C语言函数大全 本篇介绍C语言函数大全– i 开头的函数 1. imagesize 1.1 函数说明 函数声明 函数功能 unsigned imagesize(int left, int top, int right, int bottom); 获取保存位图像所需的字节数 1.2 演示示
C语言函数大全
本篇介绍C语言函数大全– i 开头的函数
1. imagesize
1.1 函数说明
unsigned imagesize(int left, int top, int right, int bottom);
获取保存位图像所需的字节数
1.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define ARROW_SIZE 10
void draw_arrow(int x, int y);
int main()
{
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
void *arrow;
int x, y, maxx;
unsigned int size;
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk)
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1);
}
maxx = getmaxx();
x = 0;
y = getmaxy() / 2;
draw_arrow(x, y);
size = imagesize(x, y-ARROW_SIZE, x+(4*ARROW_SIZE), y+ARROW_SIZE);
// 分配内存以保存图像
arrow = malloc(size);
// 抓取图像
getimage(x, y-ARROW_SIZE, x+(4*ARROW_SIZE), y+ARROW_SIZE, arrow);
// 重复,直到按键被按下
while (!kbhit())
{
// 擦除旧图像
putimage(x, y-ARROW_SIZE, arrow, XOR_PUT);
x += ARROW_SIZE;
if (x >= maxx)
x = 0;
// 绘制新图像
putimage(x, y-ARROW_SIZE, arrow, XOR_PUT);
}
free(arrow);
closegraph();
return 0;
}
void draw_arrow(int x, int y)
{
// 在屏幕上画一个箭头
moveto(x, y);
linerel(4*ARROW_SIZE, 0);
linerel(-2*ARROW_SIZE, -1*ARROW_SIZE);
linerel(0, 2*ARROW_SIZE);
linerel(2*ARROW_SIZE, -1*ARROW_SIZE);
}
1.3 运行结果

2. initgraph
2.1 函数说明
void initgraph( int *graphdriver, int *graphmode, char *pathtodriver );
初始化图形系统
2.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
// 初始化图形系统
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk)
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1);
}
line(0, 0, getmaxx(), getmaxy());
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
2.3 运行结果
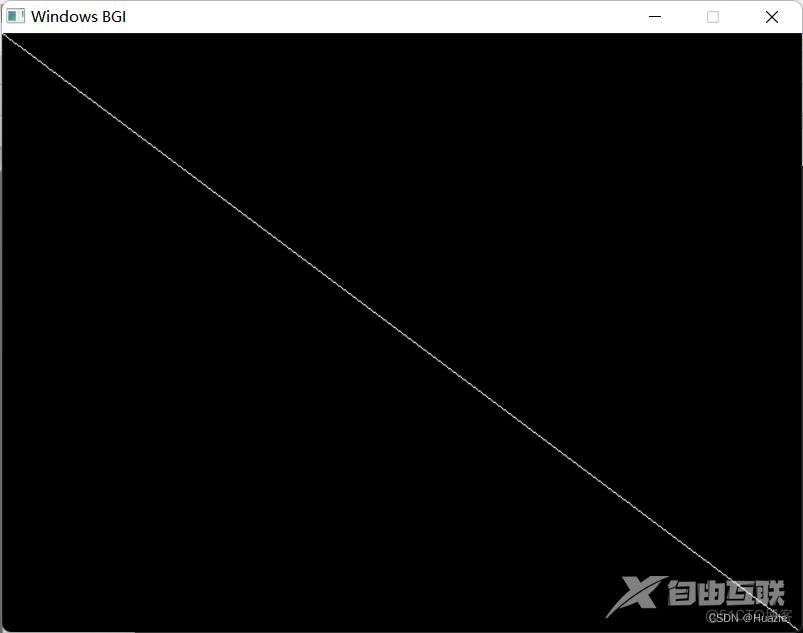
3. inport
3.1 函数说明
int inport(int protid);
从硬件端口中输入
3.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dos.h>
int main()
{
int result;
int port = 0; // 串行端口 0
// 从硬件端口中输入
result = inport(port);
printf("Word read from port %d = 0x%X\n", port, result);
return 0;
}
4. insline
4.1 函数说明
void insline(void);
在文本窗口中插入一个空行
4.2 演示示例
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
clrscr();
cprintf("INSLINE inserts an empty line in the text window\r\n");
cprintf("at the cursor position using the current text\r\n");
cprintf("background color. All lines below the empty one\r\n");
