官网给出了安装需要的最低硬件和软件的条件:https://goharbor.io/docs/2.0.0/install-config/installation-prereqs/
最低硬件要求:
最低软件要求:
Harbor 要求在目标主机上打开以下端口:
可以从 官方发布页面下载 Harbor 安装程序。下载在线安装程序或离线安装程序。
- 在线安装程序:在线安装程序从 Docker 中心下载 Harbor 镜像。因此,安装程序的尺寸非常小。
- 离线安装程序:如果要部署 Harbor 的主机没有连接到 Internet,请使用离线安装程序。离线安装程序包含预先构建的映像,因此它比在线安装程序大
在线和离线安装程序的安装过程几乎相同。
这里我主要使用离线安装,因为在线安装因为墙、内部网络等原因,有的同学会下载很慢,而离线安装包都包含了预先构建的镜像,所以直接现在离线安装包最好!
离线安装到 官方发布 页面下载离线安装包:
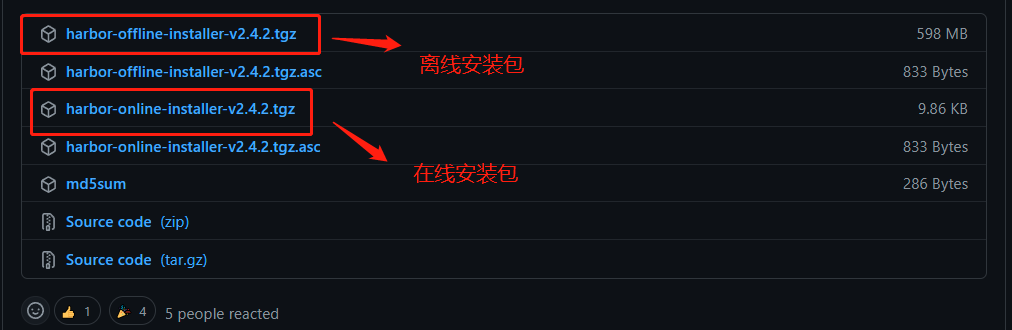
下载后将压缩包上传到服务器使用命令tar -zxf harbor-offline-installer-v2.4.2.tgz解压,解压后如下图:

解压后在当前的解压路径可以得到文件夹harbor,cd harbor 进文件夹:
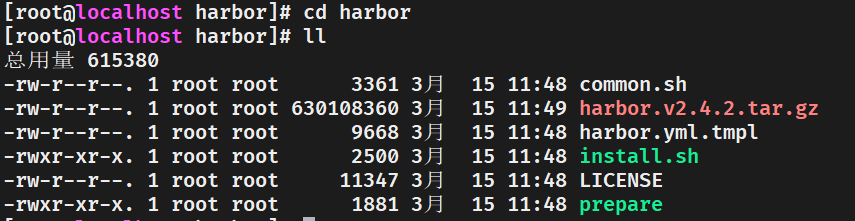
可以看到文件夹有一堆文件,其中最主要的是 harbor.yml.tmpl和 install.sh ,他们分别是配置文件和安装执行文件。
# 复制并重命名一份新的配置文件
cp harbor.yml.tmpl harbor.yml
# 使用 vim 编辑配置文件,如果提示找不到vim ,使用以下命令安装 vim
# ubuntu 使用 sudo apt-get install vim
# redHat/Fedora/CentOS 使用 yum install vim
vim harbor.yml # 或者使用 vi harbor.yml 编辑
打开harbor.yml,最主要是更改一下几点,其他的保持默认即可:
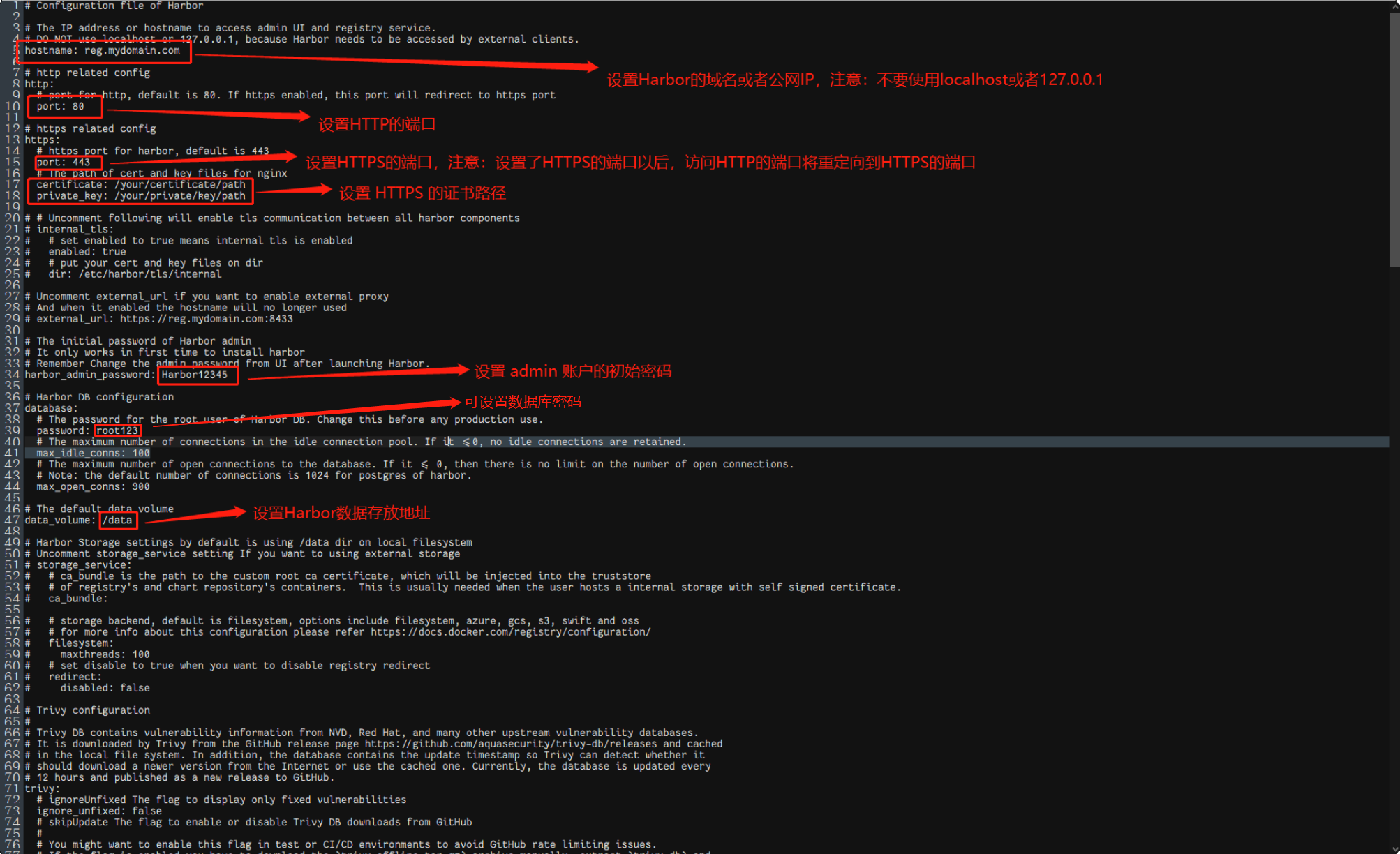
harbor.yml示例模板:
# Configuration file of Harbor
# The IP address or hostname to access admin UI and registry service.
# DO NOT use localhost or 127.0.0.1, because Harbor needs to be accessed by external clients.
hostname: 192.168.0.2
# http related config
http:
# port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https port
port: 8088
# 不使用HTTPS
# https related config
# https:
# https port for harbor, default is 443
# port: 443
# The path of cert and key files for nginx
# certificate: /your/certificate/path
# private_key: /your/private/key/path
# # Uncomment following will enable tls communication between all harbor components
# internal_tls:
# # set enabled to true means internal tls is enabled
# enabled: true
# # put your cert and key files on dir
# dir: /etc/harbor/tls/internal
# Uncomment external_url if you want to enable external proxy
# And when it enabled the hostname will no longer used
# external_url: https://reg.mydomain.com:8433
# The initial password of Harbor admin
# It only works in first time to install harbor
# Remember Change the admin password from UI after launching Harbor.
harbor_admin_password: Harbor12345
# Harbor DB configuration
database:
# The password for the root user of Harbor DB. Change this before any production use.
password: root123
# The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool. If it <=0, no idle connections are retained.
max_idle_conns: 100
# The maximum number of open connections to the database. If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections.
