目录
- 一、文件对话框
- (1)OpenFileDialog对话框
- (2)SaveFileDialog对话框
- (3)FolderBroswerDialog对话框
- 二、文件及文件夹操作
- (1)文件常用操作
- (2)文件夹常用操作
- (3)文件夹的复制和移动
- 文件和流的概念:
- 读写文本文件最常用的类有:
- 读写文件操作的基本步骤为:
- 文件流对象:
- 文件读写器常用方法:
- 三、读写文本文件
- 四、序列化与反序列化
- (1)序列化单个对象
- (2)序列化集合
一、文件对话框
C#中共有三种文件对话框,分别用于不同的功能:
- (1)用于打开文件的对话框OpenFileDialog。
- (2)用于保存文件的对话框SaveFileDialog。
- (3)打开文件夹的对话框FolderBroswerDialog。
示例:如下图,点击三个按钮分别弹出三种对话框,进行相应操作之后,将路径在文本框中显示:
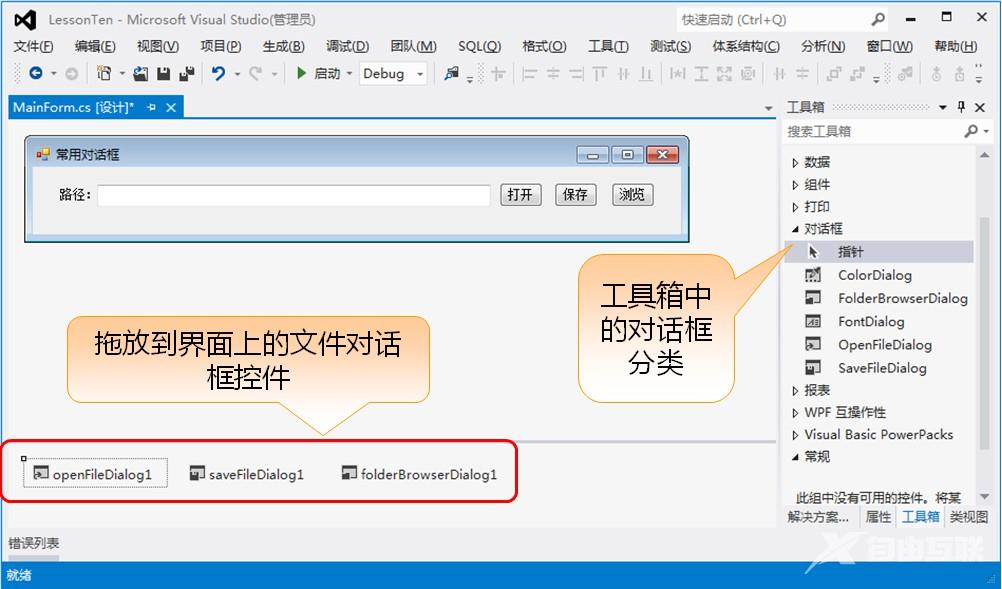
(1)OpenFileDialog对话框
修改OpenFileDialog对话框的Name属性为ofDlg。在“打开”按钮添加ofDlg.ShowDialog(); 界面如下:
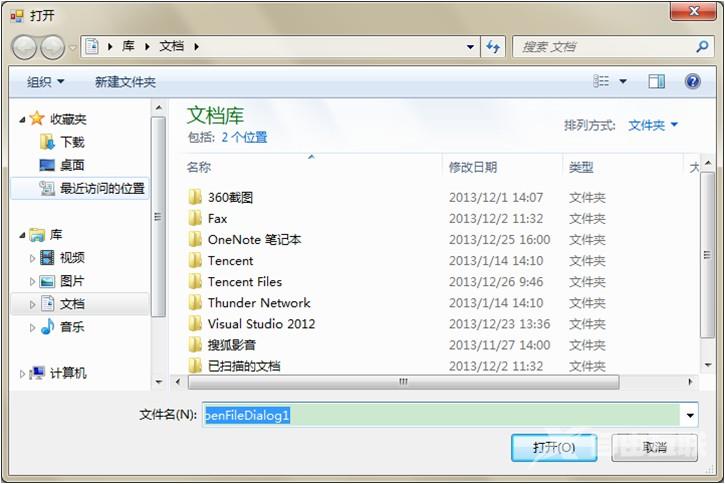
通过ShowDialog()的返回值,判断点击的是“打开”还是“取消”。在“打开”按钮点击事件中编写如下代码:
private void btnOpen_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//判断是否点击的“打开”按钮
if (ofDlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
txtPath.Text = ofDlg.FileName;
}
}
OpenFileDialog常用属性表:
(2)SaveFileDialog对话框
保存文件对话框常用于软件中的“另存为”功能。其常用属性、方法及使用方式与打开文件对话框相同。
设置保存文件对话框的Filter属性为“文本文件|*.txt”。在“保存”按钮的点击事件中编写如下代码:
private void btnSave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (sfDlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
txtPath.Text = sfDlg.FileName;
}
}
(3)FolderBroswerDialog对话框
浏览文件夹对话框常用于浏览文件夹,选择文件夹路径。
在“浏览”按钮的点击事件中编写如下代码:
private void btnBrowse_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (fbDlg.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
txtPath.Text = fbDlg.SelectedPath;
}
}
FolderBroswerDialog常用属性:
二、文件及文件夹操作
文件及文件夹管理是操作系统的重要组成部分,主要包括创建、移动、复制和删除等操作。
Directory类和DirectoryInfo类用于对磁盘和文件夹的操作管理。
File类和FileInfo类用于对文件进行常用操作管理。
(1)文件常用操作
在C#中如果对文件进行创建、复制和删除等少量操作一般使用File类。
File类是静态类,其中所有方法都是静态的,通过类名直接调用,不需要实例化。
示例,如下图,进行文件的基本操作:

点击"选择文件"按钮选择某个文件,并将文件路径在文本框显示。
点击"选择文件夹"按钮选择某个文件夹,并将文件夹路径在文本框显示。
点击"复制文件"按钮,实现将文件复制到文件夹中。
点击"移动文件"按钮,实现将文件移动到文件夹中。
点击"删除文件"按钮,实现将文件删除。
其中,"选择文件"按钮name=btOpenFile,"选择文件夹"按钮name=btOpenFolder,"复制文件"按钮name=btCopy,"移动文件"按钮name=btMove,"删除文件"按钮name=btDelete。
存放文件名的文本框name=txtFile,存放文件夹名的文本框name=txtFolder。
文件对话框name=openFileDialog1,文件夹对话框name=folderBrowserDialog1。
File类实现代码如下:
//选择文件按钮
private void btOpenFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.openFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
//FileName包含路径,SafeFileName不包含路径
this.txtFile.Text = this.openFileDialog1.FileName;
}
}
//选择文件夹按钮
private void btOpenFolder_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txtFolder.Text = this.folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
}
}
//复制文件按钮
private void btCopy_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(this.txtFile.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件不存在!");
return;
