下一篇文章接着介绍mini-web框架,《Python高级-mini-web框架、添加路由、MySQL功能-笔记》
1.服务器动态资源请求
1. 浏览器请求动态页面过程
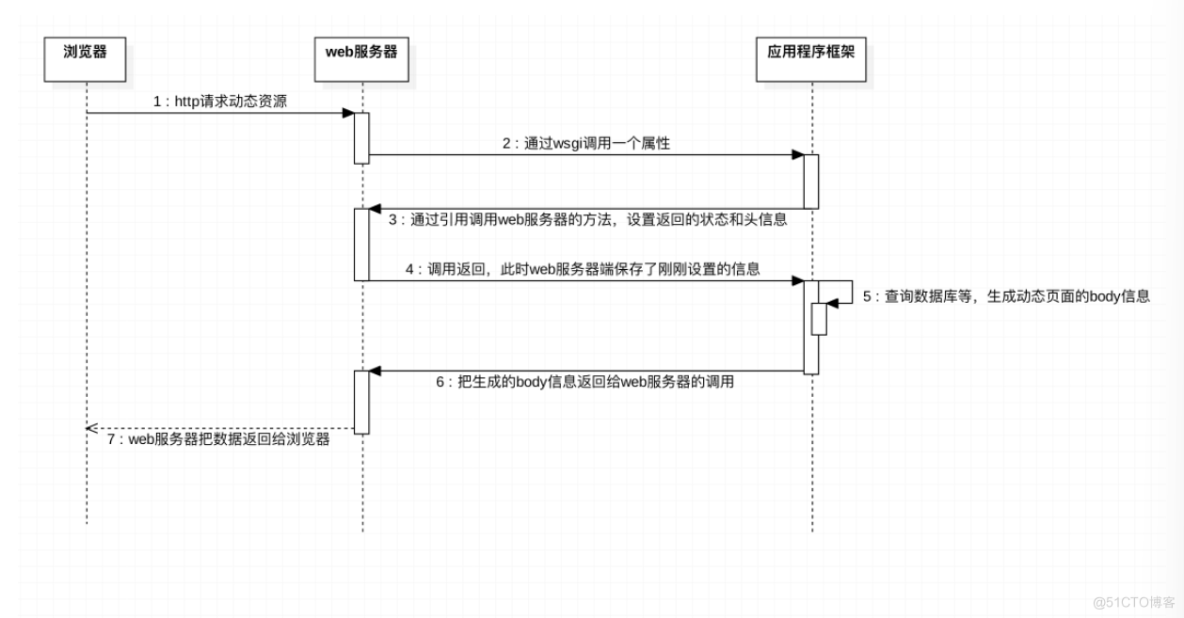
2. WSGI
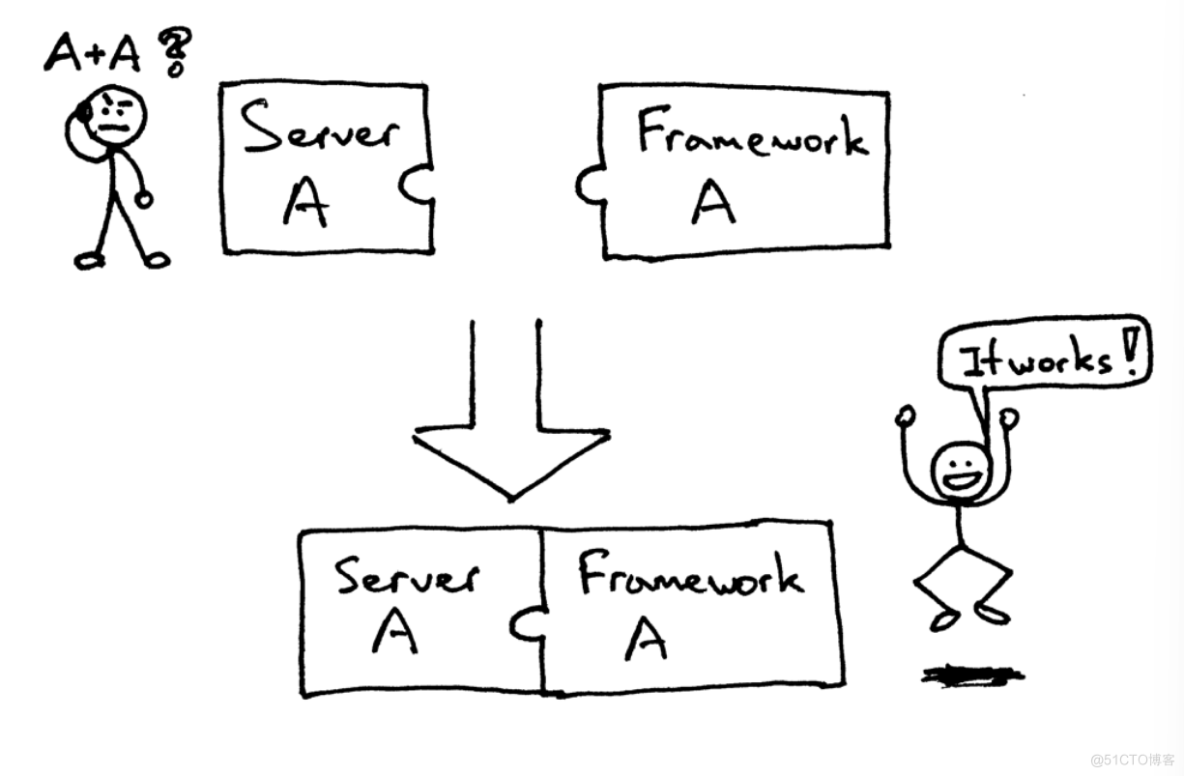
怎么在你刚建立的Web服务器上运行一个Django应用和Flask应用,如何不做任何改变而适应不同的web架构呢?
