目录
- 目录文件说明
- 一、设置文本内容
- 1、在layout文件下新建一个xml文件
- 2、配置XML文件设置文本
- 3、string文件内容
- 4、java类调用
- 二、设置文本的大小
- 三、设置文本颜色
- 四、设置视图的宽高
- 五、设置视图的间距
- 1、layout_margin
- 2、padding
- 六、设置视图的对齐方式
- 1、layout_gravity
- 2、gravity
目录文件说明
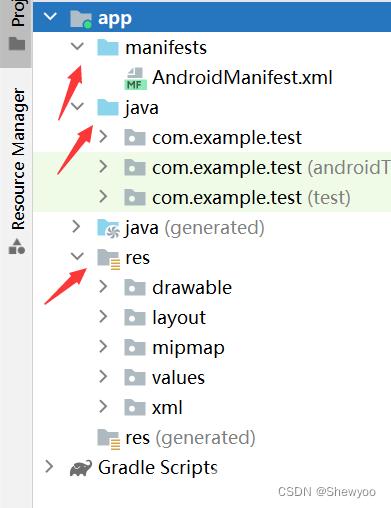
mainifests子目录:下面的AndroidMainifest.xml文件是APP的运行配置文件。
java子目录:下面有三个com.example.myapp包,第一个包存放当前模块的java源代码,后面两个包存放测试用的java代码。
res子目录:存放当前模块的资源文件,有四个子目录:
- drawable目录存放图形描述文件与图片文件
- layout目录存放app页面的布局文件
- mipmap存放app的启动图标
- values存放一些常量定义文件,如字符串常量string.xml等。
一、设置文本内容
有两种方式:在XML文件中设置和在java类中调用settext方法。
在XML文件中通过属性android:text设置
1、在layout文件下新建一个xml文件
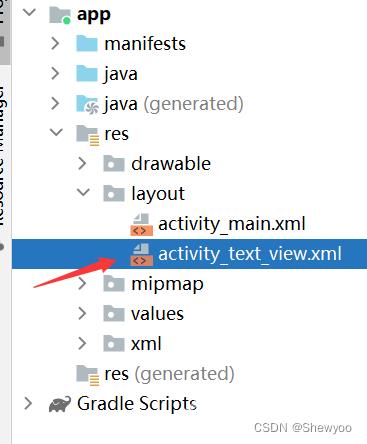
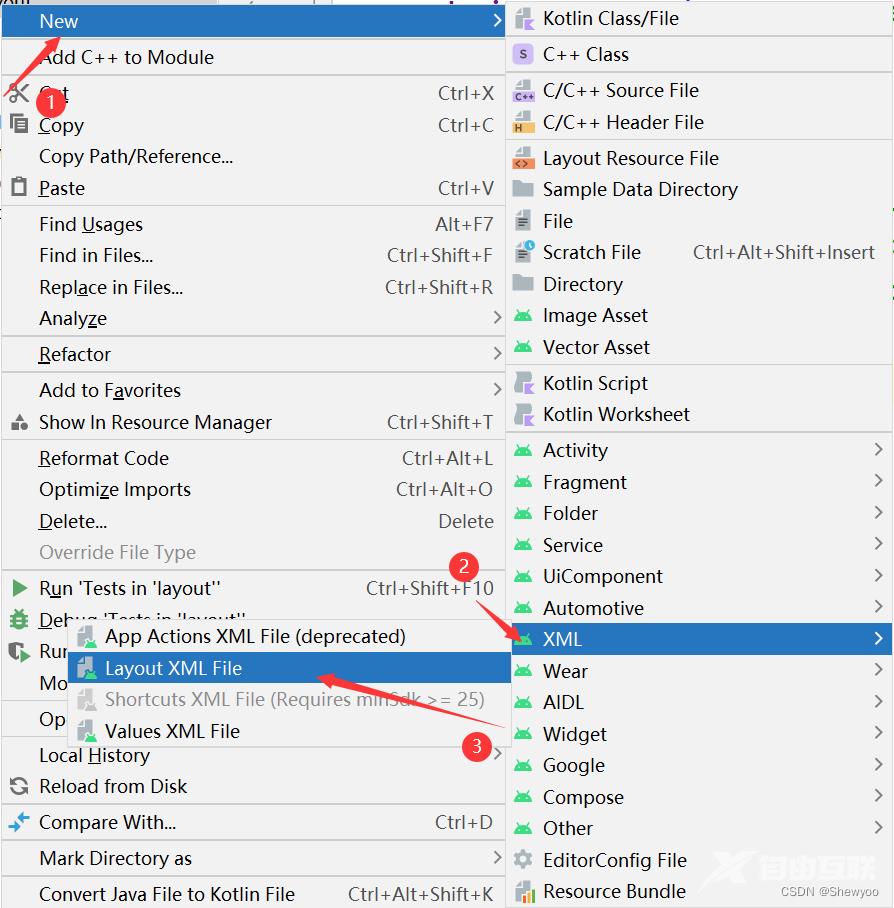
新建后会有以下默认内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</LinearLayout>
2、配置XML文件设置文本
在LinearLayout标签里添加以下内容;
text标签里不写具体的内容是因为:
情况:多个文件都用了相同的内容,但是需要修改此内容,那么就需要修改多个文件,而把内容写在string文件里,则只需要修改string文件的内容。
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_hello"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"/> //调用string文件里name为hello的文本
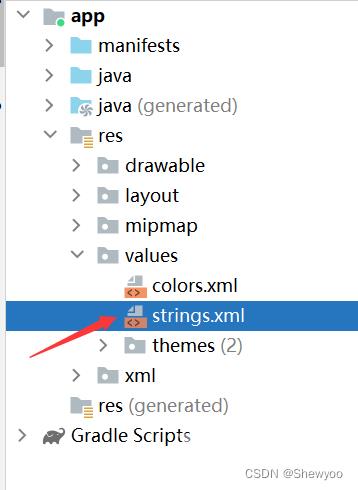
3、string文件内容
<resources>
<string name="app_name">test</string>
<string name="hello">你好</string>
</resources>
4、java类调用
新建Java类,继承AppComatActivity类,并重写onCreate方法
public class TextViewActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_text_view);
}
}
在java代码中调用文本视图对象的setText方法设置文本
与前面不同的是不需要在xml文件中写text标签,需要在java类中创建对象并调用setText方法。
public class TextViewActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_text_view);
TextView tv_hello = findViewById(R.id.tv_hello);