}
if (!Directory.Exists(this.txtFolder.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在!");
return;
}
string[] arrName = this.txtFile.Text.Split('\\');
string name = arrName[arrName.Length - 1];
//第三个参数true代表文件存在直接覆盖
//如果希望不覆盖,此处添加代码判断文件已经存在给出提示
File.Copy(this.txtFile.Text, this.txtFolder.Text + "\\" + name,true);
MessageBox.Show("复制成功!");
}
//移动文件
private void btMove_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(this.txtFile.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件不存在!");
return;
}
if (!Directory.Exists(this.txtFolder.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在!");
return;
}
string[] arrName = this.txtFile.Text.Split('\\');
string name = arrName[arrName.Length - 1];
string newFileName = this.txtFolder.Text + "\\" + name;
if (File.Exists(newFileName))
{
//方案一:提示用户有重名文件
//MessageBox.Show("目标位置有重名文件!");
//return;
//方案二:直接将目标文件删除
File.Delete(newFileName);
}
File.Move(this.txtFile.Text, newFileName);
MessageBox.Show("移动成功!");
}
//删除文件
private void btDelete_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!File.Exists(this.txtFile.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件不存在!");
return;
}
File.Delete(this.txtFile.Text);
MessageBox.Show("删除成功!");
}
和FileInfo类相比,使用File类可以避免频繁创建和释放对象的系统开销,但如果需要多次重用某个文件对象,则使用FileInfo类。
下面使用FileInfo类实现相同功能,代码如下:
//选择文件按钮
private void btOpenFile_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.openFileDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
//FileName包含路径,SafeFileName不包含路径
this.txtFile.Text = this.openFileDialog1.FileName;
}
}
//选择文件夹按钮
private void btOpenFolder_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txtFolder.Text = this.folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
}
}
//复制文件
private void btCopy_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
FileInfo fInfo = new FileInfo(this.txtFile.Text);
if (fInfo.Exists == false)
{
MessageBox.Show("文件不存在!");
return;
}
DirectoryInfo dInfo = new DirectoryInfo(this.txtFolder.Text);
if (dInfo.Exists == false)
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在!");
return;
}
string[] arrName = this.txtFile.Text.Split('\\');
string name = arrName[arrName.Length - 1];
//第二个参数true代表文件存在直接覆盖
fInfo.CopyTo(this.txtFolder.Text + "\\" + name, true);
MessageBox.Show("复制成功!");
}
//移动文件
private void btMove_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
FileInfo fInfo = new FileInfo(this.txtFile.Text);
if (fInfo.Exists == false)
{
MessageBox.Show("文件不存在!");
return;
}
DirectoryInfo dInfo = new DirectoryInfo(this.txtFolder.Text);
if (dInfo.Exists == false)
