前言
SpringBoot1.x只区分web环境和非web环境,而在2.x版本中引入了Reactive环境,即响应式环境.那么现在SpringBoot支持三种环境: Servlet的web环境、Reactive的web环境以及非web环境。90%以上的公司使用的是Servlet的web环境,而该环境默认使用的是tomcat容器,本章内容主要就是介绍Servlet容器启动流程。
Tomcat 是什么
Tomcat 是由 Apache 开发的一个 Servlet 容器,实现了对 Servlet 和 JSP 的支持,并提供了作为Web服务器的一些特有功能,如Tomcat管理和控制平台、安全域管理和Tomcat阀等。
由于 Tomcat 本身也内含了一个 HTTP 服务器,它也可以被视作一个单独的 Web 服务器。但是,不能将 Tomcat 和 Apache HTTP 服务器混淆,Apache HTTP 服务器是一个用 C 语言实现的 HTTP Web 服务器;这两个 HTTP web server 不是捆绑在一起的。Tomcat 包含了一个配置管理工具,也可以通过编辑XML格式的配置文件来进行配置。
容器架构
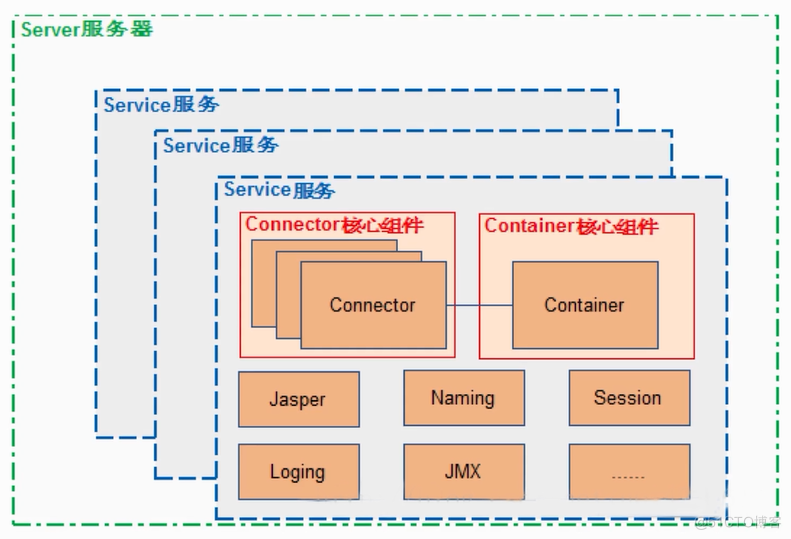
容器处理
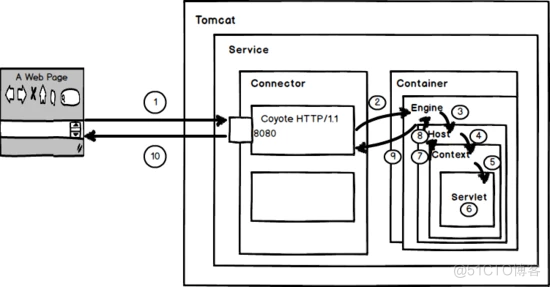
启动流程解析
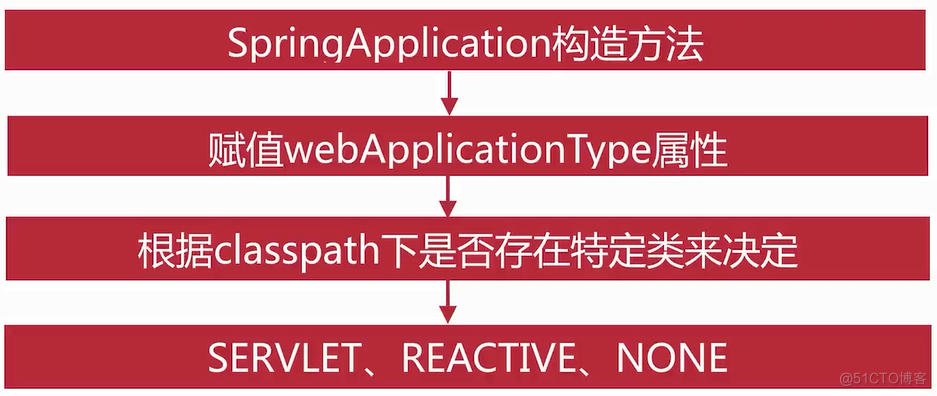
在SpringApplication.run(Application.class,args)里面会构造一个SpringApplication对象,进入其构造函数中
public class SpringApplication { private WebApplicationType webApplicationType; public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) { this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader; Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null"); this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources)); //webApplicationType属性决定了后续容器启动是servlet还是reactive this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath(); setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); } } public enum WebApplicationType { /** * The application should not run as a web application and should not start an * embedded web server. */ NONE, /** * The application should run as a servlet-based web application and should start an * embedded servlet web server. */ SERVLET, /** * The application should run as a reactive web application and should start an * embedded reactive web server. */ REACTIVE; private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet", "org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" }; private static final String WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework." + "web.servlet.DispatcherServlet"; private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org." + "springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler"; private static final String JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer"; private static final String SERVLET_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext"; private static final String