在以前,选择 Python web 架构会受制于可用的web服务器,反之亦然。如果架构和服务器可以协同工作,那就好了:
但有可能面对(或者曾有过)下面的问题,当要把一个服务器和一个架构结合起来时,却发现他们不是被设计成协同工作的:
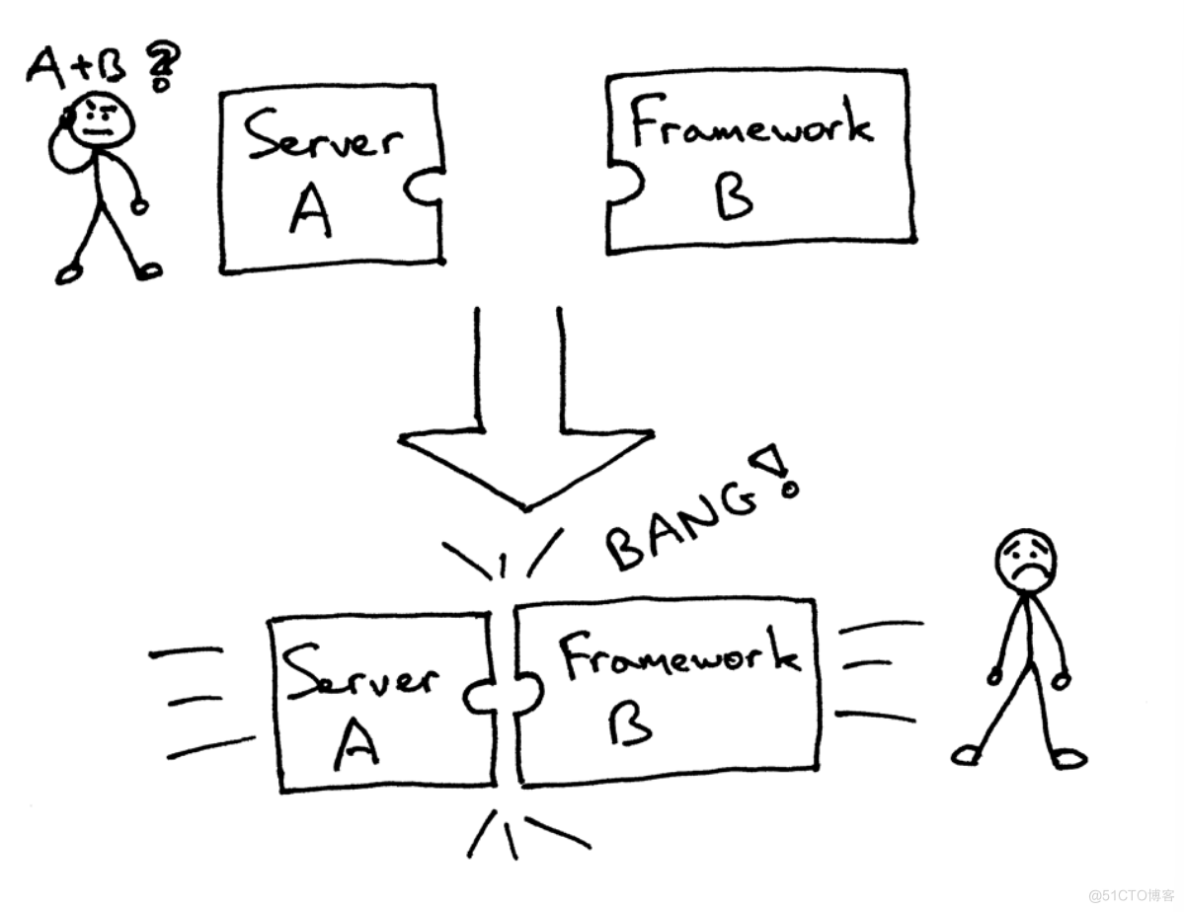
那么,怎么可以不修改服务器和架构代码而确保可以在多个架构下运行web服务器呢?答案就是 Python Web Server Gateway Interface (或简称 WSGI,读作“wizgy”)。
WSGI允许开发者将选择web框架和web服务器分开。可以混合匹配web服务器和web框架,选择一个适合的配对。比如,可以在Gunicorn 或者 Nginx/uWSGI 或者 Waitress上运行 Django, Flask, 或 Pyramid。真正的混合匹配,得益于WSGI同时支持服务器和架构:
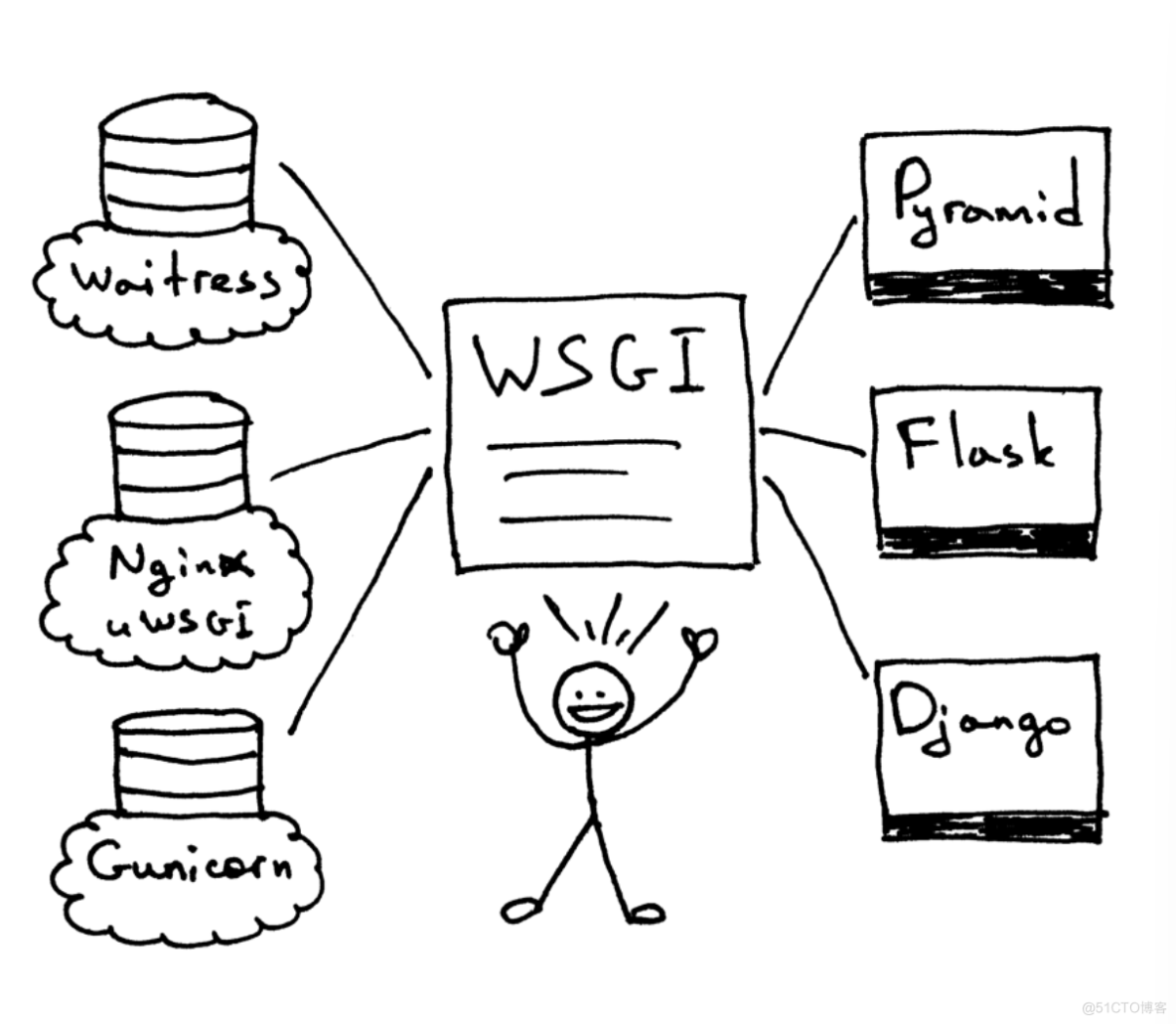
web服务器必须具备WSGI接口,所有的现代Python Web框架都已具备WSGI接口,它让你不对代码作修改就能使服务器和特点的web框架协同工作。
WSGI由web服务器支持,而web框架允许你选择适合自己的配对,但它同样对于服务器和框架开发者提供便利使他们可以专注于自己偏爱的领域和专长而不至于相互牵制。其他语言也有类似接口:java有Servlet API,Ruby 有 Rack。
3.定义WSGI接口
WSGI接口定义非常简单,它只要求Web开发者实现一个函数,就可以响应HTTP请求。我们来看一个最简单的Web版本的“Hello World!”:
def application(environ, start_response): start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')]) return 'Hello World!'