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在!");
return;
}
string[] arrName = this.txtFile.Text.Split('\\');
string name = arrName[arrName.Length - 1];
string newFileName = this.txtFolder.Text + "\\" + name;
FileInfo deskFile = new FileInfo(newFileName);
if (deskFile.Exists == true)
{
//方案一:提示用户有重名文件
//MessageBox.Show("目标位置有重名文件!");
//return;
//方案二:直接将目标文件删除
deskFile.Delete();
}
fInfo.MoveTo(newFileName);
MessageBox.Show("移动成功!");
}
//删除文件
private void btDelete_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
FileInfo fInfo = new FileInfo(this.txtFile.Text);
if (fInfo.Exists == false)
{
MessageBox.Show("文件不存在!");
return;
}
fInfo.Delete();
MessageBox.Show("删除成功!");
}
(2)文件夹常用操作
Directory类是静态类,其中所有方法都是静态的,通过类名直接调用。
示例,如下图,进行文件夹的基本操作:
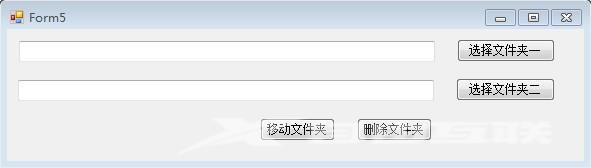
点击"选择文件夹一"按钮,选择文件夹,并把文件夹路径显示在第一个文本框。
点击"选择文件夹二"按钮,选择文件夹,并把文件夹路径显示在第二个文本框。
点击"移动文件夹"按钮,将第一个文本框路径的文件夹移动到第二个文本框路径的文件夹下。
点击"删除文件夹"按钮,将第一个文本框路径的文件夹进行删除。
其中"选择文件夹一"按钮name=btOpen1,"选择文件夹二"按钮name=btOpen2,"移动文件夹"按钮name=btMove,"删除文件夹"按钮name=btDelete。
第一个文本框name=txtFolder1,第二个文本框name=txtFolder2。
文件对话框name=openFileDialog1,文件夹对话框name=folderBrowserDialog1。
Directory实现代码如下:
//选择文件夹一
private void btOpen1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txtFolder1.Text = this.folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
}
}
//选择文件夹二
private void btOpen2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txtFolder2.Text = this.folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
}
}
//移动文件夹
private void btMove_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!Directory.Exists(this.txtFolder1.Text) || !Directory.Exists(this.txtFolder2.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在!");
return;
}
//获取文件夹名称
string[] arrFolderName = this.txtFolder1.Text.Split('\\');
string folderName = arrFolderName[arrFolderName.Length - 1];
string newFolderName = this.txtFolder2.Text + "\\" + folderName;
//判断目标地址是否已经有该文件夹了
if (Directory.Exists(newFolderName))
{
//方案一:给出提示
//MessageBox.Show("在目标位置,该文件夹已经存在了");
//return;
//方案二:删除目标位置的文件夹
Directory.Delete(newFolderName,true);
}
//此移动操作只能在同一个根盘符上操作
Directory.Move(this.txtFolder1.Text, newFolderName);
MessageBox.Show("移动文件夹成功!");
}
private void btDelete_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!Directory.Exists(this.txtFolder1.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在!");
return;
}
//第二个参数代表删除所有的子文件夹和文件
Directory.Delete(this.txtFolder1.Text, true);
MessageBox.Show("删除文件夹成功!");
}
同样上述功能,使用DirectoryInfo实现如下:
//选择文件夹一
private void btOpen1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txtFolder1.Text = this.folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