REACTIVE_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.ReactiveWebApplicationContext"; //通过判断Classpath路径下是否存在某些特定的类,来决定当前是什么样的环境 static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() { if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) { return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE; } for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) { if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) { return WebApplicationType.NONE; } } return WebApplicationType.SERVLET; } }在SpringApplication的run方法中,context = createApplicationContext()代表创建应用上下文,其就是根据属性webApplicationType来构造什么类
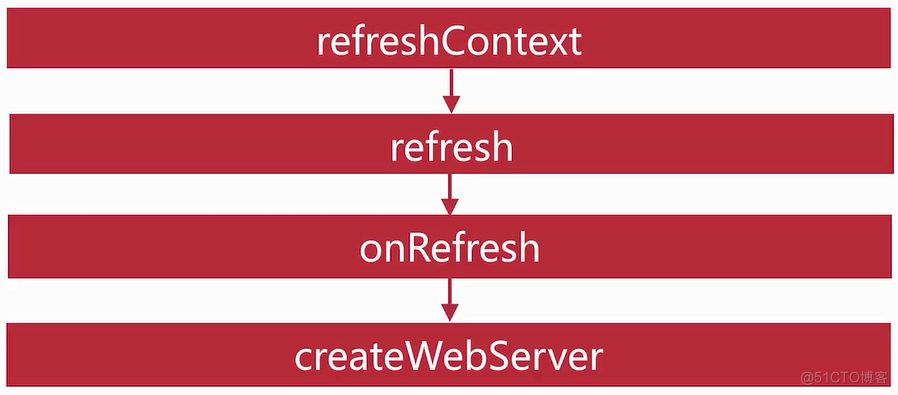
public class SpringApplication { /** * The class name of application context that will be used by default for non-web * environments. */ public static final String DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.context." + "annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext"; /** * The class name of application context that will be used by default for web * environments. */ public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot." + "web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext"; /** * The class name of application context that will be used by default for reactive web * environments. */ public static final String DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework." + "boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext"; public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { ...... try { ...... //创建应用上下文 context = createApplicationContext(); ...... } catch (Throwable ex) { ...... } ...... return context; } protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass; if (contextClass == null) { try { switch (this.webApplicationType) { case SERVLET: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; case REACTIVE: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); break; default: contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS); } } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable create a default ApplicationContext, " + "please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex); } } return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); } }servlet容器启动是在refreshContext(context)方法当中,该方法最终会调用AbstractApplicationContext类中的refresh()方法,该方法会调用onRefresh()方法
