SpringMVC的核心流程
-
建立请求和Controller方法的映射集合的流程。
-
根据请求查找对应的Controller方法的流程。
-
请求参数绑定到方法形参,执行方法处理请求,返回结果进行视图渲染的流程。
SpringMVC的处理流程图

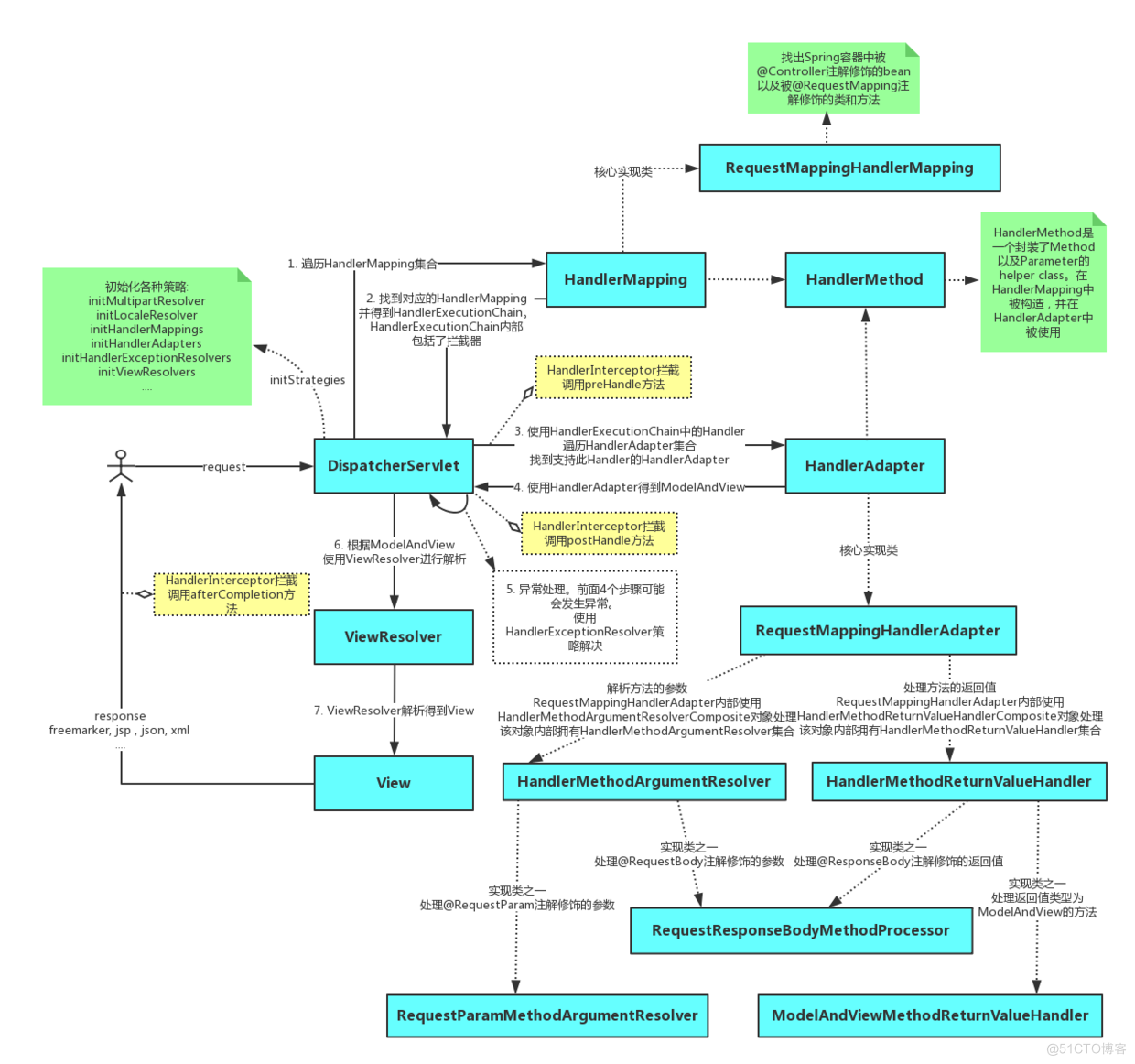
SpringMVC的核心组件和请求处理流程:
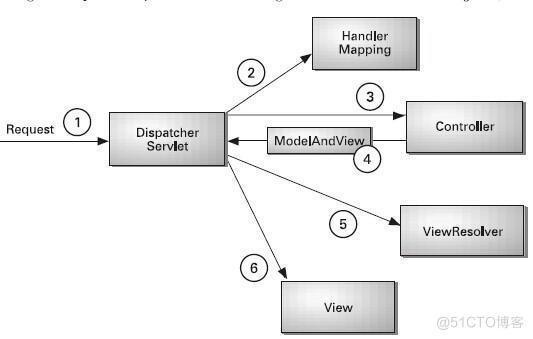
-
1、浏览器发出一个url请求,通过Nginx的反向代理,web容器如Tomcat就会接收到这个请求,并委派给其内置的线程池去调用Servlet进行处理,在SpringMVC中这个Servlet的名字就叫做DispatcherServlet。
-
2、DispatcherServlet在接收到请求之后,将请求派发给处理器映射器HanlerMapping实现类,HanlerMapping会去解析请求向DispatcherServlet返回Handler,HandlerMapping会把请求映射为HandlerExecutionChain对象(包含一个Handler处理器(页面控制器)对象,多个HandlerInterceptor拦截器对象),并找到和请求相对应的Controller和对应的方法实例。
-
3、随后DispatcherServlet调用处理器适配器去执行Handler,处理器适配器HandlerAdapter将会根据适配的结果去执行Handler调用对应的方法进行处理,Handler执行完成给适配器返回ModelAndView。
-
4、处理器适配器向DispatcherServlet返回ModelAndView (ModelAndView是springmvc框架的一个底层对象,包括 Model和view)
-
5、随后DispatcherServlet会将其委派给视图解析器ViewReslover,去完成对视图的解析(根据逻辑视图名解析成真正的视图(jsp)),通过这种策略很容易更换其他视图技术,只需要更改视图解析器即可。
-
6、视图解析器向DispatcherServlet返回视图对象View,DispatcherServlet进行视图渲染 (视图渲染将模型数据(在ModelAndView对象中)填充到request域)。
-
7、视图渲染完成之后,DispatcherServlet就会将视图对象放入到响应流中回发给浏览器,浏览器就会将渲染后的视图展现给用户。
SpringMVC的工作机制
在容器初始化时会建立所有url和controller的对应关系,保存到Map<url,controller>中。tomcat启动时会通知spring初始化容器(加载bean的定义信息和初始化所有单例bean),然后springmvc会遍历容器中的bean,获取每一个controller中的所有方法访问的url,然后将url和Controller保存到一个Map中。
这样就可以根据request快速定位到Controller,因为最终处理request的是Controller中的方法,Map中只保留了url和Controller中的对应关系,所以要根据request的url进一步确认Controller中的method,这一步工作的原理就是拼接Controller的url(Controller上@RequestMapping的值)和方法的url(method上@RequestMapping的值),与request的url进行匹配,找到匹配的那个方法。
确定处理请求的method后,接下来的任务就是参数绑定,把request中参数绑定到方法的形式参数上,这一步是整个请求处理过程中最复杂的一个步骤。SpringMVC提供了两种request参数与方法形参的绑定方法: * ① 通过注解进行绑定 @RequestParam * ② 通过参数名称进行绑定
使用注解进行绑定,我们只要在方法参数前面声明@RequestParam("a"),就可以将request中参数a的值绑定到方法的该参数上。使用参数名称进行绑定的前提是必须要获取方法中参数的名称,Java反射只提供了获取方法的参数的类型,并没有提供获取参数名称的方法。SpringMVC解决这个问题的方法是用asm框架读取字节码文件,来获取方法的参数名称。asm框架是一个字节码操作框架,关于asm更多介绍可以参考它的官网。个人建议,使用注解来完成参数绑定,这样就可以省去asm框架的读取字节码的操作。
注解方式初始化分析
SpringServletContainerInitializer#onStartup
