头文件: 在unix下是unistd.h,VS下是direct.h 代码: #include stdio.h#include string// 区分此函数是在Windows环境调用还是Linux环境调用#if defined (_WIN64) || defined (WIN32) || defined (_WIN32)//printf("---Windows
头文件:
在unix下是unistd.h,VS下是direct.h
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
// 区分此函数是在Windows环境调用还是Linux环境调用
#if defined (_WIN64) || defined (WIN32) || defined (_WIN32)
//printf("---Windows---\n");
#include <direct.h>
#else
//printf("---Linux---\n");
#include <unistd.h>
#endif
/******************************************************************************
*
* 功能:
* 获得当前程序的工作路径(绝对路径),即运行路径!
*
* 注意:
* 头文件在unix下是unistd.h,VS下是direct.h,应该依编程者的环境而定.
* 这里解释一下运行路径,即是程序开始运行的路径,例如:
* 1.如果是在Windows环境的VS编译器中运行项目,则返回的是项目路径,
* 即代码文件路径(.h和.cpp路径),因为是在编译器中运行的项目,所以
* 程序的运行路径也是才项目路径中开始运行的。
* 2.如果是在Windows环境,运行已经编译好的.exe程序,则返回的是当前
* .exe程序所在的路径,因为是在当前路径所运行的!
* 3.在Linux环境,返回的都是可执行程序的路径!
*
* 参数:
* 无.
*
* 返回值:
* 成功返回程序的工作路径(绝对路径);失败返回空串
*
******************************************************************************/
std::string getOperationFilePath() {
char *buffer = NULL;
// 区分此函数是在Windows环境调用还是Linux环境调用
#if defined (_WIN64) || defined (WIN32) || defined (_WIN32)
// 获取项目的工作路径
buffer = _getcwd(NULL, 0);
#else
// 获取项目的工作路径
buffer = getcwd(NULL, 0);
#endif
if (buffer) {
std::string path = buffer;
free(buffer);
return path ;
}
return "";
}
测试运行:
int main(void) {
printf("getOperationFilePath = %s\n", getOperationFilePath().c_str());
system("pause");
return 0;
}
在VS中运行截图:
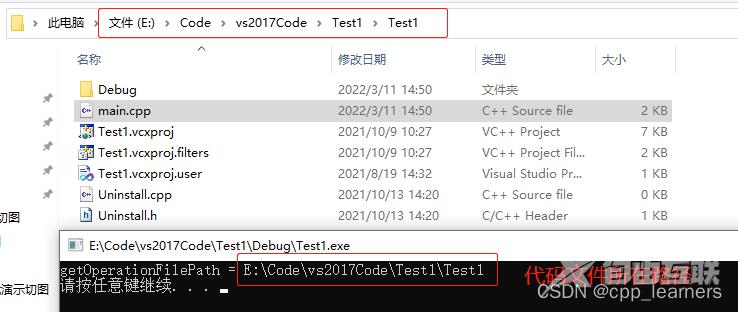
直接运行.exe截图:

解释上面提到的问题:
这里解释一下运行路径,即是程序开始运行的路径,例如:
- 如果是在Windows环境的VS编译器中运行项目,则返回的是项目路径,即代码文件路径(.h和.cpp路径),因为是在编译器中运行的项目,所以程序的运行路径也是才项目路径中开始运行的。
- 如果是在Windows环境,运行已经编译好的.exe程序,则返回的是当前.exe程序所在的路径,因为是在当前路径所运行的!
- 在Linux环境,返回的都是可执行程序的路径!
Windows有一个api可以直接获得项目的运行路径,不用区分是在项目中运行还是.exe运行!
头文件:
#include < Windows.h >
#include <Windows.h>
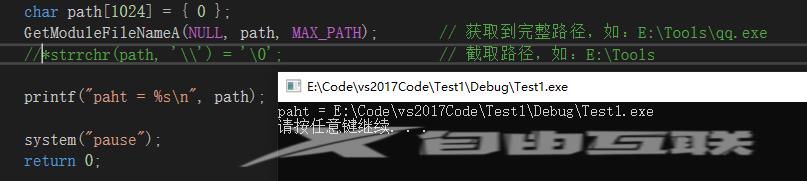
int main(void) {
char path[1024] = { 0 };
GetModuleFileNameA(NULL, path, MAX_PATH); // 获取到完整路径,如:E:\Tools\qq.exe
*strrchr(path, '\\') = '\0'; // 截取路径,如:E:\Tools
printf("paht = %s\n", path);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行截图:
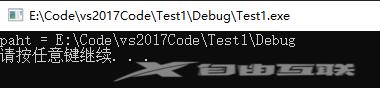
如果把代码:*strrchr(path, ‘\’) = ‘\0’; // 截取路径,如:E:\Tools
注释掉,则可以获得全路径:
如果第一种方式没法正确获取的话,可以尝试使用此种方式:
头文件: #include < unistd.h >
linux系统中有个符号链接:/proc/self/exe它代表当前程序,可以用readlink读取它的源路径就可以获取当前程序的绝对路径了。
std::string getOperationFilePath() {
char buf[256] = { 0 };
int ret = readlink("/proc/self/exe", buf, 256);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("%d: readlink error:%s", __LINE__, strerror(errno));
return "";
}
*strrchr(buf, '/') = '\0'; // 去掉可执行程序名 /tmp/test/a.exe ==> /tmp/test
return buf;
}
总结:
这也是一个小小的细节问题,也有点小坑,今天这个坑我踩过,下次就不会再踩了。
到此这篇关于C++ getcwd函数获取项目运行路径方法详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++ getcwd函数内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