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { refresh(context); if (this.registerShutdownHook) { try { context.registerShutdownHook(); } catch (AccessControlException ex) { // Not allowed in some environments. } } } @Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { ...... try { ...... // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); ...... } catch (BeansException ex) { ...... } finally { ...... } } }onRefresh()方法由子类实现,根据不同的应用上下文去调用不同的方法,这里为Servlet容器环境,所以调用ServletWebServerApplicationContext类中的onRefresh()方法
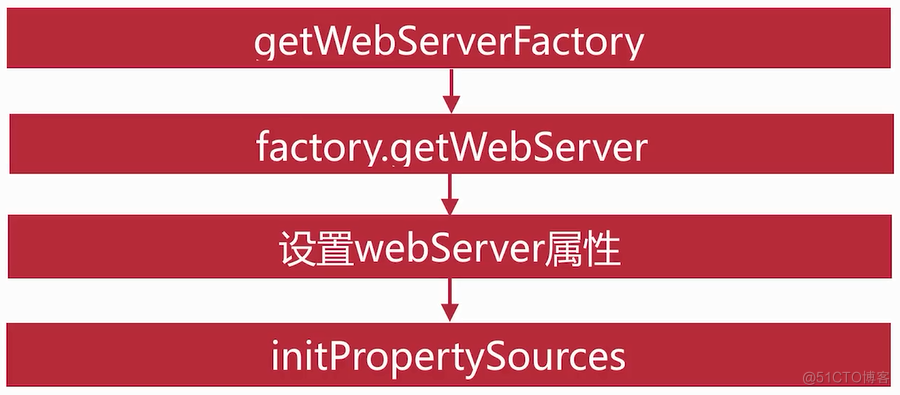
public class ServletWebServerApplicationContext extends GenericWebApplicationContext implements ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext { @Override protected void onRefresh() { super.onRefresh(); try { //构建web服务器 createWebServer(); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex); } } private void createWebServer() { // 刚开始这两个属性都为null WebServer webServer = this.webServer; ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext(); if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) { // 走到这步获取WebServerFactory ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory(); //获取WebServerFactory的具体实现之后,调用getWebServer获取一个具体的WebServer, //默认调用TomcatServletWebServerFactory中的getWebServer()方法 this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer()); } else if (servletContext != null) { try { getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext); } catch (ServletException ex) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex); } } initPropertySources(); } protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() { // Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy // 默认返回只有一个,tomcatServletWebServerFactory String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class); if (beanNames.length == 0) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing " + "ServletWebServerFactory bean."); } if (beanNames.length > 1) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple " + "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames)); } // 获得BeanFactory后调用getBean创建单例bean return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class); } } public class TomcatServletWebServerFactory extends AbstractServletWebServerFactory implements ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory, ResourceLoaderAware { // 调用此方法创建webServer @Override public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) { // 创建一个tomcat Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); // 设置基础目录等属性 File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat"); tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath()); Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol); tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector); customizeConnector(connector); tomcat.setConnector(connector); tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false); configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine()); for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) { tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector); } prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers); return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat); } protected TomcatWebServer getTomcatWebServer(Tomcat tomcat) { // 这步就创建一个TomcatWebServer,里面还会做一些事情...... return new TomcatWebServer(tomcat, getPort() >= 0); } }接着看initPropertySources()方法
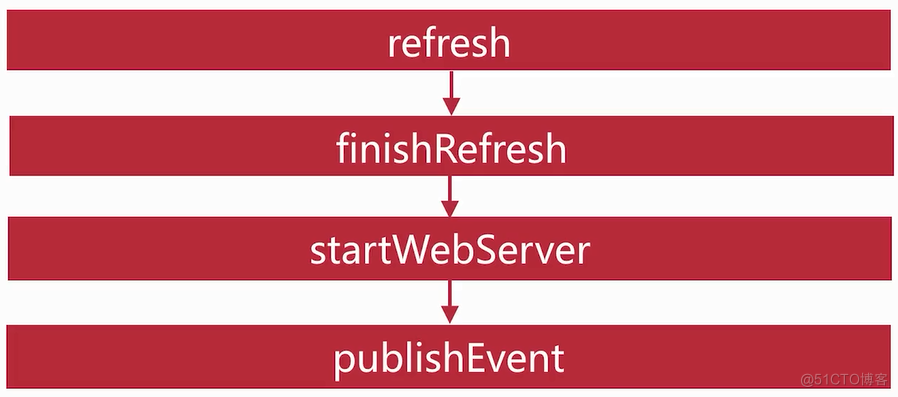
protected void initPropertySources() { ConfigurableEnvironment env = this.getEnvironment(); if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) { ((ConfigurableWebEnvironment)env).initPropertySources(this.servletContext, (ServletConfig)null); } } public void initPropertySources(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) { WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(this.getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig); } public static void initServletPropertySources(MutablePropertySources sources, @Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) { Assert.notNull(sources, "'propertySources' must not be null"); String name = "servletContextInitParams"; // 判断servletContext不为null且包含这个servletContextInitParams属性集 if (servletContext != null && sources.contains(name) && sources.get(name) instanceof StubPropertySource) { // 封装一个ServletContextPropertySource属性集替换原有的 sources.replace(name, new ServletContextPropertySource(name, servletContext)); } name = "servletConfigInitParams"; // servletConfig默认为null if (servletConfig != null && sources.contains(name) && sources.get(name) instanceof StubPropertySource) { sources.replace(name, new ServletConfigPropertySource(name, servletConfig)); } }这样就完成了webServer即Tomcat服务器的创建 在进入AbstractApplicationContext中refresh()方法中的finishRefresh()方法中,该方法会根据web容器的环境进行调用,这里会进入ServletWebServerApplicationContext类中的finishRefresh()方法中