- Tomcat容器启动首先会调用SpringServletContainerInitializer类中的onStartup方法
WebApplicationInitializer#onStartup
- 随后会调用WebApplicationInitializer实现类中的onStartup方法
- 在AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer中的onStartup方法中调用registerDispatcherServlet方法去读入相关的配置,去创建Spring web ioc 容器和DispatcherServlet实例等操作。
ContextLoaderListener#contextInitialized
- 之后会调用ContextLoaderListener里面的contextInitialized方法
这意味着注解配置方式的初始化会先于web.xml配置方式的初始化执行,并且在执行到这里的时候,Spring里面相关的Root容器、子容器和DispatcherServlet实例都已经被创建好了。
ContextLoader#initWebApplicationContext
- 随后调用ContextLoader类中的initWebApplicationContext方法。
-
尝试从SpringMVC子容器中获取Root容器,由于在AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer类中的registerDispatcherServlet方法中只是创建了父子容器,并没有做关联。
-
在该方法中的configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法会调用refresh()方法对Root容器(Root WebApplicationContext)和Servlet容器(dispatcher-servlet mvc子容器)进行刷新。
-
在dispatcher-servlet子容器调用refresh()方法刷新之前会调用HttpServletBean的init方法和FrameworkServlet类的initServletBean、initWebApplicationContext、configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext等方法。
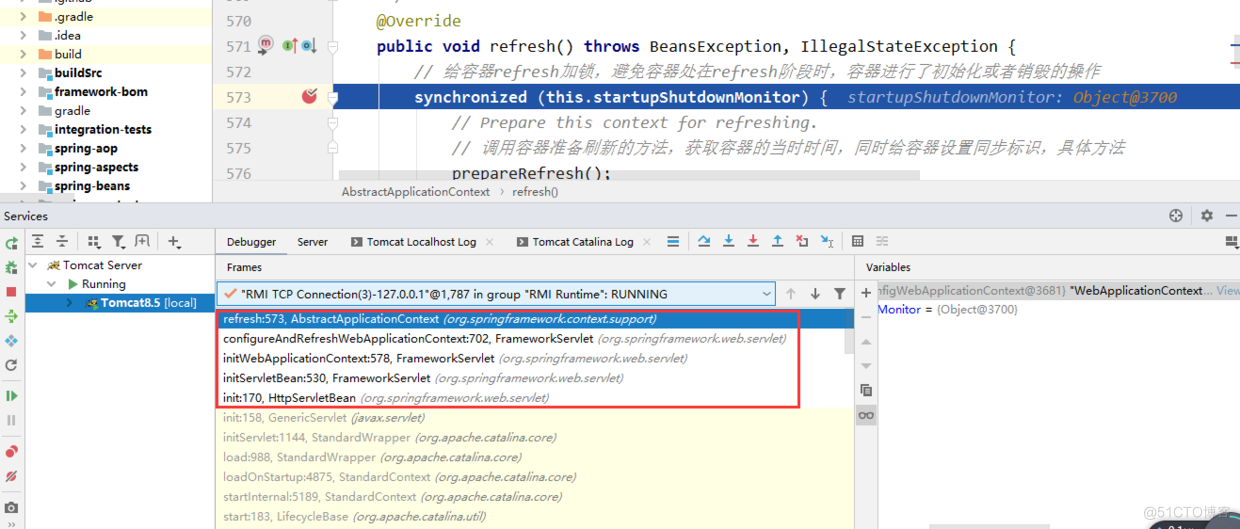
- 而SpringMVC里面只有一个Servlet即DispatcherServlet,因此推测DispatcherServlet和HttpServletBean、FrameworkServlet有着密切相关的关系。
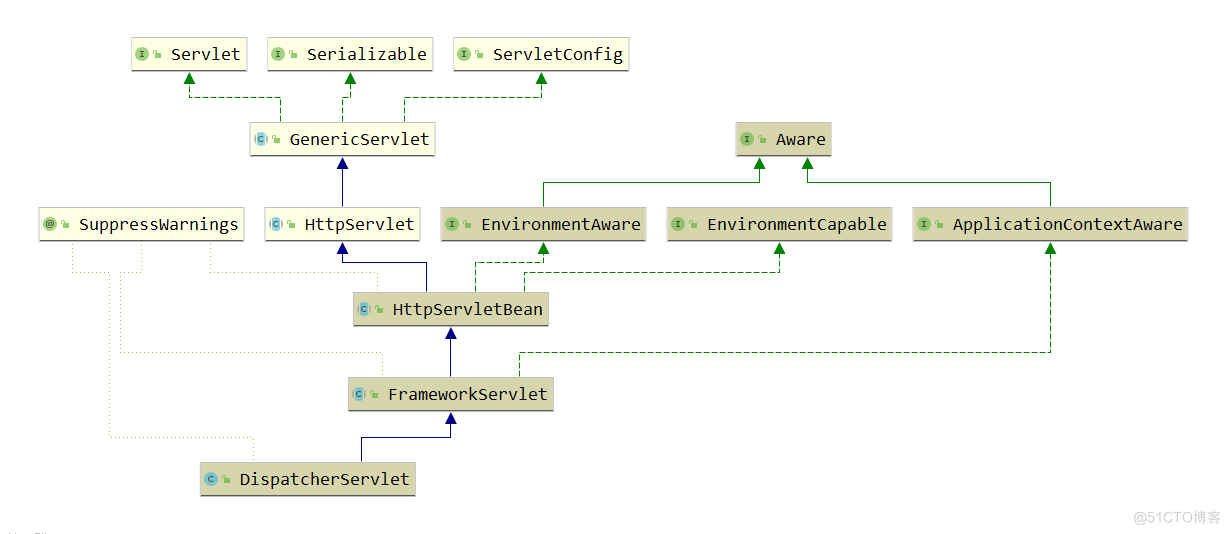
- Servlet初始化的时候会调用init方法,所以这里的dispatcher-servlet子容器的刷新是在DispatcherServlet初始化的时候进行的,即调用的是HttpServletBean的init方法和FrameworkServlet类的initServletBean、initWebApplicationContext、configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext等方法。
HttpServlet
HttpServlet是Servlet规范中的核心类,实现Servlet接口,继承此类用于处理用户请求
HttpServletBean
HttpServletBean主要配置servlet中初始化参数。继承HttpServlet,并实现无参的init()方法,用于设置在web.xml中配置的contextConfigLocation属性,此属性指定Spring MVC的配置文件地址,默认为WEB-INF/[servlet-name]-servlet.xml。
HttpServletBean#init
