目录 图像拼接技术 一、需求分析 二、具体步骤 三、代码实现 图像拼接技术 一、需求分析 将下面两张图像进行拼接 拼接得到一张完整的图像 二、具体步骤 1.选择特征点 //1、选择特征
目录
- 图像拼接技术
- 一、需求分析
- 二、具体步骤
- 三、代码实现
图像拼接技术
一、需求分析
将下面两张图像进行拼接
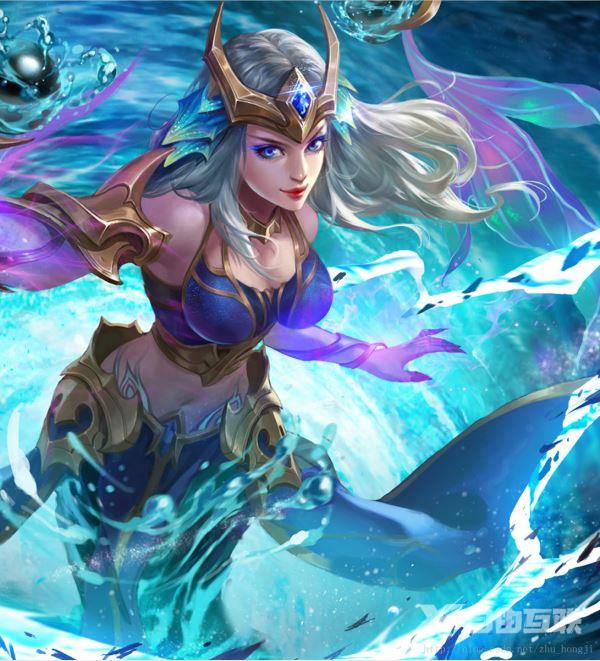


拼接得到一张完整的图像
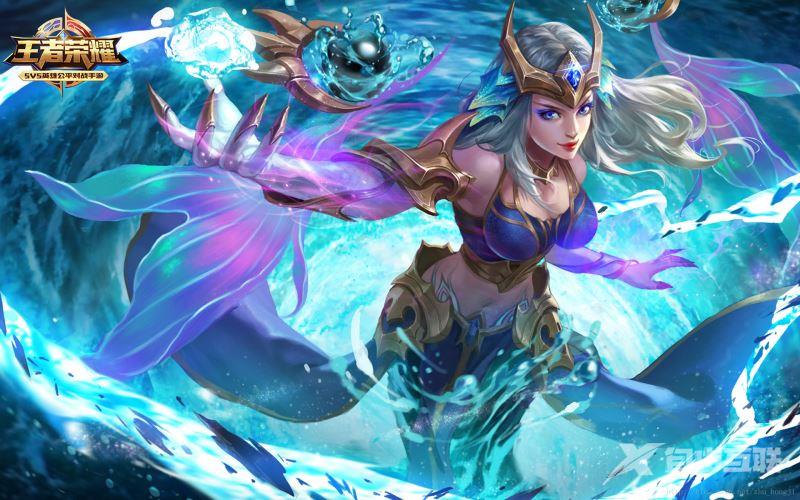

二、具体步骤
1.选择特征点
//1、选择特征点
//左图 右图 识别特征点 是Mat对象 用c d保存
surf->detectAndCompute(left,Mat(),key2,d);
surf->detectAndCompute(right,Mat(),key1,c);
//特征点对比,保存 特征点为中心点区域比对
vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher.match(d,c,matches);
//排序从小到大 找到特征点连线
sort(matches.begin(),matches.end());
2.保存最优的特征点对象
//2、保存最优的特征点对象
vector<DMatch>good_matches;
int ptrpoint = std::min(50,(int)(matches.size()*0.15));
for (int i = 0;i < ptrpoint;i++)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
//2-1、画线 最优的特征点对象连线
Mat outimg;
drawMatches(left,key2,right,key1,good_matches,outimg,
Scalar::all(-1),Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(),DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
//imshow("outimg",outimg);
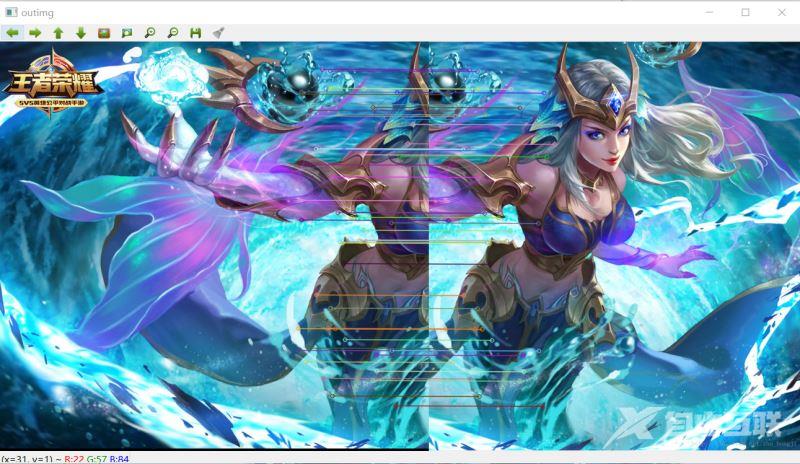
3.特征点匹配
//3、特征点匹配
vector<Point2f>imagepoint1,imagepoint2;
for (int i= 0 ;i < good_matches.size();i++)
{
//查找特征点可连接处 变形
imagepoint1.push_back(key1[good_matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
//查找特征点可连接处 查找基准线
imagepoint2.push_back(key2[good_matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
}
4.透视转换 图像融合
//4、透视转换 图形融合
Mat homo = findHomography(imagepoint1,imagepoint2,CV_RANSAC);
//imshow("homo",homo);
//根据透视转换矩阵进行计算 四个坐标
CalcCorners(homo,right);
//接收透视转换结果
Mat imageTransForm;
//透视转换
warpPerspective(right,imageTransForm,homo,
Size(MAX(corners.right_top.x,corners.right_bottom.x),left.rows));
//右图透视变换 由于本次图片材料是自己截图拼接的 因此看不出透视变换的明显特征
//imshow("imageTransForm",imageTransForm);
//结果进行整合
int dst_width = imageTransForm.cols;