# Note: the default number of connections is 1024 for postgres of harbor.
max_open_conns: 900
# The default data volume
data_volume: /mnt/harbor/data
# Harbor Storage settings by default is using /data dir on local filesystem
# Uncomment storage_service setting If you want to using external storage
# storage_service:
# # ca_bundle is the path to the custom root ca certificate, which will be injected into the truststore
# # of registry's and chart repository's containers. This is usually needed when the user hosts a internal storage with self signed certificate.
# ca_bundle:
# # storage backend, default is filesystem, options include filesystem, azure, gcs, s3, swift and oss
# # for more info about this configuration please refer https://docs.docker.com/registry/configuration/
# filesystem:
# maxthreads: 100
# # set disable to true when you want to disable registry redirect
# redirect:
# disabled: false
# Trivy configuration
#
# Trivy DB contains vulnerability information from NVD, Red Hat, and many other upstream vulnerability databases.
# It is downloaded by Trivy from the GitHub release page https://github.com/aquasecurity/trivy-db/releases and cached
# in the local file system. In addition, the database contains the update timestamp so Trivy can detect whether it
# should download a newer version from the Internet or use the cached one. Currently, the database is updated every
# 12 hours and published as a new release to GitHub.
trivy:
# ignoreUnfixed The flag to display only fixed vulnerabilities
ignore_unfixed: false
# skipUpdate The flag to enable or disable Trivy DB downloads from GitHub
#
# You might want to enable this flag in test or CI/CD environments to avoid GitHub rate limiting issues.
# If the flag is enabled you have to download the `trivy-offline.tar.gz` archive manually, extract `trivy.db` and
# `metadata.json` files and mount them in the `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db` path.
skip_update: false
#
# The offline_scan option prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies.
# Scanning JAR files and pom.xml may require Internet access for better detection, but this option tries to avoid it.
# For example, the offline mode will not try to resolve transitive dependencies in pom.xml when the dependency doesn't
# exist in the local repositories. It means a number of detected vulnerabilities might be fewer in offline mode.
# It would work if all the dependencies are in local.
# This option doesn’t affect DB download. You need to specify "skip-update" as well as "offline-scan" in an air-gapped environment.
offline_scan: false
#
# insecure The flag to skip verifying registry certificate
insecure: false
# github_token The GitHub access token to download Trivy DB
#
# Anonymous downloads from GitHub are subject to the limit of 60 requests per hour. Normally such rate limit is enough
# for production operations. If, for any reason, it's not enough, you could increase the rate limit to 5000
# requests per hour by specifying the GitHub access token. For more details on GitHub rate limiting please consult
# https://developer.github.com/v3/#rate-limiting
#
# You can create a GitHub token by following the instructions in
# https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/creating-a-personal-access-token-for-the-command-line
#
# github_token: xxx
jobservice:
# Maximum number of job workers in job service
max_job_workers: 10
notification:
# Maximum retry count for webhook job
webhook_job_max_retry: 10
chart:
# Change the value of absolute_url to enabled can enable absolute url in chart
absolute_url: disabled
# Log configurations
log:
# options are debug, info, warning, error, fatal
level: info
# configs for logs in local storage
local:
# Log files are rotated log_rotate_count times before being removed. If count is 0, old versions are removed rather than rotated.
rotate_count: 50
# Log files are rotated only if they grow bigger than log_rotate_size bytes. If size is followed by k, the size is assumed to be in kilobytes.
# If the M is used, the size is in megabytes, and if G is used, the size is in gigabytes. So size 100, size 100k, size 100M and size 100G
# are all valid.
rotate_size: 200M
# The directory on your host that store log
location: /var/log/harbor
# Uncomment following lines to enable external syslog endpoint.
# external_endpoint:
# # protocol used to transmit log to external endpoint, options is tcp or udp
# protocol: tcp
# # The host of external endpoint
# host: localhost
# # Port of external endpoint
# port: 5140
#This attribute is for migrator to detect the version of the .cfg file, DO NOT MODIFY!