@Override protected void finishRefresh() { super.finishRefresh(); //启动WebServer WebServer webServer = startWebServer(); if (webServer != null) { // 发布Server初始完毕事件 publishEvent(new ServletWebServerInitializedEvent(webServer, this)); } } private WebServer startWebServer() { WebServer webServer = this.webServer; if (webServer != null) { webServer.start(); } return webServer; } @Override public void start() throws WebServerException { synchronized (this.monitor) { if (this.started) { return; } try { addPreviouslyRemovedConnectors(); Connector connector = this.tomcat.getConnector(); if (connector != null && this.autoStart) { performDeferredLoadOnStartup(); } checkThatConnectorsHaveStarted(); this.started = true; logger.info("Tomcat started on port(s): " + getPortsDescription(true) + " with context path '" + getContextPath() + "'"); } catch (ConnectorStartFailedException ex) { stopSilently(); throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { throw new WebServerException("Unable to start embedded Tomcat server", ex); } finally { Context context = findContext(); ContextBindings.unbindClassLoader(context, context.getNamingToken(), getClass().getClassLoader()); } } }启动前准备
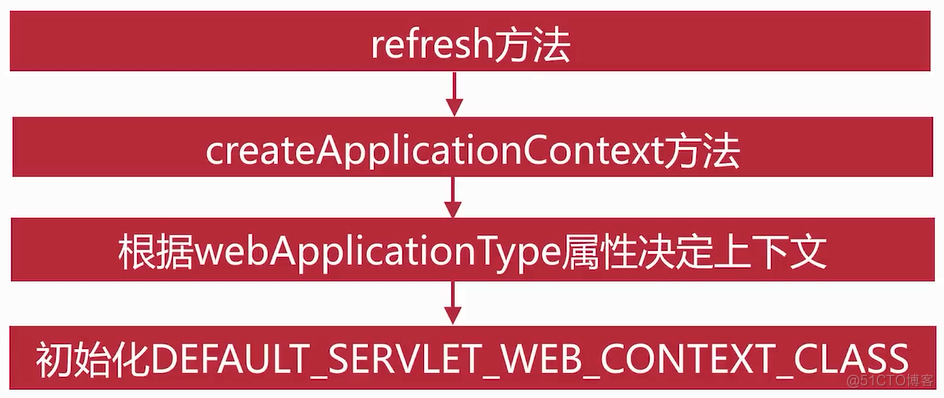
webServer创建入口
servlet启动
web容器工厂类加载解析
默认返回只有一个TomcatServletWebServerFactory,那么这个bean定义什么时候被加载到容器中
String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class);它是通过ConfigurationClassParser类中的parse方法,通过@Import注解导入到容器中的
class ConfigurationClassParser { public void parse(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> configCandidates) { for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : configCandidates) { BeanDefinition bd = holder.getBeanDefinition(); try { if (bd instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { parse(((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) bd).getMetadata(), holder.getBeanName()); } else if (bd instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition && ((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).hasBeanClass()) { parse(((AbstractBeanDefinition) bd).getBeanClass(), holder.getBeanName()); } else { parse(bd.