int dst_height = left.rows;
Mat dst(dst_height,dst_width,CV_8UC3);
dst.setTo(0);
imageTransForm.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,imageTransForm.cols,imageTransForm.rows)));
left.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,left.cols,left.rows)));
右图的透视转换,由于图像材料是自己截图拼接的,因此看不出透视变换的明显特征,但根据上图可知已经做出透视变换图像处理操作

左图与右图的透视转换结果 拼接 【这里只是将窗口移动测试看下前面步骤是否正确】
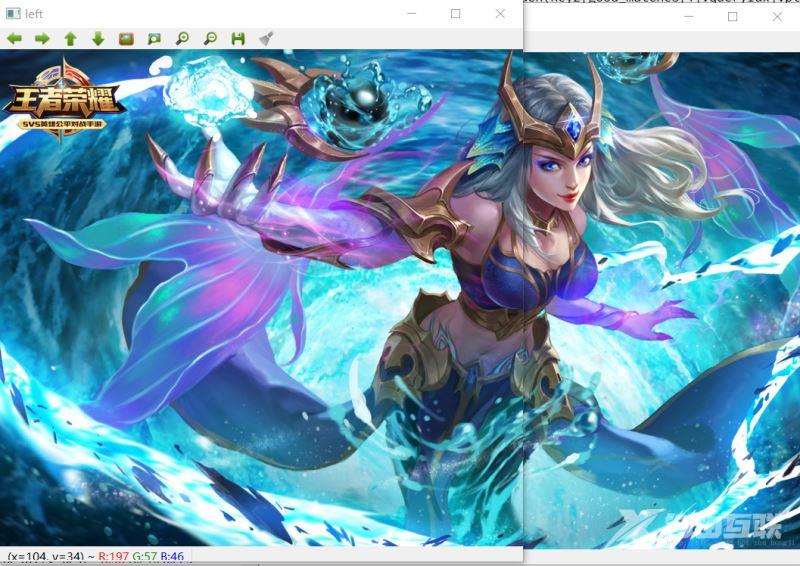
可以看出左图与右图的透视转换结果 是可以进行接下来的图像融合操作的
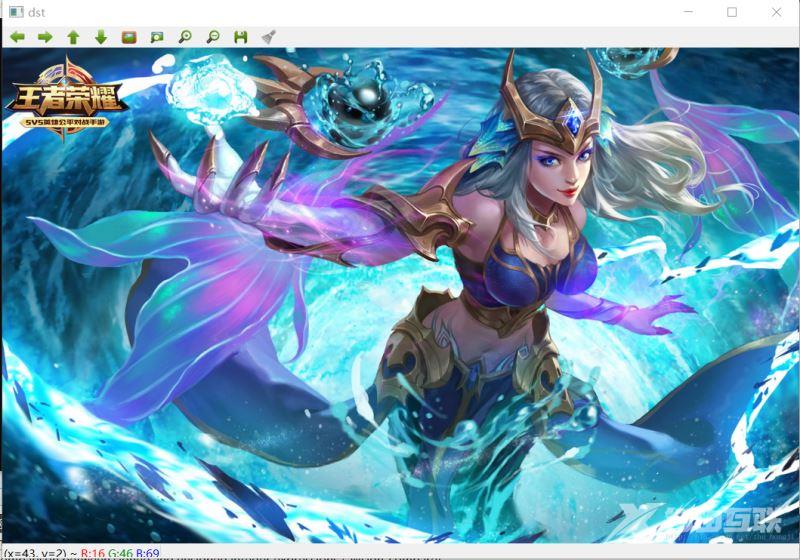
5.优化图像 进行最终的结果展示
//5、优化图像
OptimizeSeam(left,imageTransForm,dst);
//最终图像拼接结果
imshow("dst",dst);

可以看出 顺利完成 两张图像拼接的图像处理操作
三、代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>//图像融合
#include <opencv2/xfeatures2d.hpp>//拼接算法
#include <opencv2/calib3d.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::xfeatures2d;
typedef struct
{
Point2f left_top;
Point2f left_bottom;
Point2f right_top;
Point2f right_bottom;
}four_corners_t;
four_corners_t corners;
void CalcCorners(const Mat& H, const Mat& src)
{
double v2[] = { 0, 0, 1 };//左上角
double v1[3];//变换后的坐标值
Mat V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
Mat V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
//左上角(0,0,1)
cout << "V2: " << V2 << endl;
cout << "V1: " << V1 << endl;
corners.left_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//左下角(0,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = 0;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.left_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.left_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右上角(src.cols,0,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = 0;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_top.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_top.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