}
}
//选择文件夹二
private void btOpen2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txtFolder2.Text = this.folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
}
}
//移动文件夹
private void btMove_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DirectoryInfo startInfo = new DirectoryInfo(this.txtFolder1.Text);
DirectoryInfo endInfo = new DirectoryInfo(this.txtFolder2.Text);
if (startInfo.Exists == false || endInfo.Exists == false)
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在");
return;
}
string[] arrFolderName = this.txtFolder1.Text.Split('\\');
string folderName = arrFolderName[arrFolderName.Length - 1];
string newFolderName = this.txtFolder2.Text + "\\" + folderName;
//判断目标地址是否已经有该文件夹了
DirectoryInfo tmp = new DirectoryInfo(newFolderName);
if (tmp.Exists == true)
{
//方案一:给出提示
//MessageBox.Show("在目标位置,该文件夹已经存在了");
//return;
//方案二:删除目标位置的文件夹
tmp.Delete(true);
}
//此移动操作只能在同一个根盘符上操作
startInfo.MoveTo(newFolderName);
MessageBox.Show("移动成功!");
}
private void btDelete_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DirectoryInfo startInfo = new DirectoryInfo(this.txtFolder1.Text);
if (startInfo.Exists == false)
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在");
return;
}
//参数代表删除所有的子文件夹和文件
startInfo.Delete(true);
MessageBox.Show("删除文件夹成功!");
}
(3)文件夹的复制和移动
关于文件夹的移动,系统提供给我们的功能,只能在同一个根盘符上操作。
关于文件夹的复制,系统根本就没有提供相应的API。
所以关于文件夹的复制以及文件移动跨磁盘只能自己写,自己实现了,如图:
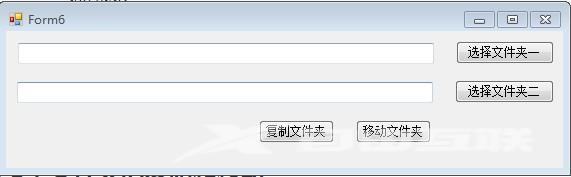
点击"选择文件夹一"按钮:可以选择一个文件夹,并且将文件夹的路径显示在第一个文本框。
点击"选择文件夹二"按钮:可以选择一个文件夹,并且将文件夹的路径显示在第二个文本框。
点击"复制文件夹"按钮:将第一个文件夹及文件夹内容复制到第二个文件夹中。
点击"移动文件夹"按钮:将第一个文件夹及文件夹内容移动到第二个文件夹中。
其中:"选择文件夹一"按钮name=btOpen1,"选择文件夹二"按钮name=btOpen2,"复制文件夹"按钮name=btCopy,"移动文件夹"按钮name=btMove。
第一个文本框name=txtFolder1,第二个文本框name=txtFolder2。
文件对话框name=openFileDialog1,文件夹对话框name=folderBrowserDialog1。
具体实现代码如下:
编写通用的递归方法,实现文件夹的复制:
//endFolderPath为处理之后的目标路径
//例如将"C:\abc"复制到"D:123\",endFolderPath需要传递处理之后的"D:123\abc"
private void CopyFolder(string startFolderPath, string endFolderPath)
{
//在创建目标文件夹
Directory.CreateDirectory(endFolderPath);
DirectoryInfo startDir = new DirectoryInfo(startFolderPath);
//循环复制文件夹下的所有文件
foreach (FileInfo item in startDir.GetFiles())
{
File.Copy(item.FullName, endFolderPath + "\\" + item.Name);
}
//循环所有子文件夹形成递归调用
foreach (DirectoryInfo item in startDir.GetDirectories())
{
string startPath = item.FullName;
string newFolderName = endFolderPath + "\\" + item.Name;
CopyFolder(startPath, newFolderName);
}
}
各个按钮的代码如下:
private void btOpen1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txtFolder1.Text = this.folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