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName()); } } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Failed to parse configuration class [" + bd.getBeanClassName() + "]", ex); } } // 这边会处理@Import注解导入的配置类 this.deferredImportSelectorHandler.process(); } } class ConfigurationClassParser { private class DeferredImportSelectorHandler { public void process() { List<DeferredImportSelectorHolder> deferredImports = this.deferredImportSelectors; this.deferredImportSelectors = null; try { if (deferredImports != null) { DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler handler = new DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler(); deferredImports.sort(DEFERRED_IMPORT_COMPARATOR); // 排序并依此遍历调用register方法 deferredImports.forEach(handler::register); handler.processGroupImports(); } } finally { this.deferredImportSelectors = new ArrayList<>(); } } } } class ConfigurationClassParser { private class DeferredImportSelectorGroupingHandler { private final Map<Object, DeferredImportSelectorGrouping> groupings = new LinkedHashMap<>(); private final Map<AnnotationMetadata, ConfigurationClass> configurationClasses = new HashMap<>(); public void register(DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport) { // 这个返回的Selector就是AutoConfigurationImportSelector,这也是@SpringBootApplication上通过@Import注解 // 导入的Selector. getImportGroup返回的是AutoConfigurationGroup.class Class<? extends Group> group = deferredImport.getImportSelector() .getImportGroup(); // computeIfAbsent就是不存在就创建,这边也是创建一个grouping DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping = this.groupings.computeIfAbsent( (group != null ? group : deferredImport), key -> new DeferredImportSelectorGrouping(createGroup(group))); // this.deferredImports.add(deferredImport); // 加入到了deferredImports中,List<deferredimportselectorholder> deferredImports = new ArrayList<>() grouping.add(deferredImport); // 放入到configurationClasses中 this.configurationClasses.put(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(), deferredImport.getConfigurationClass()); } } }deferredImports.forEach(handler::register),这边主要是构造了一个grouping,在下一步进行处理handler.processGroupImports()