//右下角(src.cols,src.rows,1)
v2[0] = src.cols;
v2[1] = src.rows;
v2[2] = 1;
V2 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v2); //列向量
V1 = Mat(3, 1, CV_64FC1, v1); //列向量
V1 = H * V2;
corners.right_bottom.x = v1[0] / v1[2];
corners.right_bottom.y = v1[1] / v1[2];
}
//图像融合的去裂缝处理操作
void OptimizeSeam(Mat& img1, Mat& trans, Mat& dst)
{
int start = MIN(corners.left_top.x, corners.left_bottom.x);//开始位置,即重叠区域的左边界
double processWidth = img1.cols - start;//重叠区域的宽度
int rows = dst.rows;
int cols = img1.cols; //注意,是列数*通道数
double alpha = 1;//img1中像素的权重
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++)
{
uchar* p = img1.ptr<uchar>(i); //获取第i行的首地址
uchar* t = trans.ptr<uchar>(i);
uchar* d = dst.ptr<uchar>(i);
for (int j = start; j < cols; j++)
{
//如果遇到图像trans中无像素的黑点,则完全拷贝img1中的数据
if (t[j * 3] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 1] == 0 && t[j * 3 + 2] == 0)
{
alpha = 1;
}
else
{
//img1中像素的权重,与当前处理点距重叠区域左边界的距离成正比,实验证明,这种方法确实好
alpha = (processWidth - (j - start)) / processWidth;
}
d[j * 3] = p[j * 3] * alpha + t[j * 3] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 1] = p[j * 3 + 1] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 1] * (1 - alpha);
d[j * 3 + 2] = p[j * 3 + 2] * alpha + t[j * 3 + 2] * (1 - alpha);
}
}
}
int main()
{
//左图
Mat left = imread("D:/00000000000003jieduanshipincailliao/a1.png");
//右图
Mat right = imread("D:/00000000000003jieduanshipincailliao/a2.png");
//左右图显示
imshow("left",left);
imshow("right",right);
//创建SURF对象
Ptr<SURF> surf;
//create 函数参数 海森矩阵阀值 800特征点以内
surf = SURF::create(800);
//创建一个暴力匹配器 用于特征点匹配
BFMatcher matcher;
//特征点容器 存放特征点KeyPoint
vector<KeyPoint>key1,key2;
//保存特征点
Mat c,d;
//1、选择特征点
//左图 右图 识别特征点 是Mat对象 用c d保存
surf->detectAndCompute(left,Mat(),key2,d);