上面的application()函数就是符合WSGI标准的一个HTTP处理函数,它接收两个参数:
- environ:一个包含所有HTTP请求信息的dict对象;
- start_response:一个发送HTTP响应的函数。
整个application()函数本身没有涉及到任何解析HTTP的部分,也就是说,把底层web服务器解析部分和应用程序逻辑部分进行了分离,这样开发者就可以专心做一个领域了
不过,等等,这个application()函数怎么调用?如果我们自己调用,两个参数environ和start_response我们没法提供,返回的str也没法发给浏览器。
所以application()函数必须由WSGI服务器来调用。有很多符合WSGI规范的服务器。而我们此时的web服务器项目的目的就是做一个既能解析静态网页还可以解析动态网页的服务器
4. web服务器-----WSGI协议---->web框架 传递的字典
{ 'HTTP_ACCEPT_LANGUAGE': 'zh-cn', 'wsgi.file_wrapper': <built-infunctionuwsgi_sendfile>, 'HTTP_UPGRADE_INSECURE_REQUESTS': '1', 'uwsgi.version': b'2.0.15', 'REMOTE_ADDR': '172.16.7.1', 'wsgi.errors': <_io.TextIOWrappername=2mode='w'encoding='UTF-8'>, 'wsgi.version': (1,0), 'REMOTE_PORT': '40432', 'REQUEST_URI': '/', 'SERVER_PORT': '8000', 'wsgi.multithread': False, 'HTTP_ACCEPT': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8', 'HTTP_HOST': '172.16.7.152: 8000', 'wsgi.run_once': False, 'wsgi.input': <uwsgi._Inputobjectat0x7f7faecdc9c0>, 'SERVER_PROTOCOL': 'HTTP/1.1', 'REQUEST_METHOD': 'GET', 'HTTP_ACCEPT_ENCODING': 'gzip,deflate', 'HTTP_CONNECTION': 'keep-alive', 'uwsgi.node': b'ubuntu', 'HTTP_DNT': '1', 'UWSGI_ROUTER': 'http', 'SCRIPT_NAME': '', 'wsgi.multiprocess': False, 'QUERY_STRING': '', 'PATH_INFO': '/index.html', 'wsgi.url_scheme': 'http', 'HTTP_USER_AGENT': 'Mozilla/5.0(Macintosh;IntelMacOSX10_12_5)AppleWebKit/603.2.4(KHTML,likeGecko)Version/10.1.1Safari/603.2.4', 'SERVER_NAME': 'ubuntu'}
2.应用程序示例
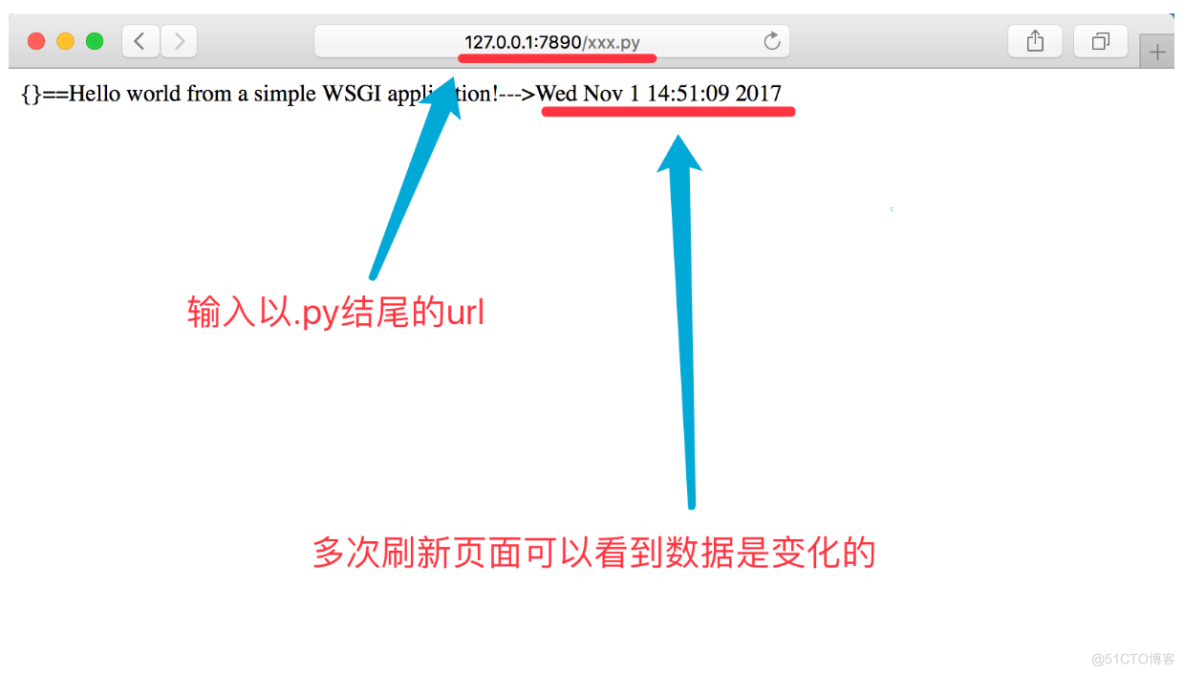
import timedef application(environ, start_response): status = '200 OK' response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')] start_response(status, response_headers) return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
3.Web动态服务器-基本实现
文件结构
├── web_server.py├── web│ └── my_web.py└── html └── index.html .....