tv_hello.setText(R.string.hello);// 调用setText方法设置文本
}
}
二、设置文本的大小
px:是手机屏幕的最小显示单位,与设备的显示屏有关。
dp/dip:是与设备无关的显示单位,只与屏幕的尺寸有关,相同尺寸手机,即使分辨率不同,同dp组件占用屏幕比例也相同,如果屏幕尺寸差异过大,需要做dp适配。
sp:专门用来设置字体大小,在系统设置中可以调整字体大小,跟随系统字体设置而变化。
在java代码中调用setTextSize方法
新建XML文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_hello"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello" />
</LinearLayout>
新建java类
public class TextSizeActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_text_size);
TextView tv_px = findViewById(R.id.tv_hello);
tv_px.setTextSize(30);//这里不用指定单位,默认为sp,所以官方推荐字体设置单位是sp
}
在XML文件中通过属性android:textSize指定 XML文件
android:textSize="30px"/>
java类
public class TextSizeActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_text_size);
}
}
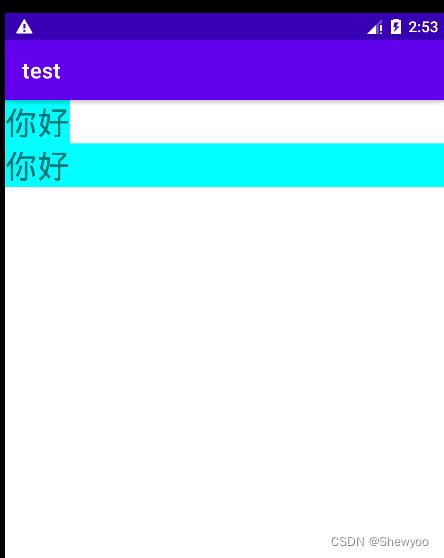
三、设置文本颜色
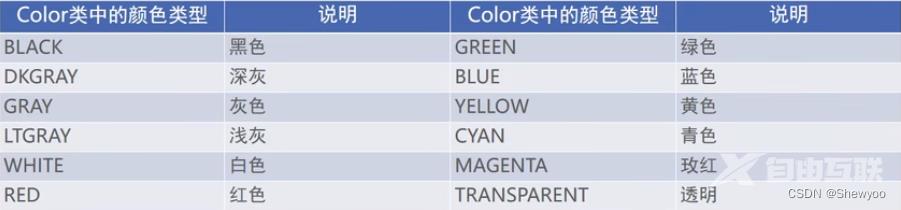
在java代码中调用setTextColor方法设置文本颜色
具体色值可从Color获取
XML文件
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_code_system"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="设置系统自带颜色"
android:textSize="17sp"/>
java类
public class TextColorActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_text_color);
//布局文件中获取文本视图
TextView tv_code_system = findViewById(R.id.tv_code_system);
//设置文本颜色
tv_code_system.setTextColor(Color.GREEN);
}
四、设置视图的宽高
视图宽度通过属性android:layout_width表达,高度通过android:layout_height
宽高的取值主要有下列三种:
- match_parent:表示与上级视图保持一致
- wrap_content:表示与内容自适应
- 以dp为单位的具体尺寸
例:
//上面的
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
//下面的
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