cprintf("move down one line and the bottom line scrolls\r\n");
cprintf("off the bottom of the window.\r\n");
cprintf("\r\nPress any key to continue:");
gotoxy(1, 3);
getch();
// 在文本窗口中插入一个空行
insline();
getch();
return 0;
}
5. installuserdriver
5.1 函数说明
int installuserdriver(char *name, int (*detect)(void));
安装设备驱动程序到BGI设备驱动程序表中
注意: 该函数在 WinBGI 中不可用
5.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int huge detectEGA(void);
void checkerrors(void);
int main(void)
{
int gdriver, gmode;
// 安装用户编写的设备驱动程序
gdriver = installuserdriver("EGA", detectEGA);
// 必须强制使用检测程序
gdriver = DETECT;
// 检查是否有任何安装错误
checkerrors();
// 初始化图形程序
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
// 检查是否有任何初始化错误
checkerrors();
// 画一条对象线
line(0, 0, getmaxx(), getmaxy());
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
/*
检测EGA或VGA卡
*/
int huge detectEGA(void);
{
int driver, mode, sugmode = 0;
detectgraph(&driver, &mode);
if ((driver == EGA) || (driver == VGA))
return sugmode; // 返回建议的视频模式编号
else
return grError; // 返回错误代码
}
/*
检查并报告任何图形错误
*/
void checkerrors(void)
{
// 获取上次图形操作的读取结果
int errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk)
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1);
}
}
6. installuserfont
6.1 函数说明
int installuserfont( char *name );
安装未嵌入BGI系统的字体文件(CHR)
注意: 该函数在 WinBGI 中不可用
6.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
void checkerrors(void);
int main()
{
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode;
int userfont;
int midx, midy;
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
midx = getmaxx() / 2;
midy = getmaxy() / 2;
checkerrors();
// 安装用户定义的字体文件
userfont = installuserfont("USER.CHR");
checkerrors();
// 选择用户字体
settextstyle(userfont, HORIZ_DIR, 4);
outtextxy(midx, midy, "Testing!");
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
/*
检查并报告任何图形错误
*/
void checkerrors(void)
{
// 获取上次图形操作的读取结果
int errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk)
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1);
}
}
7. int86
7.1 函数说明
int int86(int intr_num, union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs);
通用8086软中断接口
7.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <dos.h>
#define VIDEO 0x10
void movetoxy(int x, int y)
{
union REGS regs;
regs.h.ah = 2; /* set cursor postion */
