Python中的文件读写函数open详解
- open()函数的定义:def open(file, mode='r', buffering=None, encoding=None, errors=None, newline=None, closefd=True)
- 常用的参数有 file、mode、encoding
- file是文件名称, mode是文件的打开方式、encoding是文件编码格式
- mode常见的有 只读模式(r)、写入模式(w)、追加模式(a)、读写模式(r+/w+/a+)
- r+要求文件必须存在;锚点置于末行末位字符处
- w+文件不存在时新建,文件存在时将文件内容清空,锚点置于首行首字符处
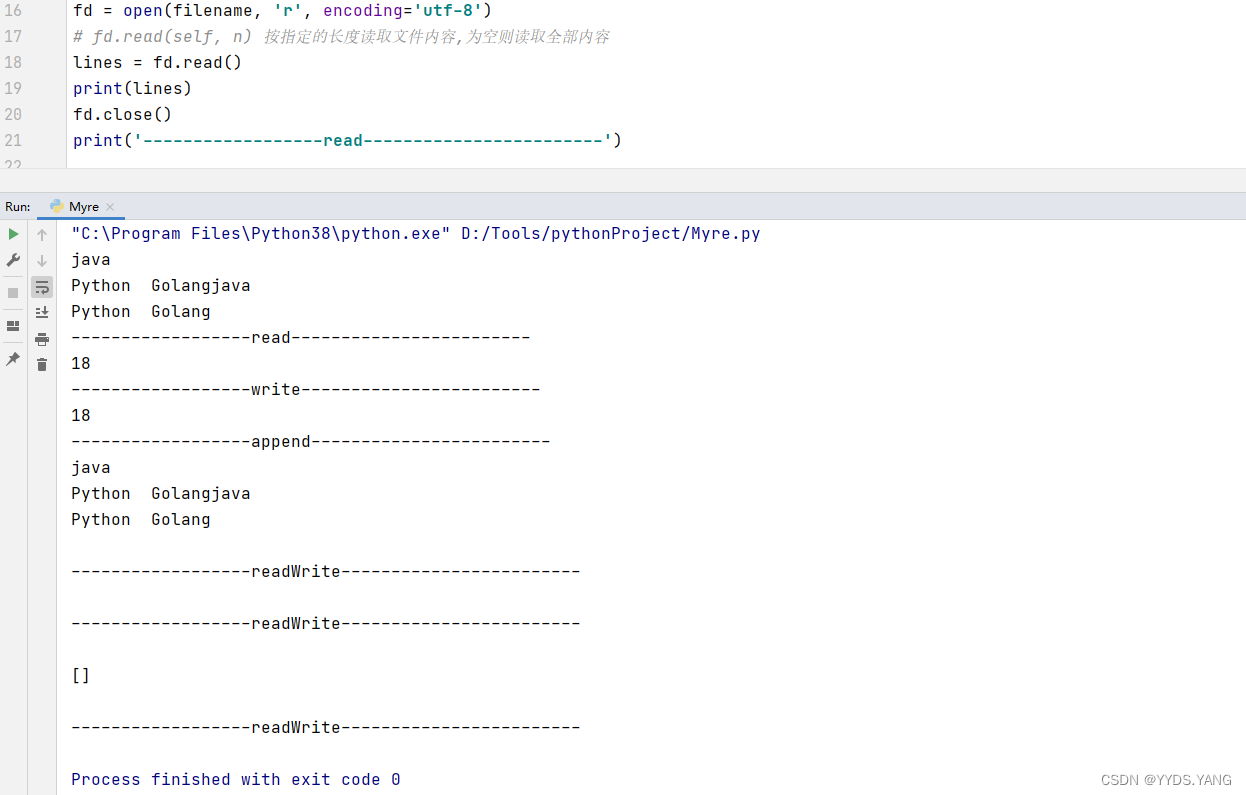
- a+文件不存在时新建,文件存在时打开文件,将锚点置于末行末位字符处 filename = 'test.txt' # 以只读方式打开test.txt文件 fd = open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8') # fd.read(self, n) 按指定的长度读取文件内容,为空则读取全部内容 lines = fd.read() print(lines) fd.close() print('------------------read------------------------')
以写入模式打开test.txt文件
fd = open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8')
fd.write(self, str) 将str写入文件
lines_w = fd.write('java\nPython\tGolang')print(lines_w)fd.close()print('------------------write------------------------')
以追加模式打开文件
fd = open(filename, 'a', encoding='utf-8')lines_a = fd.write('java\nPython\tGolang')print(lines_a)fd.close()print('------------------append------------------------')
以读写模式打开文件(r+)
fd = open(filename, 'r+', encoding='utf-8')print(fd.read())lines_str = fd.write('java\nPython\tGolang')print(fd.read())fd.close()print('------------------readWrite------------------------')
以读写模式打开文件(w+)
fd = open(filename, 'w+', encoding='utf-8')lines_str = fd.write('java\nPython\tGolang')print(fd.read()) # 文件打开时清空文件内容,虽然写入了文件,但未保存,因此读取文件为空fd.close()print('------------------readWrite------------------------')
以读写模式打开文件(a+)
fd = open(filename, 'a+', encoding='utf-8')print(fd.read())
按行读取
print(fd.readlines(2))lines_str = fd.write('java\nPython\tGolang')print(fd.read())fd.close()print('------------------readWrite------------------------')