}
}
private void btOpen2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (this.folderBrowserDialog1.ShowDialog() == DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txtFolder2.Text = this.folderBrowserDialog1.SelectedPath;
}
}
//复制文件夹
private void btCopy_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!Directory.Exists(this.txtFolder1.Text) || !Directory.Exists(this.txtFolder2.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在!");
return;
}
string[] arrFolderName = this.txtFolder1.Text.Split('\\');
string folderName = arrFolderName[arrFolderName.Length - 1];
string newFolderName = this.txtFolder2.Text + "\\" + folderName;
//判断目标地址是否已经有该文件夹了
if (Directory.Exists(newFolderName))
{
//方案一:给出提示
//MessageBox.Show("在目标位置,该文件夹已经存在了");
//return;
//方案二:删除目标位置的文件夹
Directory.Delete(newFolderName, true);
}
CopyFolder(this.txtFolder1.Text, newFolderName);
MessageBox.Show("复制成功!");
}
//移动文件夹
private void btMove_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!Directory.Exists(this.txtFolder1.Text) || !Directory.Exists(this.txtFolder2.Text))
{
MessageBox.Show("文件夹不存在!");
return;
}
string[] arrFolderName = this.txtFolder1.Text.Split('\\');
string folderName = arrFolderName[arrFolderName.Length - 1];
string newFolderName = this.txtFolder2.Text + "\\" + folderName;
//判断目标地址是否已经有该文件夹了
if (Directory.Exists(newFolderName))
{
//方案一:给出提示
//MessageBox.Show("在目标位置,该文件夹已经存在了");
//return;
//方案二:删除目标位置的文件夹
Directory.Delete(newFolderName, true);
}
CopyFolder(this.txtFolder1.Text, newFolderName);
//复制完成后,删除原始位置的文件夹
Directory.Delete(this.txtFolder1.Text, true);
MessageBox.Show("移动成功!");
}
三、读写文本文件
文件和流的概念:
--文件是在各种媒质上永久存储的数据的有序集合。它是进行数据读写操作的基本对象。
--流是一种向存储器读取和写入字节的方式,也是进行数据读写操作的基本对象。
--流提供了连续的字节流存储空间,其实际存储位置可以不连续。
--C#中所有表示流的类都继承于抽象类Stream。
读写文本文件最常用的类有:
--FileStream(文件流)
--StreamReader(流读取器)
--StreamWriter(流写入器)
读写文件操作的基本步骤为:
- 创建文件流
- 创建读、写器
- 执行读、写操作
- 关闭读写器
- 关闭文件流
文件流对象:
实例化文件流对象语法如下:
FileStream fs = new FileStream(FileName, FileMode,FileAccess);
其中FileMode的枚举值如下:
其中FileAccess的枚举值如下:
文件读写器常用方法:
StreamReader的常用方法:
StreamWriter的常用方法:
示例:如下图,编写一个文本文件读写器
--点击"打开文件"按钮,选择一个文本文件,并且将文本文件路径显示在上面单行文本框中,将文本文件的内容显示在下面的多行文本框中。
--多行文本框,可以进行修改其文本内容。
--点击"保存文件"按钮,将多行文本框的文本保存到打开的文本文件中。
其中"打开文件"按钮name=btOpen,"保存文件"按钮name=btSave,单行文本框name=txtFilePath,多行文本框name=txtContent。
实现代码如下:
private void btOpen_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
OpenFileDialog dialog = new OpenFileDialog();
DialogResult result = dialog.ShowDialog();
//点击打开按钮之后
if (result == System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txtFilePath.Text = dialog.FileName;