public void processGroupImports() { for (DeferredImportSelectorGrouping grouping : this.groupings.values()) { // 下面先分析这个getImports方法 grouping.getImports().forEach(entry -> { ConfigurationClass configurationClass = this.configurationClasses.get( entry.getMetadata()); try { processImports(configurationClass, asSourceClass(configurationClass), asSourceClasses(entry.getImportClassName()), false); } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Failed to process import candidates for configuration class [" + configurationClass.getMetadata().getClassName() + "]", ex); } }); } } public Iterable<Group.Entry> getImports() { // 这边的deferredImports是通过grouping.add(deferredImport)添加进去的 for (DeferredImportSelectorHolder deferredImport : this.deferredImports) { this.group.process(deferredImport.getConfigurationClass().getMetadata(), deferredImport.getImportSelector()); } return this.group.selectImports(); } // 两个参数如下图所示,annotationMetadata是主配置类上面的注解 @Override public void process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector) { Assert.state(deferredImportSelector instanceof AutoConfigurationImportSelector, () -> String.format("Only %s implementations are supported, got %s", AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class.getSimpleName(), deferredImportSelector.getClass().getName())); // 下面先分析下这个getAutoConfigurationEntry方法 AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = ((AutoConfigurationImportSelector) deferredImportSelector) .getAutoConfigurationEntry(getAutoConfigurationMetadata(), annotationMetadata); this.autoConfigurationEntries.add(autoConfigurationEntry); for (String importClassName : autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()) { // 接着依次遍历放入到这个map中,Map<string, annotationmetadata> entries = new LinkedHashMap() this.entries.putIfAbsent(importClassName, annotationMetadata); } } 这边就到了AutoConfigurationImportSelector类的getAutoConfigurationEntry方法中
这边就到了AutoConfigurationImportSelector类的getAutoConfigurationEntry方法中
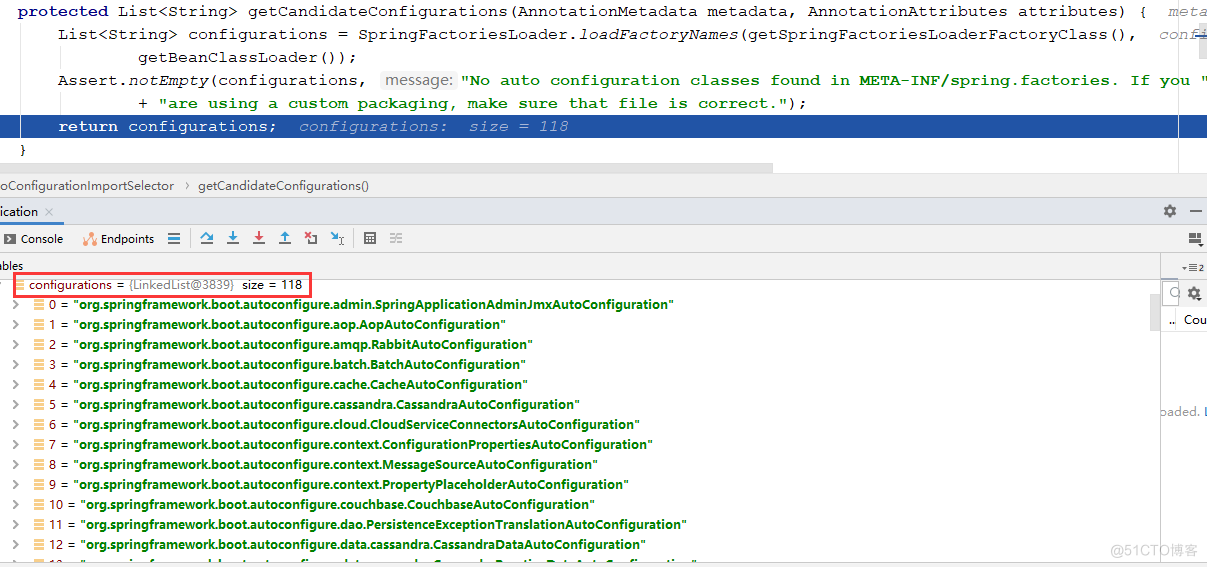 通过filter方法过滤,过滤完发现只有22个了
通过filter方法过滤,过滤完发现只有22个了
过滤完之后会发现此时List<String> configurations集合中有29个,其中有一个org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration
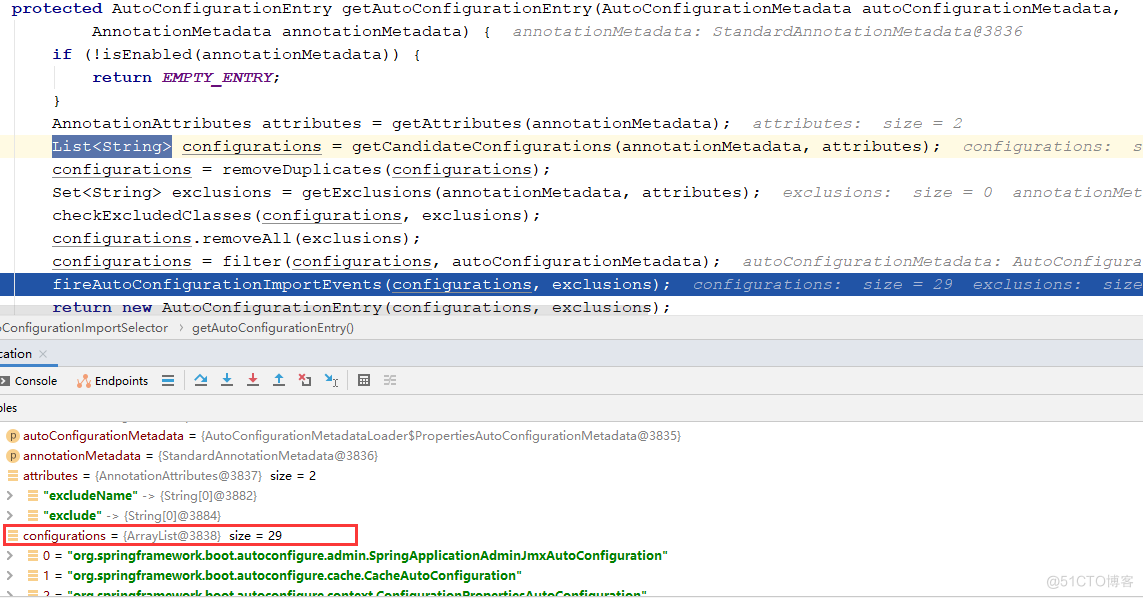
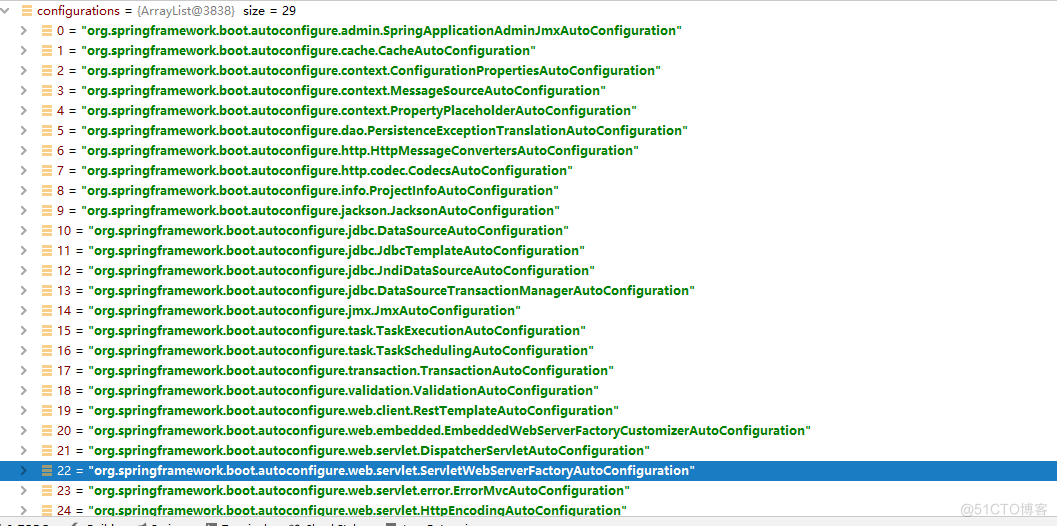
到此为止grouping.getImports方法分析完了,它是返回之前加载的29个自动配置类

web容器个性化配置解析
属性注入
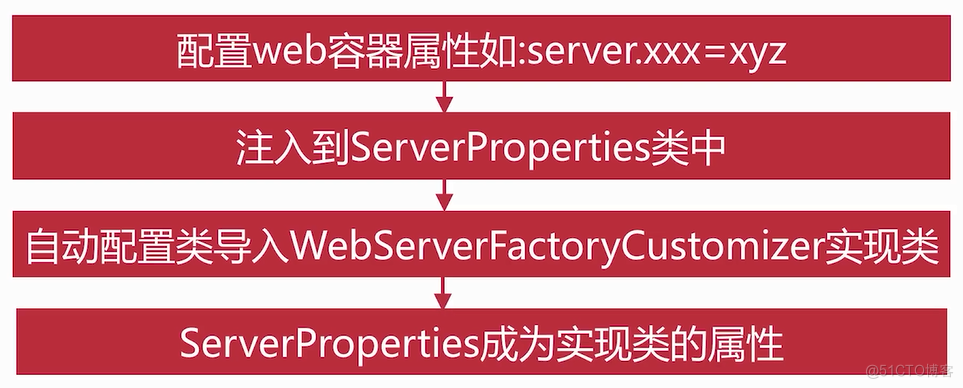
