一.包装类 1.概念 包装类是将基本类型封装到一个类中,包含属性和方法,方便对象操作 包装类位于java.lang包中 2.转换 包装类与基本数据类型 包装类是将基本数据类型封装成一个类,
一.包装类
1.概念
- 包装类是将基本类型封装到一个类中,包含属性和方法,方便对象操作
- 包装类位于java.lang包中
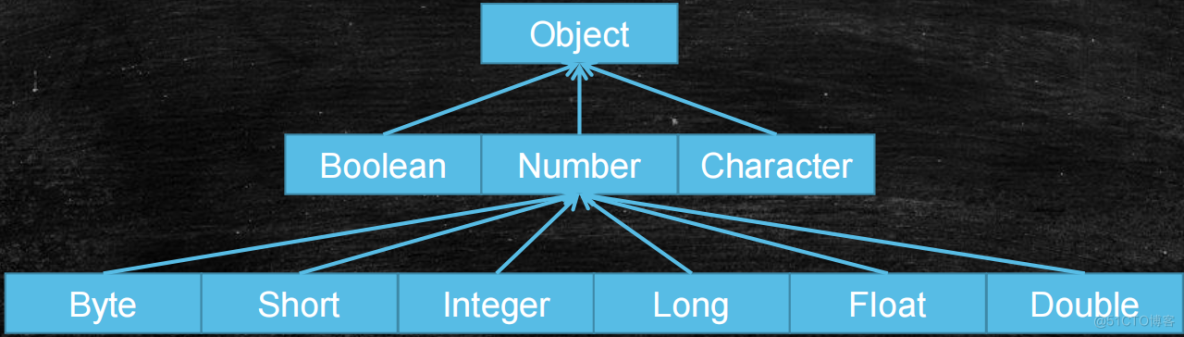
2.转换
包装类与基本数据类型
包装类是将基本数据类型封装成一个类,包含属性和方法
使用
在使用过程中,会涉及到自动装箱和自动拆箱
- 装箱:将基本数据类型转换成包装类
- 基本类型就自动地封装到与它相同类型的包装中,如:
- Integer i = 100;
- 本质上,编译器编译时为我们添加了:
- Integer i = Integer.valueOf(100);
- 拆箱:将包装类转换成基本数据类型
- 包装类对象自动转换成基本类型数据。如:
- int a = new Integer(100);
- 本质上,编译器编译时为我们添加了:
- – int a = new Integer(100).intValue();
案例
// int i =100;// Integer i1 = 100;// Integer i2 = 100;// Integer i3 = 200;// Integer i4 = 200;// System.out.println(i1==i2);// System.out.println(i3==i4);// 结果//true//false看valueOf的实现
值在-128---127之间返回相同Integer
超过这个范围后就返回new Integer(i);
// Double d1 = 1.0;// Double d2 = 1.0;// Double d3 = 2.0;// Double d4 = 2.0;// System.out.println(d1==d2);// System.out.println(d3==d4);// 结果//false//false都返回new
二.String
注意:常量池在1.7之后放置在了堆空间之中
字符串的使用:
1.创建
2.字符串的本质
3.常用方法
- char charAt(int index)
- 返回字符串中第index个字符。
- boolean equals(String other)
- 如果字符串与other相等,返回true
- boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String other)
- 如果字符串与other相等(忽略大小写),则返回true
- int indexOf(String str) lastIndexOf(String str,int idx)
- int length()
- 返回字符串的长度。
- String replace(char oldChar,char newChar)
- 返回一个新串,它是通过用 newChar 替换此字符串中出现的所有oldChar而生成的
- boolean startsWith(String prefix)
- 如果字符串以prefix开始,则返回true
- boolean endsWith(String prefix)
- 如果字符串以prefix结尾,则返回true
- String substring(int beginIndex)
- String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex)
- 返回一个新字符串,该串包含从原始字符串beginIndex到串尾戒endIndex-1的所有字符