}
else
{
return;
}
//方案一:使用Filestream将文本一次性全部转换为字节数组,之后转换为string
//FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.txtFilePath.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
////fs.Seek(0, SeekOrigin.Begin); //定位流,从开始位置移动0个字节,也就是流的最开始位置
//int len = (int)fs.Length; //获取文件的字节长度
//byte[] arrByte = new byte[len]; //定义字节数组
//fs.Read(arrByte, 0, arrByte.Length); //将文件流读入字节数组
//this.txtContent.Text = Encoding.Default.GetString(arrByte,0,len);
//fs.Close();
//方案二:使用Filestream,逐字节读取文本,后将字节转换为string
//FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.txtFilePath.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
//int len = (int)fs.Length; //获取文件的字节长度
//byte[] arrByte = new byte[len]; //定义字节数组
//int index = 0; //保存字节数组变化的下标
//int code = fs.ReadByte(); //读取一个字节
//while (code != -1) //读取内容等于-1即表示读取完毕
//{
// //将读取内容转换成字节存入数组
// arrByte[index] = Convert.ToByte(code);
// code = fs.ReadByte(); //继续逐字节读取
// index++;
//}
//this.txtContent.Text = Encoding.Default.GetString(arrByte, 0, len);
//fs.Close();
//方案三:直接使用File的Read All Text 函数将文本文件内容全部读入text
//File.ReadAllBytes可以读取成字节数组
//this.txtContent.Text = File.ReadAllText(this.txtFilePath.Text, Encoding.Default);
//方案四:使用StreamReader流读取器读取
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.txtFilePath.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
StreamReader sd = new StreamReader(fs, Encoding.Default);
//这里可以逐行读入
//string line = sd.ReadLine();
//while (line != null)
//{
// this.txtContent.Text = this.txtContent.Text + line + "\r\n";
// line = sd.ReadLine();
//}
//也可以全部读入
this.txtContent.Text = sd.ReadToEnd();
sd.Close();
fs.Close();
}
private void btSave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//方案一:File类静态方法
//File.WriteAllText(this.txtFileName.Text, this.txtContent.Text,Encoding.Default);
//MessageBox.Show("保存成功!");
//方案二:使用StreamWriter流写入器
FileStream fs = new FileStream(this.txtFileName.Text, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Write);
StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(fs, Encoding.Default);
sw.Write(this.txtContent.Text);
sw.Close();
fs.Close();
MessageBox.Show("保存成功!");
}
四、序列化与反序列化
序列化就是将对象实例的状态存储到存储媒介的过程。
序列化和反序列化的实现步骤(二进制序列化):
- (1)引入System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters.Binary命名空间
- (2)要序列化的对象需要标记Serializable特性
- (3)其父类和属性中的引用类型也标记Serializable特性
- (4)使用BinaryFormatter 对象的Serialize()方法和Deserialize()方法
(1)序列化单个对象
示例:如下图,实现单个对象的序列化与反序列化
--输入学生信息,点击"保存信息"按钮,将学生信息永久序列化保存到电脑上。
--关闭程序后,在启动程序,可以将本地序列化文件读取,将信息显示在界面的文本框中。
其中,学号,姓名,年龄文本框的name分别为txtNo,txtName,txtAge。