五、设置视图的间距
有两种方式:采用layout_margin属性、padding属性
1、layout_margin
指定了当前视图与周围平级视图之间的距离,即外边距,包括:layout_margin、layout_marginLeft、layout_marginTop、layout_marginRight、layout_marginBottom
2、padding
指定当前视图与内部下级视图之间的距离,即内边距,包括:padding、paddingLeft、paddingTop、paddingRight、paddingBottom
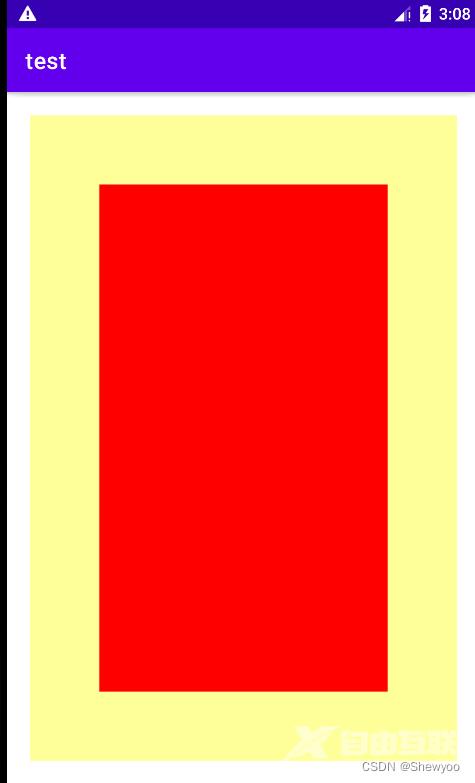
例:
View标签在LinearLayout内,所以为其下级视图
<!-- 中间层的布局背景为黄色-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="20dp"//外边距20dp
android:background="#FFFF99"
android:padding="60dp">//内边距60dp
<!-- 最内层的视图背景为红色-->
<View
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FF0000"/>
</LinearLayout>
六、设置视图的对齐方式
有两种方式:采用layout_gravity属性、采用gravity属性;
取值包括:left、top、right、bottom,可以用竖线连接各取值,如:left|top表示朝左上角对齐。
1、layout_gravity
指定当前视图相对于上级视图的对齐方式。
2、gravity
指定下级视图相对于当前视图的对齐方式。
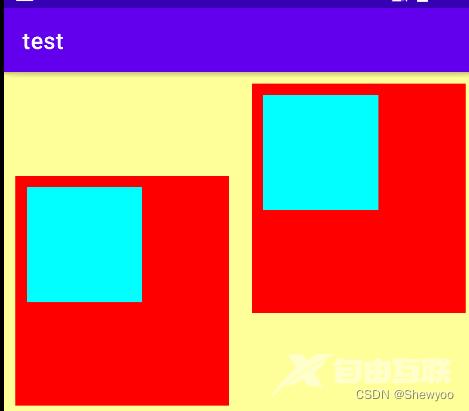
例:
<!--第一个子布局背景为红色,它在上级视图中朝下对齐,下级视图靠左对齐-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:padding="10dp"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:layout_gravity="bottom"
android:gravity="left">
<!-- 内部视图-->
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#00ffff"/>
</LinearLayout>
<!--第二个子布局背景为红色,它在上级视图中朝上对齐,下级视图靠右对齐-->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:padding="10dp"
android:background="#ff0000"
android:layout_gravity="top">
<View
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="#00ffff"
android:gravity="right"/>
</LinearLayout>
到此这篇关于Android文本与视图基本操作梳理介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android文本与视图内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