_version: 2.5.0
# Uncomment external_database if using external database.
# external_database:
# harbor:
# host: harbor_db_host
# port: harbor_db_port
# db_name: harbor_db_name
# username: harbor_db_username
# password: harbor_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# max_idle_conns: 2
# max_open_conns: 0
# notary_signer:
# host: notary_signer_db_host
# port: notary_signer_db_port
# db_name: notary_signer_db_name
# username: notary_signer_db_username
# password: notary_signer_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# notary_server:
# host: notary_server_db_host
# port: notary_server_db_port
# db_name: notary_server_db_name
# username: notary_server_db_username
# password: notary_server_db_password
# ssl_mode: disable
# Uncomment external_redis if using external Redis server
# external_redis:
# # support redis, redis+sentinel
# # host for redis: <host_redis>:<port_redis>
# # host for redis+sentinel:
# # <host_sentinel1>:<port_sentinel1>,<host_sentinel2>:<port_sentinel2>,<host_sentinel3>:<port_sentinel3>
# host: redis:6379
# password:
# # sentinel_master_set must be set to support redis+sentinel
# #sentinel_master_set:
# # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeable
# registry_db_index: 1
# jobservice_db_index: 2
# chartmuseum_db_index: 3
# trivy_db_index: 5
# idle_timeout_seconds: 30
# Uncomment uaa for trusting the certificate of uaa instance that is hosted via self-signed cert.
# uaa:
# ca_file: /path/to/ca
# Global proxy
# Config http proxy for components, e.g. http://my.proxy.com:3128
# Components doesn't need to connect to each others via http proxy.
# Remove component from `components` array if want disable proxy
# for it. If you want use proxy for replication, MUST enable proxy
# for core and jobservice, and set `http_proxy` and `https_proxy`.
# Add domain to the `no_proxy` field, when you want disable proxy
# for some special registry.
proxy:
http_proxy:
https_proxy:
no_proxy:
components:
- core
- jobservice
- trivy
# metric:
# enabled: false
# port: 9090
# path: /metrics
# Trace related config
# only can enable one trace provider(jaeger or otel) at the same time,
# and when using jaeger as provider, can only enable it with agent mode or collector mode.
# if using jaeger collector mode, uncomment endpoint and uncomment username, password if needed
# if using jaeger agetn mode uncomment agent_host and agent_port
# trace:
# enabled: true
# # set sample_rate to 1 if you wanna sampling 100% of trace data; set 0.5 if you wanna sampling 50% of trace data, and so forth
# sample_rate: 1
# # # namespace used to differenciate different harbor services
# # namespace:
# # # attributes is a key value dict contains user defined attributes used to initialize trace provider
# # attributes:
# # application: harbor
# # # jaeger should be 1.26 or newer.
# # jaeger:
# # endpoint: http://hostname:14268/api/traces
# # username:
# # password:
# # agent_host: hostname
# # # export trace data by jaeger.thrift in compact mode
# # agent_port: 6831
# # otel:
# # endpoint: hostname:4318
# # url_path: /v1/traces
# # compression: false
# # insecure: true
# # timeout: 10s
# enable purge _upload directories
upload_purging:
enabled: true
# remove files in _upload directories which exist for a period of time, default is one week.
age: 168h
# the interval of the purge operations
interval: 24h
dryrun: false
编辑完成后按ESC,然后使用命令:wq保存并推出。
然后继续用命令执行安装./install.sh。
安装过程(从别人博客上扒下来的图):


当出现红箭头指向的提示的时候,就表示安装成功了!
然后根据在harbor.yml文件中配置的端口与IP地址(或域名)进行访问

现在Harbor已经可以使用了!
由于我部署的时候没有使用HTTPS,所以使用docker登录的时候会出现一下异常信息(还是借的别人的图):

原因:Docker自从1.3.X之后docker registry交互默认使用的是HTTPS,但是搭建私有镜像默认使用的是HTTP服务,所以与私有镜像交时出现以上错误。
解决办法:
找到docker 的 daemon.json 配置文件,CentOS 7 的路径:/etc/docker/daemon.json(系统版本不同所处位置不同,其他版本的请自行百度),如果路径下没有这个文件自己创建即可。然后再配置文件里加上:
{
// docker 镜像下载地址
"registry-mirrors": ["https://mirror.ccs.tencentyun.com"],
// 不安全的镜像仓库(此处配置Harbor 的地址+端口号)
"insecure-registries": ["192.168.0.2:8088"],
}
操作完后让这个文件生效:
a.修改完成后reload配置文件
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
b.重启docker服务
sudo systemctl restart docker.service
本次的Harbor安装教程就到此为止了,如需了解Harbor的更多详情信息请移步其他博客!
