1 内容介绍
旅行商问题(Traveling Salesman Problem)是一个典型的组合优化问题,旅行商问题描述如下:给定 n 个城市及两两城市之间的距离,求一条经过各城市一次且仅一次的最逗路线。其图论描述为:

TSP 问题的求最优化解是很困难的。对于有着 n 个城市的 TSP问题,存在着(n-1)! /2 条可能的路径。随着城市数目 n 的增长,可能路径的数目以 n 的指数倍增加,如果使用穷举法搜索,需要考虑所以的可能情况,并两两比较,找出最优解,那么可搜索的路径及其距离之和的计算量将正比于 n! /2,算法的复杂度呈指数增长,人们把这类问题称为“NP 完全问题”。由于 TSP 具有实际应用价值,例如:城市管道铺设优化、物流等行业中的车辆调度优化、制造业中的切割路径优化以及电力系统配电网络重构等现实生活中的很多优化问题都可以归结为 TSP 模型来求解。
2 部分代码
% These lines of code, solves the Travelling Salesman Problem (TSP)
% by Teaching Learning Based Optimization Algorithm (TLBO) algorithm.
% By default, 20 points are made by "MakeModel.m鈥� file and you can
% change it if you want.
clc;
clear;
close all;
%% Problem
model=MakeModel();
CostFunctinotallow=@(s) CostF(s,model); % Cost Function
nVar=model.n; % Number of Decision Variables
VarSize=[1 nVar]; % Decision Variables Matrix Size
VarMin=0; % Lower Bound of Variables
VarMax=1; % Upper Bound of Variables
%% TLBO Parameters
MaxIt = 500; % Maximum Number of Iterations
nPop = 50; % Population Size
%% Start
% Empty Individuals
empty_individual.Position = [];
empty_individual.Cost = [];
empty_individual.Sol = [];
% Population Array
pop = repmat(empty_individual, nPop, 1);
% Initialize Best Solution
BestSol.Cost = inf;
% Population Members
for i = 1:nPop
pop(i).Position = unifrnd(VarMin, VarMax, VarSize);
[pop(i).Cost pop(i).Sol] = CostFunction(pop(i).Position);
if pop(i).Cost < BestSol.Cost
BestSol = pop(i);
end
end
% Best Cost Record
BestCosts = zeros(MaxIt, 1);
%% TLBO
for it = 1:MaxIt
% Calculate Population Mean
Mean = 0;
for i = 1:nPop
Mean = Mean + pop(i).Position;
end
Mean = Mean/nPop;
% Select Teacher
Teacher = pop(1);
for i = 2:nPop
if pop(i).Cost < Teacher.Cost
Teacher = pop(i);
end
end
% Teacher Phase
for i = 1:nPop
% Create Empty Solution
newsol = empty_individual;
% Teaching Factor
TF = randi([1 2]);
% Teaching (moving towards teacher)
newsol.Position = pop(i).Position ...
+ rand(VarSize).*(Teacher.Position - TF*Mean);
% Clipping
newsol.Position = max(newsol.Position, VarMin);
newsol.Position = min(newsol.Position, VarMax);
% Evaluation
[newsol.Cost newsol.Sol] = CostFunction(newsol.Position);
% Comparision
if newsol.Cost<pop(i).Cost
pop(i) = newsol;
if pop(i).Cost < BestSol.Cost
BestSol = pop(i);
end
end
end
% Learner Phase
for i = 1:nPop
A = 1:nPop;
A(i) = [];
j = A(randi(nPop-1));
Step = pop(i).Position - pop(j).Position;
if pop(j).Cost < pop(i).Cost
Step = -Step;
end
% Create Empty Solution
newsol = empty_individual;
% Teaching (moving towards teacher)
newsol.Position = pop(i).Position + rand(VarSize).*Step;
% Clipping
newsol.Position = max(newsol.Position, VarMin);
newsol.Position = min(newsol.Position, VarMax);
% Evaluation
[newsol.Cost newsol.Sol] = CostFunction(newsol.Position);
% Comparision
if newsol.Cost<pop(i).Cost
pop(i) = newsol;
if pop(i).Cost < BestSol.Cost
BestSol = pop(i);
end
end
end
BestCosts(it) = BestSol.Cost;
% Iteration
disp(['In ITR ' num2str(it) ': TLBO Cost Value Is = ' num2str(BestCosts(it))]);
% Plot Res
figure(1);
Plotfig(BestSol.Sol.tour,model);
end
%% ITR
figure;
plot(BestCosts, 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('ITR');
ylabel('Cost Value');
ax = gca;
ax.FontSize = 12;
ax.Fnotallow='bold';
set(gca,'Color','k')
grid on;
3 运行结果
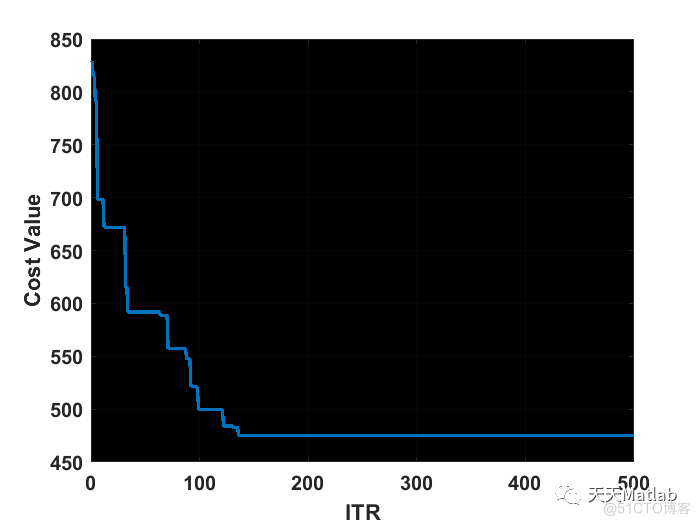
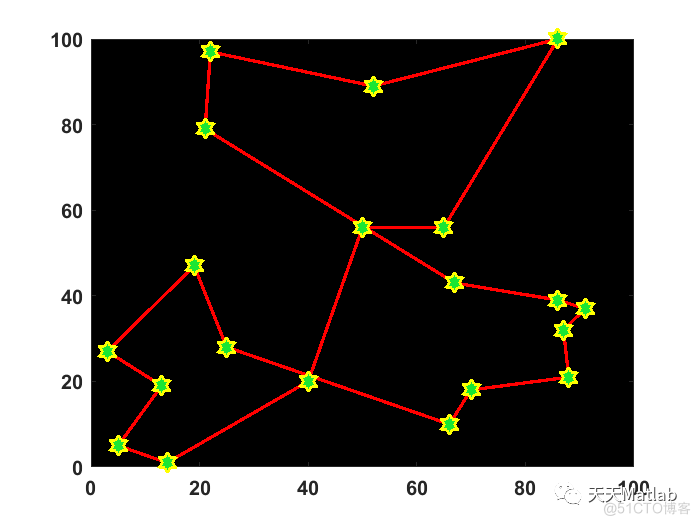
4 参考文献
[1]何湘竹. 一种改进的基于教与学的优化算法求解旅行商问题[J]. 中南民族大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 34(4):5.