工厂类初始化
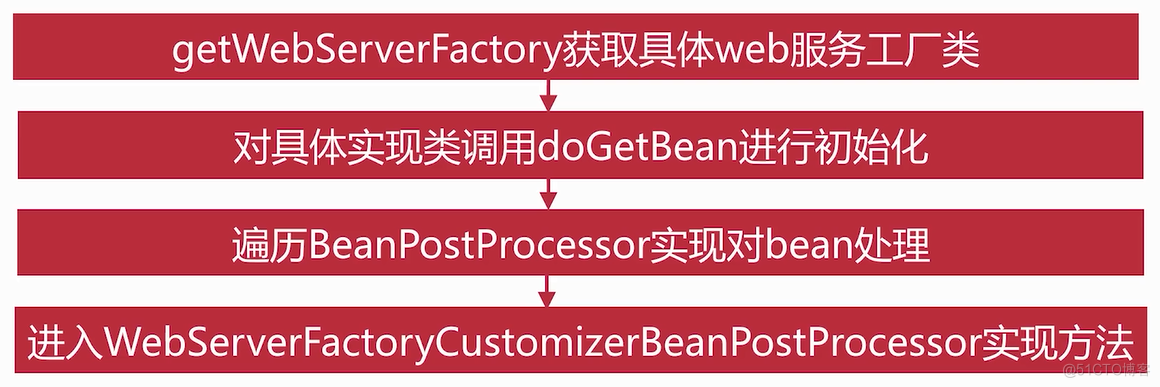
BeanPostProcessor方法实现
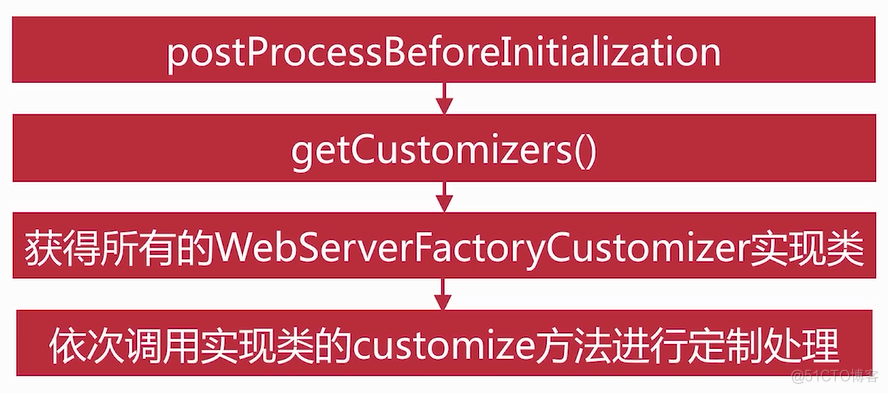
定制化流程
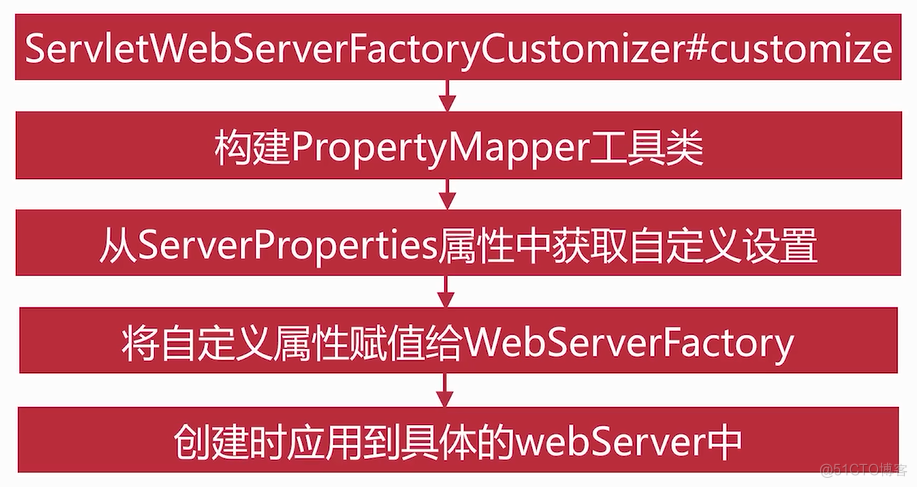
入口,onRefresh方法中会创建webServer,走到这里
public class ServletWebServerApplicationContext extends GenericWebApplicationContext implements ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext { protected ServletWebServerFactory getWebServerFactory() { // Use bean names so that we don't consider the hierarchy // 默认返回只有一个,tomcatServletWebServerFactory String[] beanNames = getBeanFactory().getBeanNamesForType(ServletWebServerFactory.class); if (beanNames.length == 0) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to missing " + "ServletWebServerFactory bean."); } if (beanNames.length > 1) { throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start ServletWebServerApplicationContext due to multiple " + "ServletWebServerFactory beans : " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(beanNames)); } // 调用getBean创建工厂类实例,这边会调用getBean开始创建bean实例对象 return getBeanFactory().getBean(beanNames[0], ServletWebServerFactory.class); } }在Bean初始化完成之后会遍历BeanFactory中所有的BeanPostProcessor实现,依次调用BeanPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法,在创建Web服务的工厂类的时候也会经历这个步骤,这个方法调用点就在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类中applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()方法
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory implements AutowireCapableBeanFactory { @Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { // 通过断点调试可以发现当中有一个WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (current == null) { return result; } result = current; } return result; } }可以看到postProcessBeforeInitialization方法多个实现中有一个WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor
 点击进入WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor类中的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
点击进入WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor类中的postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
我们在来看下图中第二个定制器,ServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer是怎么注入的呢?
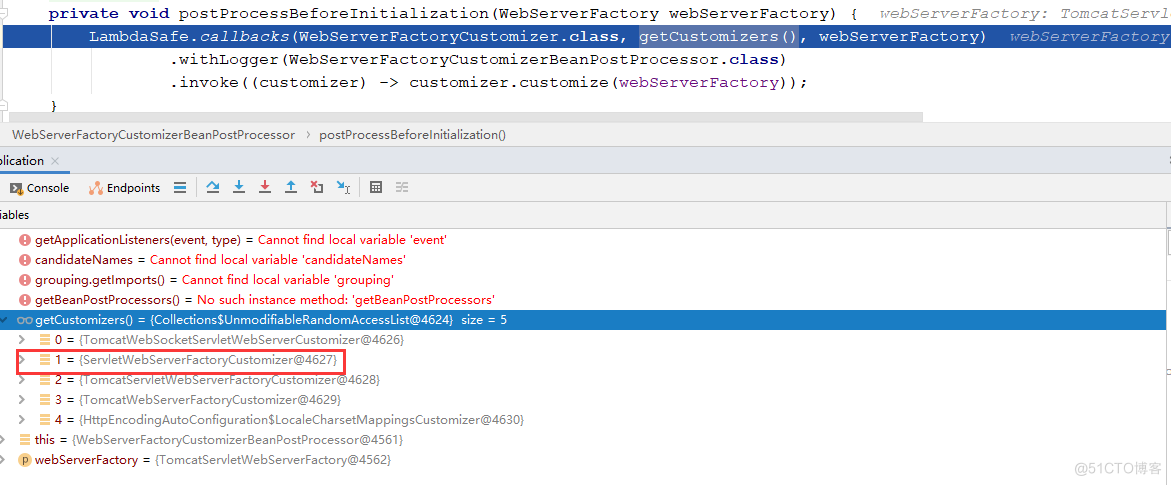
参考: https://my.oschina.net/liwanghong/blog/3168322
https://www.cnblogs.com/hggen/p/6264475.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/jingmoxukong/p/8258837.html
