本文实例讲述了Android开发使用ProgressBar实现进度条功能。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 进度条ProgressBar的使用主要有两种方向; 1.使用官方默认样式 2.使用自定义样式 先看效果:
本文实例讲述了Android开发使用ProgressBar实现进度条功能。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
进度条ProgressBar的使用主要有两种方向;
1.使用官方默认样式
2.使用自定义样式
先看效果:
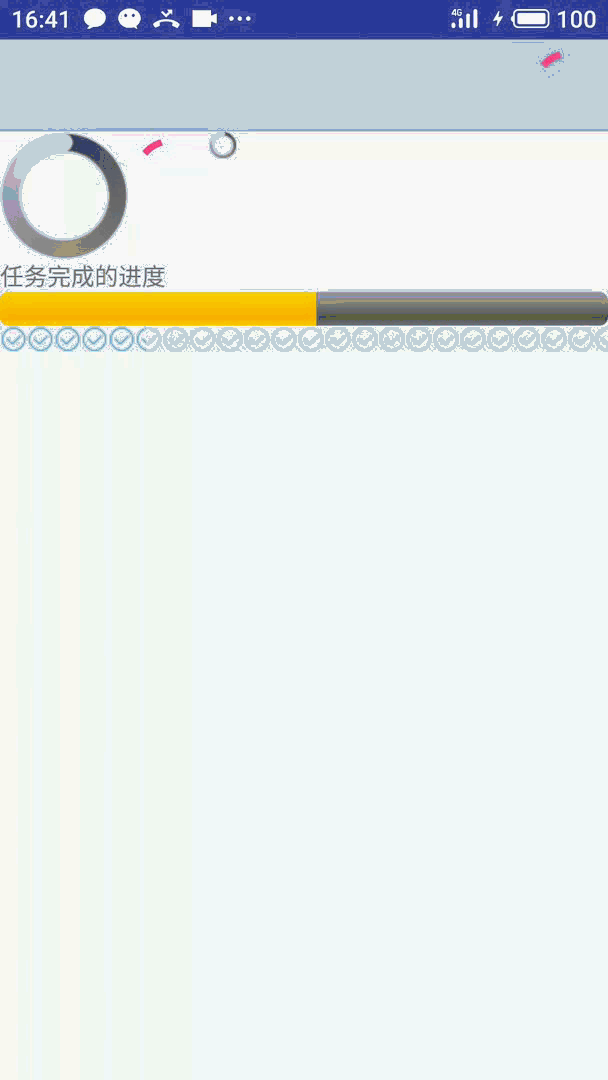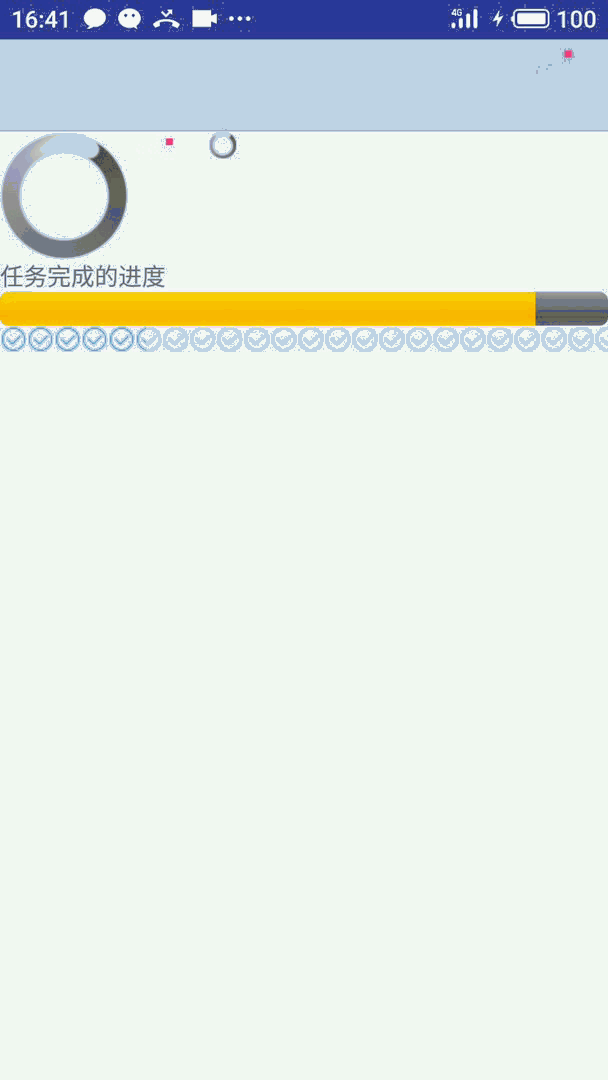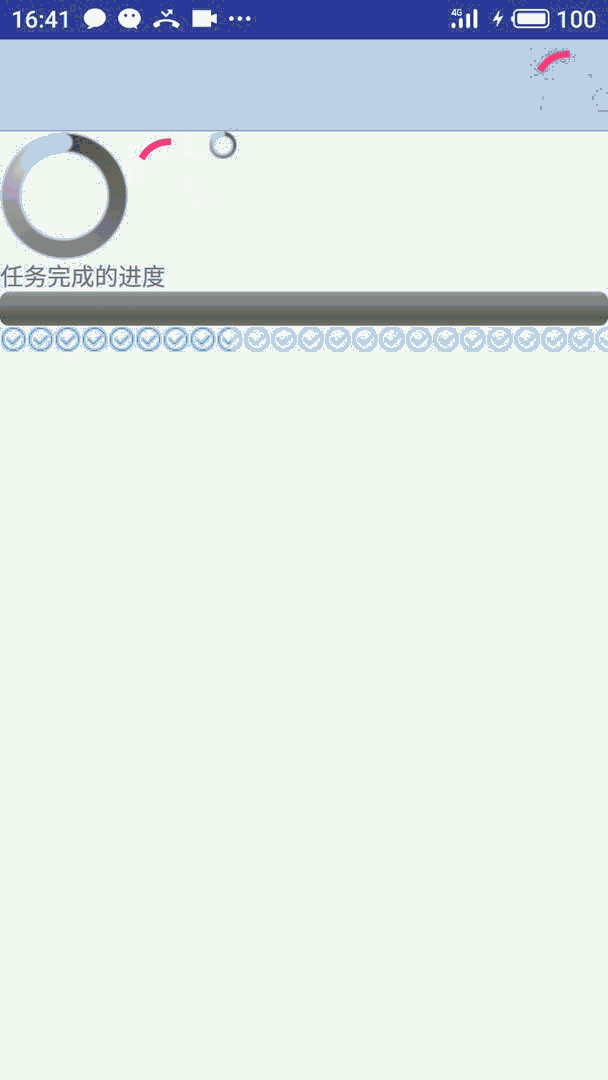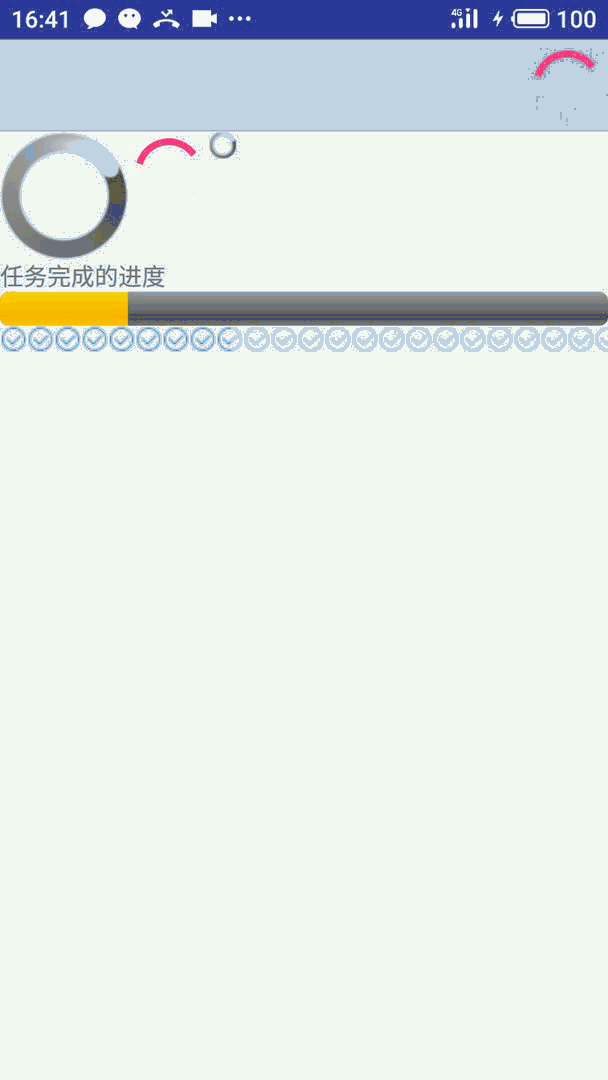
详细代码实现文末给出
关于系统自带样式:
在 style="@android:style 中有许多系统自带样式,大家可以更具自身喜好选择。
如果不选择 style 系统会默认使用上图中红色的样式。
关于自定义样式:
这里我们最好看看源码 很容易理解
主要分为三个部分:当前进度、缓冲进度、以及背景 三个属性
这里我们通过在drawable里新建my_bar.xml来实现
这里有个注意点 很多人写了xml后发现 直接就显示满进度 而不是缓慢增长
由于是替换系统自带样式,所以id必须与系统保持一致:(如:android:id="@android:id/background")
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layer-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<!--定义轨道背景-->
<item android:id="@android:id/background"
android:drawable="@drawable/no"/>
<!--定义轨道上已完成部分的样式-->
<item android:id="@android:id/progress"
android:drawable="@drawable/ok"/>
</layer-list>
这里对比下系统源码就很好理解了:
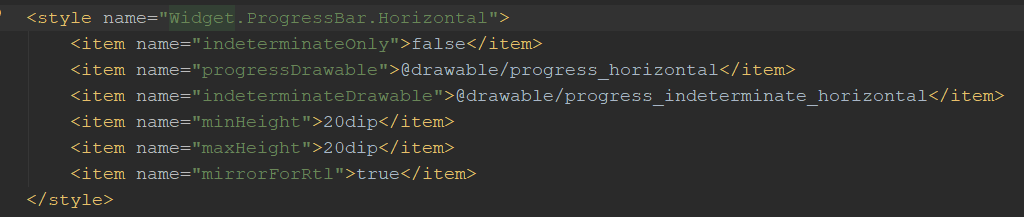
这里的模拟方法采用的是线程结合Handler