regs.h.dh = y;
regs.h.dl = x;
regs.h.bh = 0; /* video page 0 */
int86(VIDEO, ®s, ®s);
}
int main(void)
{
clrscr();
movetoxy(35, 10);
printf("Hello\n");
return 0;
}
8. int86x
8.1 函数说明
int int86x(int intr_num, union REGS *insegs, union REGS *outregs, struct SREGS *segregs);
通用8086软中断接口
8.2 演示示例
#include <dos.h>
#include <process.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
char filename[80];
union REGS inregs, outregs;
struct SREGS segregs;
printf("Enter filename: ");
gets(filename);
inregs.h.ah = 0x43;
inregs.h.al = 0x21;
inregs.x.dx = FP_OFF(filename);
segregs.ds = FP_SEG(filename);
int86x(0x21, &inregs, &outregs, &segregs);
printf("File attribute: %X\n", outregs.x.cx);
return 0;
}
9. intdos
9.1 函数说明
int intdos(union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs);
通用DOS接口
9.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dos.h>
/*
删除文件,成功返回0,失败返回非0。
*/
int delete_file(char near *filename)
{
union REGS regs;
int ret;
regs.h.ah = 0x41;
regs.x.dx = (unsigned) filename;
ret = intdos(®s, ®s);
// 如果设置了进位标志,则出现错误
return(regs.x.cflag ? ret : 0);
}
int main(void)
{
int err;
err = delete_file("NOTEXIST.$$$");
if (!err)
printf("Able to delete NOTEXIST.$$$\n");
else
printf("Not Able to delete NOTEXIST.$$$\n");
return 0;
}
10. intdosx
10.1 函数说明
int intdosx(union REGS *inregs, union REGS *outregs, struct SREGS *segregs);
通用DOS中断接口
10.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dos.h>
/*
删除文件,成功返回0,失败返回非0。
*/
int delete_file(char far *filename)
{
union REGS regs;
struct SREGS sregs;
int ret;
regs.h.ah = 0x41;
regs.x.dx = FP_OFF(filename);
sregs.ds = FP_SEG(filename);
ret = intdosx(®s, ®s, &sregs);
// 如果设置了进位标志,则出现错误
return(regs.x.cflag ? ret : 0);
}
int main(void)
{
int err;
err = delete_file("NOTEXIST.$$$");
if (!err)
printf("Able to delete NOTEXIST.$$$\n");
else
printf("Not Able to delete NOTEXIST.$$$\n");
return 0;
}
11. intr
11.1 函数说明
void intr(int intr_num, struct REGPACK *preg);
改变软中断接口
11.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <dir.h>
#include <dos.h>
#define CF 1 // 进位标志
int main(void)
{
char directory[80];
struct REGPACK reg;
printf("Enter directory to change to: ");
gets(directory);
reg.r_ax = 0x3B << 8; // 将3Bh转换为AH
reg.r_dx = FP_OFF(directory);
reg.r_ds = FP_SEG(directory);
