目录 1. 引言 2. 自定义排序规则 2.1 重写 或 运算符 2.2 普通函数 2.3 仿函数 1. 引言 在C++中,sort()函数常常用来对容器内的元素进行排序,先来了解一下sort()函数。 sort()函数有三个参数:
目录
- 1. 引言
- 2. 自定义排序规则
- 2.1 重写 < 或 > 运算符
- 2.2 普通函数
- 2.3 仿函数
1. 引言
在C++中,sort()函数常常用来对容器内的元素进行排序,先来了解一下sort()函数。
sort()函数有三个参数:
- 第一个是要排序的容器的起始迭代器。
- 第二个是要排序的容器的结束迭代器。
- 第三个参数是排序的方法,是可选的参数。默认的排序方法是从小到大排序,也就是
less<Type>(),还提供了greater<Type>()进行从大到小排序。这个参数的类型是函数指针,less和greater实际上都是类/结构体,内部分别重载了()运算符,称为仿函数,所以实际上less<Type>()和greater<Type>()都是函数名,也就是函数指针。我们还可以用普通函数来定义排序方法。
如果容器内元素的类型是内置类型或string类型,我们可以直接用less<Type>()或greater<Type>()进行排序。但是如果数据类型是我们自定义的结构体或者类的话,我们需要自定义排序函数,
有三种写法:
- 重载 < 或 > 运算符:重载
<运算符,传入less<Type>()进行升序排列。重载>运算符,传入greater<Type>()进行降序排列。这种方法只能针对一个维度排序,不灵活。 - 普通函数:写普通函数cmp,传入
cmp按照指定规则排列。这种方法可以对多个维度排序,更灵活。 - 仿函数:写仿函数cmp,传入
cmp<Type>()按照指定规则排列。这种方法可以对多个维度排序,更灵活。
2. 自定义排序规则
2.1 重写 < 或 > 运算符
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Person {
int id;
int age;
Person(int id,int age):id(id),age(age){}
//重载<运算符,进行升序排列
bool operator < (const Person& p2) const {
return id < p2.id;
}
//重载>运算符,进行降序排列
bool operator > (const Person& p2) const {
return id > p2.id;
}
};
int main()
{
Person p1(1, 10), p2(2, 20), p3(3, 30);
vector<Person> ps;
ps.push_back(p2);
ps.push_back(p1);
ps.push_back(p3);
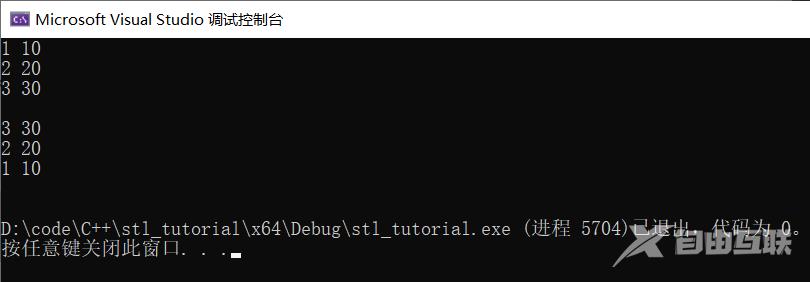
sort(ps.begin(), ps.end(), less<Person>());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << ps[i].id << " " << ps[i].age << endl;
}
cout << endl;
sort(ps.begin(), ps.end(), greater<Person>());
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << ps[i].id << " " << ps[i].age << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
2.2 普通函数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Person {
int id;
int age;
Person(int id,int age):id(id),age(age){}
};
//普通函数
bool cmp(const Person& p1, const Person& p2) {
if (p1.id == p2.id) return p1.age >= p2.age;
return p1.id < p2.id;
}
int main()
{
Person p1(1, 10), p2(2, 20), p3(3, 30), p4(3, 40);
vector<Person> ps;
ps.push_back(p2);
ps.push_back(p1);
ps.push_back(p3);
ps.push_back(p4);
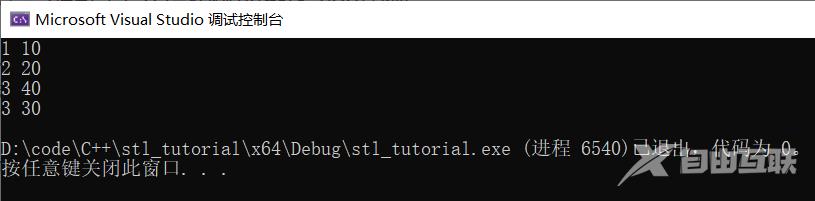
sort(ps.begin(), ps.end(), cmp);//传入函数指针cmp
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cout << ps[i].id << " " << ps[i].age << endl;
}
}
2.3 仿函数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Person {
int id;
int age;
Person(int id, int age) :id(id), age(age) {}
};
//仿函数
struct cmp {
bool operator()(const Person& p1, const Person& p2) {
if (p1.id == p2.id) return p1.age >= p2.age;
return p1.id < p2.id;
}
};
int main()
{
Person p1(1, 10), p2(2, 20), p3(3, 30), p4(3, 40);
vector<Person> ps;
ps.push_back(p2);
ps.push_back(p1);
ps.push_back(p3);
ps.push_back(p4);
sort(ps.begin(), ps.end(), cmp()); //传入函数指针cmp()
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
cout << ps[i].id << " " << ps[i].age << endl;
}
}

到此这篇关于c++自定义sort()函数的排序方法介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关c++ sort排序内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