web/my_web.py
import timedef application(environ, start_response): status = '200 OK' response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')] start_response(status, response_headers) return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
web_server.py
import selectimport timeimport socketimport sysimport reimport multiprocessingclass WSGIServer(object): """定义一个WSGI服务器的类""" def __init__(self, port, documents_root, app): # 1. 创建套接字 self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) # 2. 绑定本地信息 self.server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) self.server_socket.bind(("", port)) # 3. 变为监听套接字 self.server_socket.listen(128) # 设定资源文件的路径 self.documents_root = documents_root # 设定web框架可以调用的函数(对象) self.app = app def run_forever(self): """运行服务器""" # 等待对方链接 while True: new_socket, new_addr = self.server_socket.accept() # 创建一个新的进程来完成这个客户端的请求任务 new_socket.settimeout(3) # 3s new_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=self.deal_with_request, args=(new_socket,)) new_process.start() new_socket.close() def deal_with_request(self, client_socket): """以长链接的方式,为这个浏览器服务器""" while True: try: request = client_socket.recv(1024).decode("utf-8") except Exception as ret: print("========>", ret) client_socket.close() return # 判断浏览器是否关闭 if not request: client_socket.close() return request_lines = request.splitlines() for i, line in enumerate(request_lines): print(i, line) # 提取请求的文件(index.html) # GET /a/b/c/d/e/index.html HTTP/1.1 ret = re.match(r"([^/]*)([^ ]+)", request_lines[0]) if ret: print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(1)) print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(2)) file_name = ret.group(2) if file_name == "/": file_name = "/index.html" # 如果不是以py结尾的文件,认为是普通的文件 if not file_name.endswith(".py"): # 读取文件数据 try: f = open(self.documents_root+file_name, "rb") except: response_body = "file not found, 请输入正确的url" response_header = "HTTP/1.1 404 not found\r\n" response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n" response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body)) response_header += "\r\n" response = response_header + response_body # 将header返回给浏览器 client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) else: content = f.read() f.close() response_body = content response_header = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body)) response_header += "\r\n" # 将header返回给浏览器 client_socket.send(response_header.encode('utf-8') + response_body) # 以.py结尾的文件,就认为是浏览需要动态的页面 else: # 准备一个字典,里面存放需要传递给web框架的数据 env = {} # 存web返回的数据 response_body = self.app(env, self.set_response_headers) # 合并header和body response_header = "HTTP/1.1 {status}\r\n".format(status=self.headers[0]) response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n" response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % len(response_body) for temp_head in self.headers[1]: response_header += "{0}:{1}\r\n".format(*temp_head) response = response_header + "\r\n" response += response_body client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) def set_response_headers(self, status, headers): """这个方法,会在 web框架中被默认调用""" response_header_default = [ ("Data", time.ctime()), ("Server", "ItCast-python mini web server") ] # 将状态码/相应头信息存储起来 # [字符串, [xxxxx, xxx2]] self.headers = [status, response_header_default + headers]# 设置静态资源访问的路径g_static_document_root = "./html"# 设置动态资源访问的路径g_dynamic_document_root = "./web"def main(): """控制web服务器整体""" # python3 xxxx.py 7890 if len(sys.argv) == 3: # 获取web服务器的port port = sys.argv[1] if port.isdigit(): port = int(port) # 获取web服务器需要动态资源时,访问的web框架名字 web_frame_module_app_name = sys.argv[2] else: print("运行方式如: python3 xxx.py 7890 my_web_frame_name:application") return print("http服务器使用的port:%s" % port) # 将动态路径即存放py文件的路径,添加到path中,这样python就能够找到这个路径了 sys.path.append(g_dynamic_document_root) ret = re.match(r"([^:]*):(.*)", web_frame_module_app_name) if ret: # 获取模块名 web_frame_module_name = ret.group(1) # 获取可以调用web框架的应用名称 app_name = ret.group(2) # 导入web框架的主模块 web_frame_module = __import__(web_frame_module_name) # 获取那个可以直接调用的函数(对象) app = getattr(web_frame_module, app_name) # print(app) # for test # 启动http服务器 http_server = WSGIServer(port, g_static_document_root, app) # 运行http服务器 http_server.run_forever()if __name__ == "__main__": main()