- String toLowerCase()
- 返回一个新字符串,该串将原始字符串中的所有大写字母改成小写字母
- String toUpperCase()
- 返回一个新字符串,该串将原始字符串中的所有小写字母改成大写字母
- String trim()
- 返回一个新字符串,该串删除了原始字符串头部和尾部的空格
三.StringBuffer类与StringBuilder类
可变字符串
StringBuffer:线程安全,效率低
StringBuilder: 线程不安全,效率高
public class StringBufferDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(); stringBuffer.append(1).append(1.234).append("abc").append(true); System.out.println(stringBuffer);//11.234abctrue System.out.println(stringBuffer.length());//13 System.out.println(stringBuffer.capacity());//16 StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); stringBuilder.append("123").append(1).append(false); System.out.println(stringBuilder); }}四.时间处理相关类
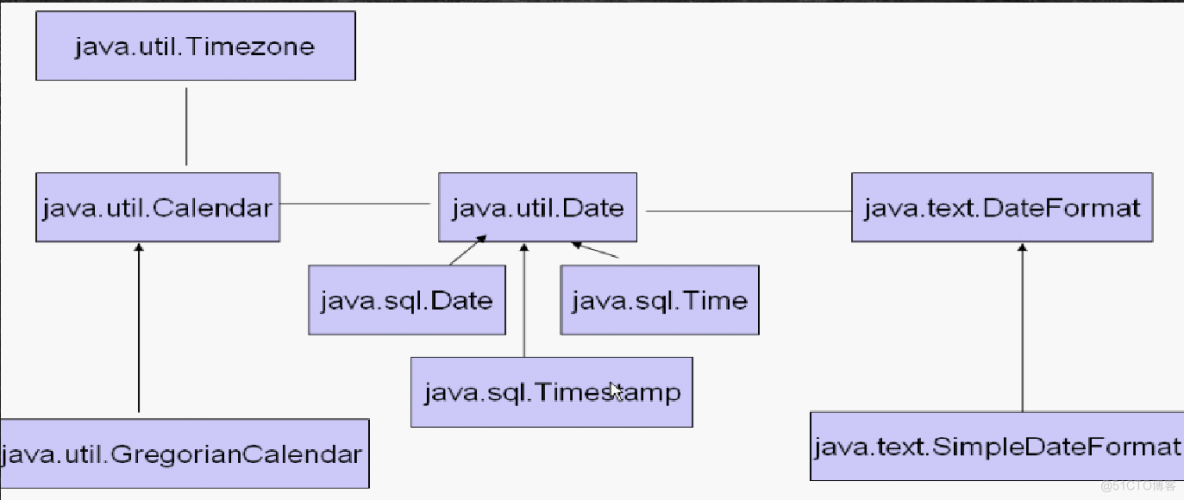
五.Math类
public class MathDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Math.abs(-1)); System.out.println(Math.sqrt(2)); System.out.println(Math.ceil(-3.14));//向上取整 System.out.println(Math.floor(-3.14));//向下取整 System.out.println(Math.pow(2,3));//次方 }}六.枚举类
枚举指由一组固定的常量组成的类型public enum Gender { 男,女}1. 只能够取特定值中的一个
2. 使用enum关键字
3. 所有的枚举类型隐性地继承自 java.lang.Enum。(枚举实质上还是类!而每个被枚举的成员实质就是一个枚举类型的实例,他们默认都是public static final的。可以直接通过枚举类型名直接使用它们。)
public enum EventEnum { LAUNCH("launch"),PAGEVIEW("pageview"),EVENT("event"); EventEnum(String name){ this.name = name; } private String name; public void show(){ System.out.println(this.name); EventEnum[] ee = values(); for(int i = 0;i<ee.length;i++){ System.out.println(ee[i]); } }}public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { EventEnum ee = EventEnum.LAUNCH; ee.show(); String name = EventEnum.PAGEVIEW.name(); System.out.println(name); }}