumper.position.z > this.cubes[this.cubes.length - 1].position.z) {
this._fallingRotate("rightBottom")
} else {
this._fallingRotate("rightTop")
}
}
} else if (this.falledStat.location == -10) {
//从当前盒子落下
if (this.cubeStat.nextDir == "left") {
this._fallingRotate("leftTop")
} else {
this._fallingRotate("rightTop")
}
} else if (this.falledStat.location == 0) {
this._fallingRotate("none")
}
};
结尾
赢也好,输也罢,人生就是一个起起伏伏的过程,处在巅峰不骄,跌落低谷不馁。这才是正确的人生姿势。当然,这里不仅仅说的是游戏。有可能是埋头玩游戏的你,也许你早注意到那个小方块的玩家形象,就是生活中的“ 自己 ”。这个世界就如 “跳一跳” 游戏:规则和目标都明确的智力游戏,玩家可以自由地行动,站对位置就可以加分。时时轻拂拭,勿使惹尘埃。便可有收获,享受生活,热爱人世间的烟火!!!
到此这篇关于如何利用Three.js实现跳一跳小游戏的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Three.js跳一跳小游戏内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