运行
1. 打开终端,输入以下命令开始服务器
python3 web_server.py my_web:application
2. 打开浏览器
4.mini web框架-1-文件结构
文件结构
├── dynamic ---存放py模块│ └── my_web.py├── templates ---存放模板文件│ ├── center.html│ ├── index.html│ ├── location.html│ └── update.html├── static ---存放静态的资源文件│ ├── css│ │ ├── bootstrap.min.css│ │ ├── main.css│ │ └── swiper.min.css│ └── js│ ├── a.js│ ├── bootstrap.min.js│ ├── jquery-1.12.4.js│ ├── jquery-1.12.4.min.js│ ├── jquery.animate-colors.js│ ├── jquery.animate-colors-min.js│ ├── jquery.cookie.js│ ├── jquery-ui.min.js│ ├── server.js│ ├── swiper.jquery.min.js│ ├── swiper.min.js│ └── zepto.min.js└── web_server.py ---mini web服务器
my_web.py
import timedef application(environ, start_response): status = '200 OK' response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')] start_response(status, response_headers) return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
web_server.py
import selectimport timeimport socketimport sysimport reimport multiprocessingclass WSGIServer(object): """定义一个WSGI服务器的类""" def __init__(self, port, documents_root, app): # 1. 创建套接字 self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) # 2. 绑定本地信息 self.server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) self.server_socket.bind(("", port)) # 3. 变为监听套接字 self.server_socket.listen(128) # 设定资源文件的路径 self.documents_root = documents_root # 设定web框架可以调用的函数(对象) self.app = app def run_forever(self): """运行服务器""" # 等待对方链接 while True: new_socket, new_addr = self.server_socket.accept() # 创建一个新的进程来完成这个客户端的请求任务 new_socket.settimeout(3) # 3s new_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=self.deal_with_request, args=(new_socket,)) new_process.start() new_socket.close() def deal_with_request(self, client_socket): """以长链接的方式,为这个浏览器服务器""" while True: try: request = client_socket.recv(1024).decode("utf-8") except Exception as ret: print("========>", ret) client_socket.close() return # 判断浏览器是否关闭 if not request: client_socket.close() return request_lines = request.splitlines() for i, line in enumerate(request_lines): print(i, line) # 提取请求的文件(index.html) # GET /a/b/c/d/e/index.html HTTP/1.1 ret = re.match(r"([^/]*)([^ ]+)", request_lines[0]) if ret: print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(1)) print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(2)) file_name = ret.group(2) if file_name == "/": file_name = "/index.html" # 如果不是以py结尾的文件,认为是普通的文件 if not file_name.endswith(".py"): # 读取文件数据 try: f = open(self.documents_root+file_name, "rb") except: response_body = "file not found, 请输入正确的url" response_header = "HTTP/1.1 404 not found\r\n" response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n" response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body)) response_header += "\r\n" response = response_header + response_body # 将header返回给浏览器 client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) else: content = f.read() f.close() response_body = content response_header = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body)) response_header += "\r\n" # 将header返回给浏览器 client_socket.send(response_header.encode('utf-8') + response_body) # 以.py结尾的文件,就认为是浏览需要动态的页面 else: # 准备一个字典,里面存放需要传递给web框架的数据 env = dict() # 存web返回的数据 response_body = self.app(env, self.set_response_headers) # 合并header和body response_header = "HTTP/1.1 {status}\r\n".format(status=self.headers[0]) response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n" response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % len(response_body) for temp_head in self.headers[1]: response_header += "{0}:{1}\r\n".format(*temp_head) response = response_header + "\r\n" response += response_body client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) def set_response_headers(self, status, headers): """这个方法,会在 web框架中被默认调用""" response_header_default = [ ("Data", time.time()), ("Server", "ItCast-python mini web server") ] # 将状态码/相应头信息存储起来 # [字符串, [xxxxx, xxx2]] self.headers = [status, response_header_default + headers]# 设置静态资源访问的路径g_static_document_root = "./static"# 设置动态资源访问的路径g_dynamic_document_root = "./dynamic"def main(): """控制web服务器整体""" # python3 xxxx.py 7890 if len(sys.argv) == 3: # 获取web服务器的port port = sys.argv[1] if port.isdigit(): port = int(port) # 获取web服务器需要动态资源时,访问的web框架名字 web_frame_module_app_name = sys.argv[2] else: print("运行方式如: python3 xxx.py 7890 my_web_frame_name:application") return print("http服务器使用的port:%s" % port) # 将动态路径即存放py文件的路径,添加到path中,这样python就能够找到这个路径了 sys.path.append(g_dynamic_document_root) ret = re.match(r"([^:]*):(.*)", web_frame_module_app_name) if ret: # 获取模块名 web_frame_module_name = ret.group(1) # 获取可以调用web框架的应用名称 app_name = ret.group(2) # 导入web框架的主模块 web_frame_module = __import__(web_frame_module_name) # 获取那个可以直接调用的函数(对象) app = getattr(web_frame_module, app_name) # print(app) # for test # 启动http服务器 http_server = WSGIServer(port, g_static_document_root, app) # 运行http服务器 http_server.run_forever()if __name__ == "__main__": main()
5.mini web框架-2-显示页面
dynamic/my_web.py (更新)
import timeimport ostemplate_root = "./templates"def index(file_name): """返回index.py需要的页面内容""" # return "hahha" + os.getcwd() # for test 路径问题 try: file_name = file_name.replace(".py", ".html") f = open(template_root + file_name) except Exception as ret: return "%s" % ret else: content = f.read() f.close() return contentdef center(file_name): """返回center.py需要的页面内容""" # return "hahha" + os.getcwd() # for test 路径问题 try: file_name = file_name.replace(".py", ".html") f = open(template_root + file_name) except Exception as ret: return "%s" % ret else: content = f.read() f.close() return contentdef application(environ, start_response): status = '200 OK' response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')] start_response(status, response_headers) file_name = environ['PATH_INFO'] if file_name == "/index.py": return index(file_name) elif file_name == "/center.py": return center(file_name) else: return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
web_server.py (更新)
import selectimport timeimport socketimport sysimport reimport multiprocessingclass WSGIServer(object): """定义一个WSGI服务器的类""" def __init__(self, port, documents_root, app): # 1. 创建套接字 self.server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) # 2. 绑定本地信息 self.server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1) self.server_socket.bind(("", port)) # 3. 变为监听套接字 self.server_socket.listen(128) # 设定资源文件的路径 self.documents_root = documents_root # 设定web框架可以调用的函数(对象) self.app = app def run_forever(self): """运行服务器""" # 等待对方链接 while True: new_socket, new_addr = self.server_socket.accept() # 创建一个新的进程来完成这个客户端的请求任务 new_socket.settimeout(3) # 3s new_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=self.deal_with_request, args=(new_socket,)) new_process.start() new_socket.close() def deal_with_request(self, client_socket): """以长链接的方式,为这个浏览器服务器""" while True: try: request = client_socket.recv(1024).decode("utf-8") except Exception as ret: print("========>", ret) client_socket.close() return # 判断浏览器是否关闭 if not request: client_socket.close() return request_lines = request.splitlines() for i, line in enumerate(request_lines): print(i, line) # 提取请求的文件(index.html) # GET /a/b/c/d/e/index.html HTTP/1.1 ret = re.match(r"([^/]*)([^ ]+)", request_lines[0]) if ret: print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(1)) print("正则提取数据:", ret.group(2)) file_name = ret.group(2) if file_name == "/": file_name = "/index.html" # 如果不是以py结尾的文件,认为是普通的文件 if not file_name.endswith(".py"): # 读取文件数据 try: print(self.documents_root+file_name) f = open(self.documents_root+file_name, "rb") except: response_body = "file not found, 请输入正确的url" response_header = "HTTP/1.1 404 not found\r\n" response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n" response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body)) response_header += "\r\n" response = response_header + response_body # 将header返回给浏览器 client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) else: content = f.read() f.close() response_body = content response_header = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n" response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % (len(response_body)) response_header += "\r\n" # 将header返回给浏览器 client_socket.send(response_header.encode('utf-8') + response_body) # 以.py结尾的文件,就认为是浏览需要动态的页面 else: # 准备一个字典,里面存放需要传递给web框架的数据 env = dict() # ----------更新--------- env['PATH_INFO'] = file_name # 例如 index.py # 存web返回的数据 response_body = self.app(env, self.set_response_headers) # 合并header和body response_header = "HTTP/1.1 {status}\r\n".format(status=self.headers[0]) response_header += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8\r\n" response_header += "Content-Length: %d\r\n" % len(response_body.encode("utf-8")) for temp_head in self.headers[1]: response_header += "{0}:{1}\r\n".format(*temp_head) response = response_header + "\r\n" response += response_body client_socket.send(response.encode('utf-8')) def set_response_headers(self, status, headers): """这个方法,会在 web框架中被默认调用""" response_header_default = [ ("Data", time.time()), ("Server", "ItCast-python mini web server") ] # 将状态码/相应头信息存储起来 # [字符串, [xxxxx, xxx2]] self.headers = [status, response_header_default + headers]# 设置静态资源访问的路径g_static_document_root = "./static"# 设置动态资源访问的路径g_dynamic_document_root = "./dynamic"def main(): """控制web服务器整体""" # python3 xxxx.py 7890 if len(sys.argv) == 3: # 获取web服务器的port port = sys.argv[1] if port.isdigit(): port = int(port) # 获取web服务器需要动态资源时,访问的web框架名字 web_frame_module_app_name = sys.argv[2] else: print("运行方式如: python3 xxx.py 7890 my_web_frame_name:app") return print("http服务器使用的port:%s" % port) # 将动态路径即存放py文件的路径,添加到path中,这样python就能够找到这个路径了 sys.path.append(g_dynamic_document_root) ret = re.match(r"([^:]*):(.*)", web_frame_module_app_name) if ret: # 获取模块名 web_frame_module_name = ret.group(1) # 获取可以调用web框架的应用名称 app_name = ret.group(2) # 导入web框架的主模块 web_frame_module = __import__(web_frame_module_name) # 获取那个可以直接调用的函数(对象) app = getattr(web_frame_module, app_name) # print(app) # for test # 启动http服务器 http_server = WSGIServer(port, g_static_document_root, app) # 运行http服务器 http_server.run_forever()if __name__ == "__main__": main()
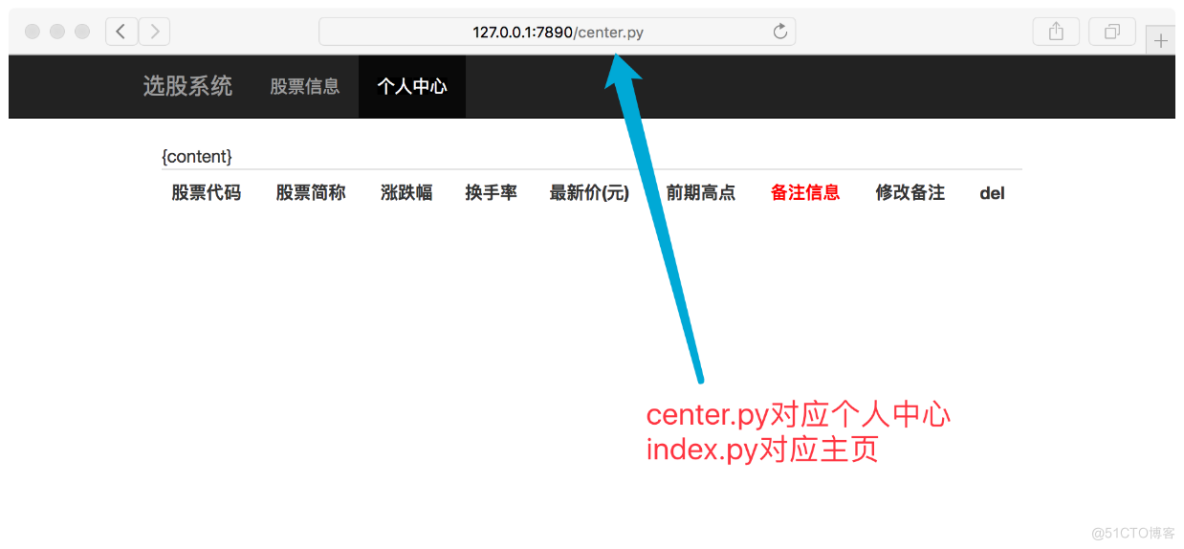
浏览器打开看效果
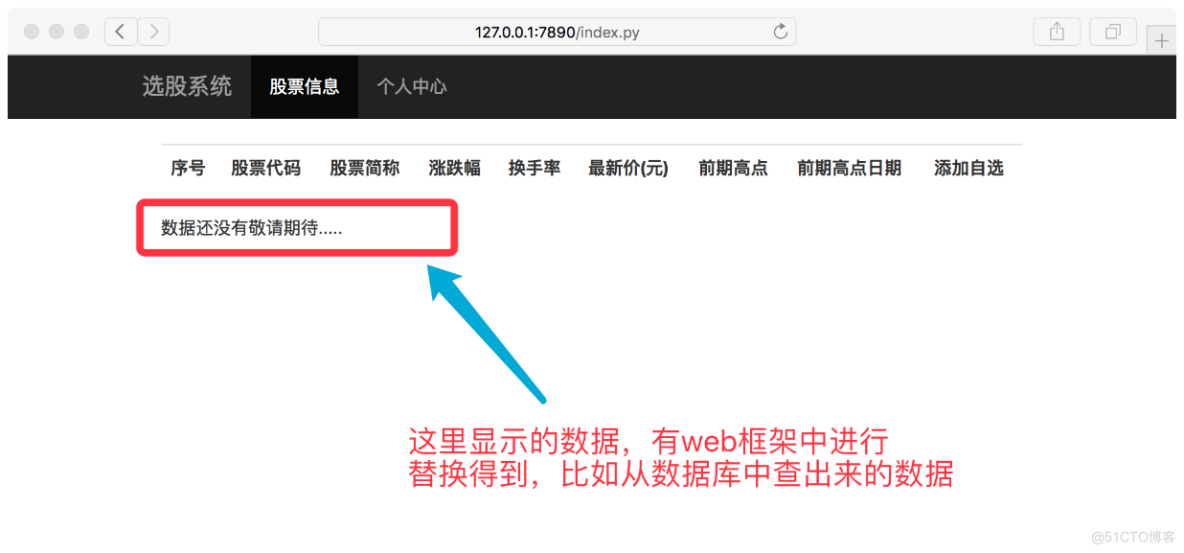
6.mini web框架-3-替换模板
dynamic/my_web.py
import timeimport osimport retemplate_root = "./templates"def index(file_name): """返回index.py需要的页面内容""" # return "hahha" + os.getcwd() # for test 路径问题 try: file_name = file_name.replace(".py", ".html") f = open(template_root + file_name) except Exception as ret: return "%s" % ret else: content = f.read() f.close() # --------更新------- data_from_mysql = "数据还没有敬请期待...." content = re.sub(r"\{%content%\}", data_from_mysql, content) return contentdef center(file_name): """返回center.py需要的页面内容""" # return "hahha" + os.getcwd() # for test 路径问题 try: file_name = file_name.replace(".py", ".html") f = open(template_root + file_name) except Exception as ret: return "%s" % ret else: content = f.read() f.close() # --------更新------- data_from_mysql = "暂时没有数据,,,,~~~~(>_<)~~~~ " content = re.sub(r"\{%content%\}", data_from_mysql, content) return contentdef application(environ, start_response): status = '200 OK' response_headers = [('Content-Type', 'text/html')] start_response(status, response_headers) file_name = environ['PATH_INFO'] if file_name == "/index.py": return index(file_name) elif file_name == "/center.py": return center(file_name) else: return str(environ) + '==Hello world from a simple WSGI application!--->%s\n' % time.ctime()
浏览器打开看效果