保存信息和读取信息按钮name分别为btSave和btRead。
具体实现代码如下:
定义一个学生类:
[Serializable]
class Student
{
public string StuNo { get; set; } //学号
public string StuName { get; set; } //姓名
public int StuAge { get; set; } //年龄
}
其中[Serializable]关键字代表此类是可以被序列化的。
编写按钮响应事件代码:
private void btSave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.StuNo = this.txtNo.Text;
stu.StuName = this.txtName.Text;
stu.StuAge = int.Parse(this.txtAge.Text);
FileStream fs = new FileStream("stu.ini", FileMode.Create, FileAccess.ReadWrite);
BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();
bf.Serialize(fs, stu); //序列化
fs.Close();
MessageBox.Show("保存成功!");
}
private void btRead_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
FileStream fs = new FileStream("stu.ini", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.ReadWrite);
BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();
Student stu = bf.Deserialize(fs) as Student; //反序列化
this.txtNo.Text = stu.StuNo;
this.txtName.Text = stu.StuName;
this.txtAge.Text = stu.StuAge.ToString();
fs.Close();
}
(2)序列化集合
示例:如下图,实现集合的序列化

--打开窗体,自动从序列化文件中读取信息,并在listView列表上进行展示。
--输入学生信息,点击"添加信息"按钮,添加学生,并且序列化学生列表,刷新ListView列表数据。
其中展示列表的ListView控件的name=listView1。
学号,姓名,年龄文本框的name分别为txtNo,txtName,txtAge。
添加信息按钮name=btSave。
具体实现代码如下:
定义一个学生类:
[Serializable]
class Student
{
public string StuNo { get; set; } //学号
public string StuName { get; set; } //姓名
public int StuAge { get; set; } //年龄
}
其中[Serializable]关键字代表此类是可以被序列化的。
编写按钮响应事件代码:
List<Student> list = new List<Student>();
private void BindData()
{
if (!File.Exists("list.ini"))
return;
//读取序列化文件
FileStream fs = new FileStream("list.ini", FileMode.Open, FileAccess.ReadWrite);
BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();
list = bf.Deserialize(fs) as List<Student>; //反序列化
fs.Close();
//将list集合数据绑定到ListView控件
this.listView1.Items.Clear();
foreach (Student stu in list)
{
ListViewItem item = new ListViewItem(stu.StuNo);
item.SubItems.Add(stu.StuName);
item.SubItems.Add(stu.StuAge.ToString());
this.listView1.Items.Add(item);
}
}
private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
BindData();
}
private void btSave_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.StuNo = this.txtNo.Text;
stu.StuName = this.txtName.Text;
stu.StuAge = int.Parse(this.txtAge.Text);
list.Add(stu);
FileStream fs = new FileStream("list.ini", FileMode.Create, FileAccess.ReadWrite);
BinaryFormatter bf = new BinaryFormatter();
bf.Serialize(fs, list); //序列化
fs.Close();
MessageBox.Show("保存成功!");
BindData();
}
到此这篇关于C#开发Winform实现文件操作案例的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持自由互联。
