目录 先看应用 实现思路 具体实现 订阅监听时做下对不传匹配路径等情况的处理 请求发布时根据是否具有路由表route属性进行判断从而对中间件区分处理 总结流程 先看应用 应用规则:
目录
- 先看应用
- 实现思路
- 具体实现
- 订阅监听时做下对“不传匹配路径”等情况的处理
- 请求发布时根据“是否具有路由表route属性”进行判断从而对中间件区分处理
- 总结流程
先看应用
应用规则:
- express 中 use 的第一个参数是匹配路径 不传相当于"/"
- 中间件匹配机制是惰性匹配,即匹配路径为
/a的中间件,访问/aa时同样会被执行(这也意味着不传匹配路径时即所有请求都会应用此中间件)
const express = require("./express");
const app = express();
// 第一个参数是匹配路径 不传相当于"/"
app.use(function (req, res, next) {
req.a = 1;
next();
});
app.use("/", function (req, res, next) {
req.a++;
next();
});
app.get("/", function (req, res, next) {
res.end(req.a + "");
});
app.use("/a", function (req, res, next) {
req.a++;
next();
});
app.get("/a", function (req, res, next) {
res.end(req.a + "");
});
app.listen(3000);
实现思路
结合之前的路由实现,其实中间件就是【没有路由表】的 Layer,我们只需要
- 订阅监听时做下对“不传匹配路径”等情况的处理
- 请求发布时根据“是否具有路由表
route属性”进行判断从而对中间件区分处理
如此即可
具体实现
订阅监听时做下对“不传匹配路径”等情况的处理
定义use方法
Router.prototype.use = function (path, ...handlers) {
if (!handlers[0]) {
// 只传递了一个函数
handlers.push(path); // app.use(function(){}) app.use()
path = "/";
}
handlers.forEach((handler) => {
let layer = new Layer(path, handler);
layer.route = undefined; // 不写也是 undefined , 主要告诉你 中间件没有 route
this.stack.push(layer);
});
};
请求发布时根据“是否具有路由表route属性”进行判断从而对中间件区分处理
改写handle方法
Router.prototype.handle = function (req, res, done) {
let { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
let method = req.method.toLowerCase();
let idx = 0;
const next = (err) => {
// 中间件 和内部的 next 方法 出错都会走这个 next
if (idx >= this.stack.length) return done(); // 路由处理不了 传递给应用层
let layer = this.stack[idx++];
// 无论是路由还是中间件 前提是路径必须匹配
if (layer.match(pathname)) {
// match 还没有更改
if (!layer.route) {
// 没有说明是中间件 注意 此处就是对中间件的区分处理
layer.handle_request(req, res, next); // 直接执行中间件函数
} else {
// 路由必须匹配方法
if (layer.route.methods[method]) {
// 这个 next 可以让路由层扫描下一个 layer
layer.handle_request(req, res, next); // route.dispatch
} else {
next();
}
}
} else {
next();
}
};
next(); // 请求来了取出第一个执行
};
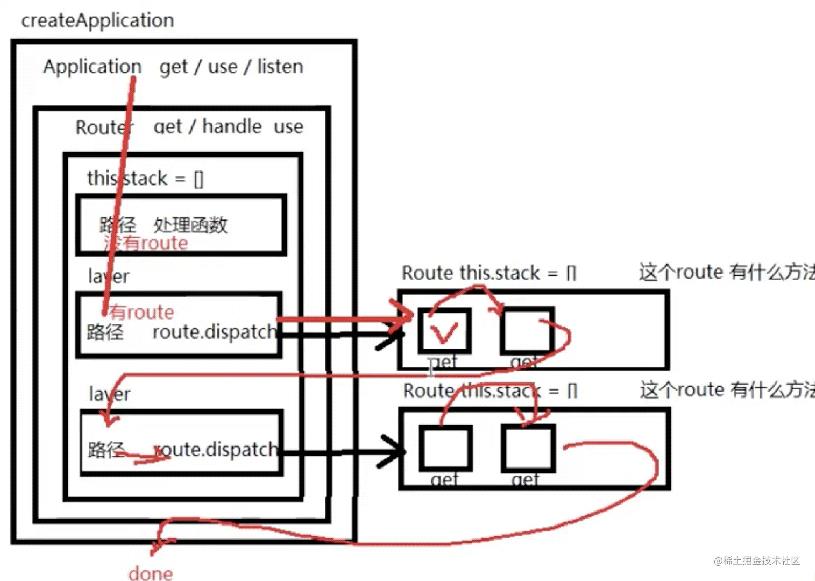
总结流程
以上就是nodejs express实现中间件的详细内容,更多关于nodejs express中间件的资料请关注易盾网络其它相关文章!