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware { @Override public final void init() throws ServletException { // Set bean properties from init parameters. //获取在web.xml配置的初始化参数<init-param>,并将其设置到DispatcherServlet中 PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties); if (!pvs.isEmpty()) { try { BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex); } throw ex; } } // Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like. //调用子类FrameworkServlet进行初始化 //模板方法,此方法在HttpServletBean本身是空的,但是因为调用方法的对象是DispatcherServlet //所以优先在DispatcherServlet找,找不到再去父类找,最后在FrameworkServlet找 initServletBean(); } }HttpServletBean的作用:
- 获取web.xml的中配置DispatcherServlet的初始化参数,存放到一个参数容器ServletConfigPropertyValues中。
- 根据传进来的this创建BeanWrapper,本质上它就是DispatcherServlet
- 通过bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true),把参数设置到bw(即DispatcherServlet)里面去。
- 最后调用子类的initServletBean()。
FrameworkServlet
FrameworkServlet主要创建WebApplicationContext上下文,重写了HttpServletBean的initServletBean()方法。
initServletBean
- 该方法只有两句关键代码,其作用一个是调用initWebApplicationContext()方法初始化WebApplicationContext上下文,另一个是调用子类方法initFrameworkServlet()方法。
initWebApplicationContext
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware { protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() { // 获取root WebApplicationContext,即web.xml中配置的listener(ContextLoaderListener) WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null; // 判断容器是否由编程式传入(即是否已经存在了容器实例),存在的话直接赋值给wac,给springMVC容器设置父容器 // 最后调用刷新函数configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac),作用是把Spring MVC配置文件的配置信息加载到容器中去 if (this.webApplicationContext != null) { // A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it // context上下文在构造是注入 wac = this.webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc // context没有被refreshed,提供一些诸如设置父context、设置应用context id等服务 if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set // the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } // 在ServletContext中寻找是否有Spring MVC容器,初次运行是没有的,Spring MVC初始化完毕ServletContext就有了Spring MVC容器 if (wac == null) { // No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one // has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed // that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the // user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } // 当wac既没有没被编程式注册到容器中的,也没在ServletContext找得到,此时就要新建一个Spring MVC容器 if (wac == null) { // No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one // 如果没有WebApplicationContext则创建 wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } // 到这里Spring MVC容器已经创建完毕,接着真正调用DispatcherServlet的初始化方法onRefresh(wac) // 此处仍是模板模式的应用 if (!this.refreshEventReceived) { // Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh // support or the context injected at construction time had already been // refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here. synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) { onRefresh(wac); } } // 将Spring MVC容器存放到ServletContext中去,方便下次取出来 if (this.publishContext) { // Publish the context as a servlet context attribute. String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); } return wac; } }createWebApplicationContext
如果没有WebApplicationContext则创建
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware { protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable WebApplicationContext parent) { return createWebApplicationContext((ApplicationContext) parent); } protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) { Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass(); if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) { throw new ApplicationContextException( "Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() + "] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext"); } // 实例化容器 ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); // 设置容器环境 wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()); // 设置父容器 wac.setParent(parent); // 加载Spring MVC的配置信息,如:bean注入、注解、扫描等等 String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation(); if (configLocation != null) { wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation); } // 刷新容器,根据Spring MVC配置文件完成初始化操作 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac); return wac; } }configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