intr(0x21, ®);
if (reg.r_flags & CF)
printf("Directory change failed\n");
getcwd(directory, 80);
printf("The current directory is: %s\n", directory);
return 0;
}
12. ioctl
12.1 函数说明
int ioctl(int fd, int cmd, ...) ;
控制 I/O 设备
12.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dir.h>
#include <io.h>
int main(void)
{
int stat = ioctl(0, 8, 0, 0);
if (!stat)
printf("Drive %c is removable.\n", getdisk() + 'A');
else
printf("Drive %c is not removable.\n", getdisk() + 'A');
return 0;
}
13. isatty
13.1 函数说明
int isatty(int handle);
检查设备类型
13.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <io.h>
int main(void)
{
int handle;
handle = fileno(stdprn);
if (isatty(handle))
printf("Handle %d is a device type\n", handle);
else
printf("Handle %d isn't a device type\n", handle);
return 0;
}
13.3 运行结果
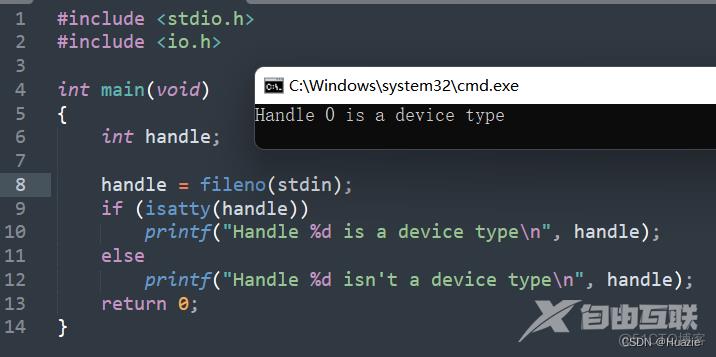
14. ilogb,ilogbf,ilogbfl
14.1 函数说明
int ilogb (double x);
获取 x 的对数的积分部分(double)
int ilogbf (float x);
获取 x 的对数的积分部分(float)
int ilogbl (long double x);
获取 x 的对数的积分部分(long double)
如果计算成功,则返回 x 的对数的整数部分。如果 x 为 0,则此函数返回FP_ILOGB0 并报告错误。如果 x 是NaN值,则此函数返回 FP_ILOGBNAN 并报告错误。如果 x 是正无穷大或负无穷大,此函数将返回 INT_MAX 并报告错误。
14.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
int result;
double x = 15.0;
result = ilogb(x);
printf("The integral part of the logarithm of double value %lf is %d\n", x, result);
float xf = 15.0f;
result = ilogbf(xf);
printf("The integral part of the logarithm of float value %f is %d\n", xf, result);
long double xL = 15.0L;
result = ilogbl(xL);
printf("The integral part of the logarithm of long double value %Lf is %d\n", xL, result);
return 0;
}
14.3 运行结果
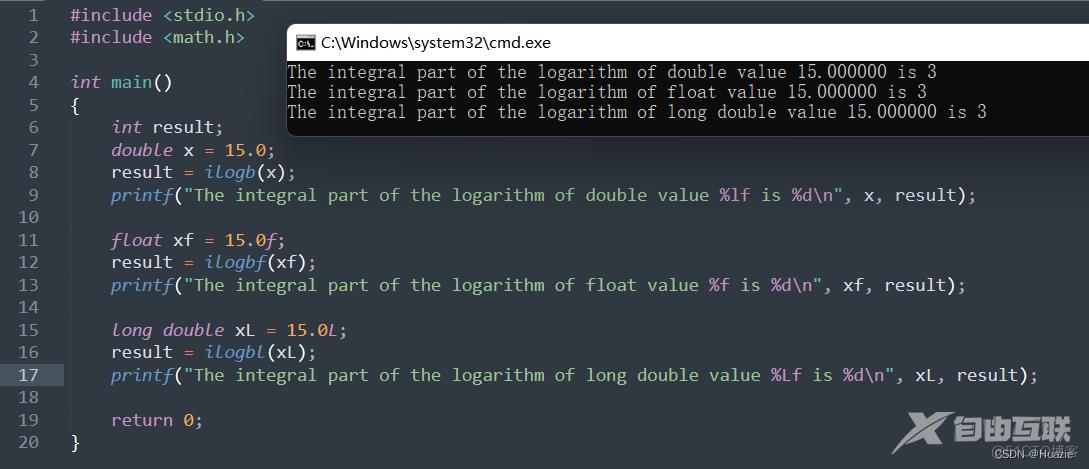
15. itoa
15.1 函数说明
char * itoa(int value, char *string, int radix);
把一整数转换为字符串
15.2 演示示例
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int number = 12345;
char string[25];
itoa(number, string, 2);
printf("integer = %d string = %s\n", number, string);
itoa(number, string, 8);
printf("integer = %d string = %s\n", number, string);
itoa(number, string, 10);
printf("integer = %d string = %s\n", number, string);
itoa(number, string, 16);
printf("integer = %d string = %s\n", number, string);
return 0;
}
15.3 运行结果
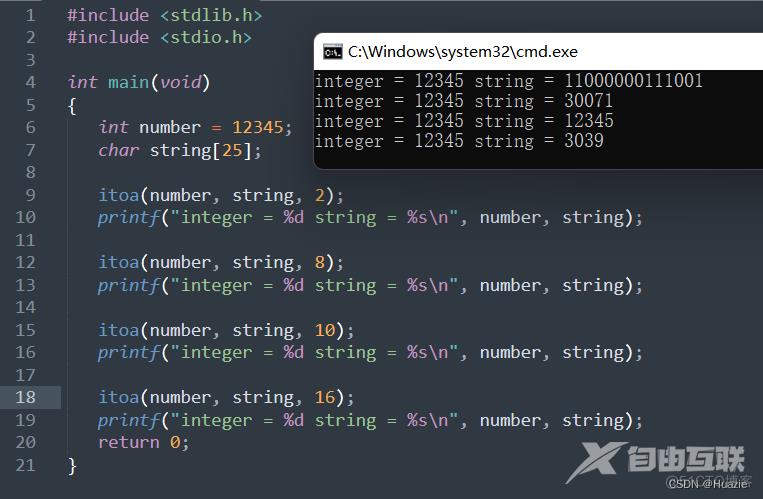
参考
- [API Reference Document]
- [ioctl]