由于线程不能直接改变控件属性 所以需要用Handler来接受线程发出的Message
具体方法如下:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
//记录ProgressBar的完成进度
private int sum1=0,sum2 = 0 ;
ProgressBar bar1,bar2;
//创建一个负责更新进度的Handler
Handler mHandler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
//表明消息是本程序发送的
if (msg.what == 0x111){
bar1.setProgress(sum1);
bar2.setProgress(sum2);
}
}
};
//模拟耗时
Thread thread = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
while (sum2 < 100){
//bar1获取完成工作的百分比
if (sum1 > 100){
sum1 = 100;
if (sum2<100){
sum2 += (int) (Math.random()*25);
}else {
sum2 = 100;
thread.stop();
}
sum1=0;
}else {
sum1 = sum1 + (int) (Math.random()*25);
}
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//更新ProgressBar
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(0x111);
}
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bar1 = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.bar);
bar2 = (ProgressBar) findViewById(R.id.bar2);
thread.start();
}
}
最后在给出布局文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:orientation="vertical">
<android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:contentInsetStart="0dp"
android:background="#9FB6CD">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/toolbar_progress"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true" />
</RelativeLayout>
</android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<!--定义一个大环型进度条-->
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large"/>
<!--定义一个中等大小环形进度条-->
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<!--定义一个小进度条-->
<ProgressBar
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small"/>
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="任务完成的进度"/>
<!--定义一个大水平进度条-->
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="100"
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal"/>
<!--顶一个水平进度条,并改变轨道外观-->
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/bar2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:max="100"
android:progressDrawable="@drawable/my_bar"
style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal"/>
</LinearLayout>
更多关于Android相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《Android控件用法总结》、《Android开发入门与进阶教程》、《Android视图View技巧总结》、《Android编程之activity操作技巧总结》、《Android数据库操作技巧总结》及《Android资源操作技巧汇总》
希望本文所述对大家Android程序设计有所帮助。
