本案例实现一个test命名空间,此命名空间内有两个函数,分别为getName()和getNameSpace(); 声明命名空间及函数 namespace test{ const std::string getName()和(); const std::string getNameSpace();} 命名空间内
本案例实现一个test命名空间,此命名空间内有两个函数,分别为getName()和getNameSpace();
- 声明命名空间及函数
namespace test{
const std::string& getName()和();
const std::string& getNameSpace();
}
- 命名空间内实现单例类
实现一个单例类,构造函数要为private,自身对象为private
静态成员函数(才可以调用静态成员变量)
namespace test{
// 实现一个单例类,构造函数要为private,自身对象为private
class ThisNode{
private:
std::string name_;
std::string namespace_;
static ThisNode *thisNode;
ThisNode():name_("empty"),namespace_("namespace"){};
public:
// 静态成员函数(才可以调用静态成员变量)
/**
* 函数:实例化类
* 返回值:ThisNode&
*/
static ThisNode& instance(){
if(thisNode==nullptr){
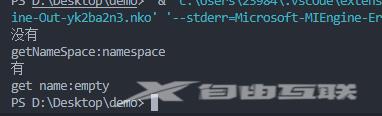
std::cout << "没有" <<std::endl;
thisNode = new ThisNode();
return *thisNode;
}else{
std::cout << "有" <<std::endl;
return *thisNode;
}
}
// 普通成员函数
const std::string& getName() const{
std::cout <<"get name:"<<name_<<std::endl;
return name_;
}
const std::string& getNameSpace() const{
std::cout <<"getNameSpace:" << namespace_ << std::endl;
return namespace_;
}
};
// 初始化静态成员
ThisNode *ThisNode::thisNode = nullptr;
// 实现命名空间内的函数,实例化一个类,并调用函数
const std::string& getNameSpace(){
return ThisNode::instance().getNameSpace();
}
const std::string& getName(){
return ThisNode::instance().getName();
}
};
- 实现命名空间函数
首先调用的是类的静态成员函数实例化唯一对象,然后调用对象中的方法;
// 实现命名空间内的函数,实例化一个类,并调用函数
const std::string& getNameSpace(){
return ThisNode::instance().getNameSpace();
}
const std::string& getName(){
return ThisNode::instance().getName();
}
- 调用
int main(){
// 使用
test::getNameSpace();
test::getName();
return 0;
}
全部代码
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
// 声明命名空间内的两个函数
namespace test{
const std::string& getName()和();
const std::string& getNameSpace();
}
namespace test{
// 实现一个单例类,构造函数要为private,自身对象为private
class ThisNode{
private:
std::string name_;
std::string namespace_;
static ThisNode *thisNode;
ThisNode():name_("empty"),namespace_("namespace"){};
public:
// 静态成员函数(才可以调用静态成员变量)
/**
* 函数:实例化类
* 返回值:ThisNode&
*/
static ThisNode& instance(){
if(thisNode==nullptr){
std::cout << "没有" <<std::endl;
thisNode = new ThisNode();
return *thisNode;
}else{
std::cout << "有" <<std::endl;
return *thisNode;
}
}
// 普通成员函数
const std::string& getName() const{
std::cout <<"get name:"<<name_<<std::endl;
return name_;
}
const std::string& getNameSpace() const{
std::cout <<"getNameSpace:" << namespace_ << std::endl;
return namespace_;
}
};
// 初始化静态成员
ThisNode *ThisNode::thisNode = nullptr;
// 实现命名空间内的函数,实例化一个类,并调用函数
const std::string& getNameSpace(){
return ThisNode::instance().getNameSpace();
}
const std::string& getName(){
return ThisNode::instance().getName();
}
};
int main(){
// 使用
test::getNameSpace();
test::getName();
return 0;
}
到此这篇关于c++使用单例模式实现命名空间函数的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c++命名空间函数内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