surf->detectAndCompute(right,Mat(),key1,c);
//特征点对比,保存 特征点为中心点区域比对
vector<DMatch> matches;
matcher.match(d,c,matches);
//排序从小到大 找到特征点连线
sort(matches.begin(),matches.end());
//2、保存最优的特征点对象
vector<DMatch>good_matches;
int ptrpoint = std::min(50,(int)(matches.size()*0.15));
for (int i = 0;i < ptrpoint;i++)
{
good_matches.push_back(matches[i]);
}
//2-1、画线 最优的特征点对象连线
Mat outimg;
drawMatches(left,key2,right,key1,good_matches,outimg,
Scalar::all(-1),Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(),DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS);
//imshow("outimg",outimg);
//3、特征点匹配
vector<Point2f>imagepoint1,imagepoint2;
for (int i= 0 ;i < good_matches.size();i++)
{
//查找特征点可连接处 变形
imagepoint1.push_back(key1[good_matches[i].trainIdx].pt);
//查找特征点可连接处 查找基准线
imagepoint2.push_back(key2[good_matches[i].queryIdx].pt);
}
//4、透视转换 图形融合
Mat homo = findHomography(imagepoint1,imagepoint2,CV_RANSAC);
//imshow("homo",homo);
//根据透视转换矩阵进行计算 四个坐标
CalcCorners(homo,right);
//接收透视转换结果
Mat imageTransForm;
//透视转换
warpPerspective(right,imageTransForm,homo,
Size(MAX(corners.right_top.x,corners.right_bottom.x),left.rows));
//右图透视变换 由于本次图片材料是自己截图拼接的 因此看不出透视变换的明显特征
//imshow("imageTransForm",imageTransForm);
//结果进行整合
int dst_width = imageTransForm.cols;
int dst_height = left.rows;
Mat dst(dst_height,dst_width,CV_8UC3);
dst.setTo(0);
imageTransForm.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,imageTransForm.cols,imageTransForm.rows)));
left.copyTo(dst(Rect(0,0,left.cols,left.rows)));
//5、优化图像
OptimizeSeam(left,imageTransForm,dst);
//最终图像拼接结果
imshow("dst",dst);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
到此这篇关于OpenCV图像处理之图像拼接详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关OpenCV图像拼接内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