- 刷新容器,根据Spring MVC配置文件完成初始化操作
总结FrameworkServlet的作用:
- 创建Spring MVC的容器,根据配置文件实例化里面各种bean,并将之与spring的容器进行关联。
- 把创建出来的Spring MVC容器存放到ServletContext中。
- 通过模板方法模式调用子类DispatcherServlet的onRefresh()方法。
DispatcherServlet
DispatcherServlet是Spring MVC核心,它是J2EE规范前端控制器的实现,负责拦截用户请求,并解析请求进行转发。
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet { @Override protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) { initStrategies(context); } protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { //初始化文件上传处理器 initMultipartResolver(context); //初始化国际化配置 initLocaleResolver(context); //初始化主题处理器 initThemeResolver(context); //初始化HanlderMapping initHandlerMappings(context); //初始化HandlerAdapter //HandlerAdapter用来调用具体的方法对用户发来的请求来进行处理 initHandlerAdapters(context); //初始化异常处理器, // HandlerExceptionResolver是用来对请求处理过程中产生的异常进行处理 initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); //RequestToViewNameTranslator用于在视图路径为空的时候,自动解析请求 //去获取ViewName initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); //初始化视图处理器 //ViewResolvers将逻辑视图转成view对象 initViewResolvers(context); //FlashMapManager用于存储、获取以及管理FlashMap实例 initFlashMapManager(context); } }总结:
-
容器启动时,加载web.xml部署描述文件,扫描到并找到DispatcherServlet核心控制器。
-
调用HttpServletBean的init()方法,把DispatcherServlet初始化参数设置到DispatcherServlet中,并调用子类FrameworkServlet的initServletBean()方法。
-
FrameworkServlet的initServletBean()创建Spring MVC容器并初始化,并且和Spring父容器进行关联,使得Spring MVC容器能访问Spring容器中定义的bean,之后调用子类DispatcherServlet的onRefresh()方法。
-
DispatcherServlet的onRefresh(ApplicationContext context)对DispatcherServlet的策略组件进行初始化。
参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/yoci/p/10642493.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/fangjian0423/p/springMVC-directory-summary.html
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000014674239
https://blog.csdn.net/win7system/article/details/90674757
https://www.cnblogs.com/liwangcai/p/10743943.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/myitnews/p/11565941.html
