什么是SpringMVC
SpringMVC是一个基于MVC的web框架,属于Spring中的一个模块,它和Spring不需要通过中间层进行整合就可以一起使用。
SpringMVC框架是以请求为驱动,围绕Servlet设计,将请求发给控制器,然后通过模型对象,分派器来展示请求结果视图。其中核心类是DispatcherServlet,它是一个Servlet,顶层是实现的Servlet接口。
SpringMVC请求处理流程
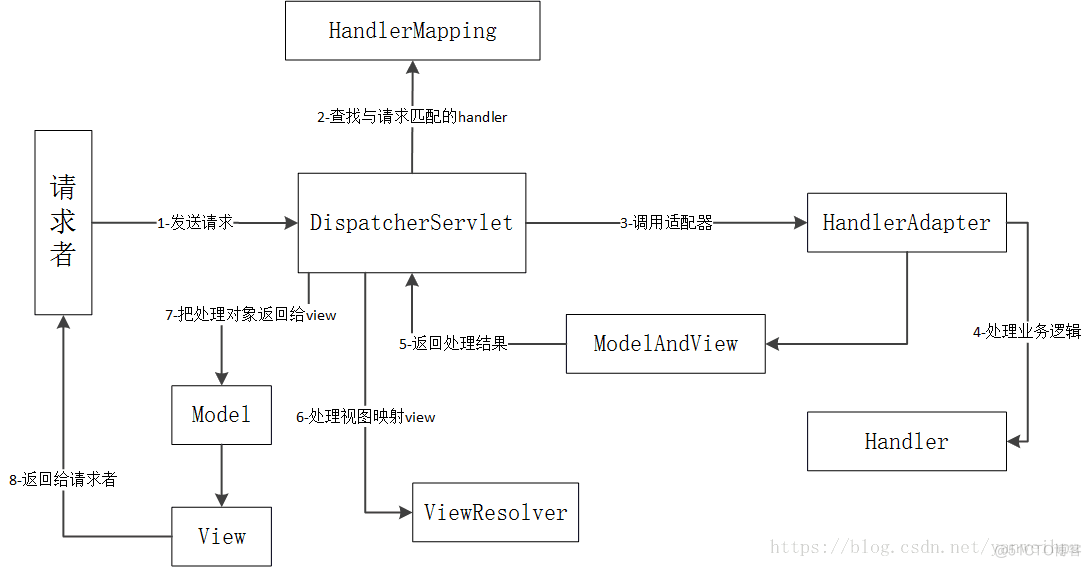 流程说明:
流程说明:
-
1、客户端(浏览器)发送请求,直接请求到DispatcherServlet。
-
2、DispatcherServlet根据请求信息调用HandlerMapping,解析请求对应的Handler。
-
3、解析到对应的Handler后,开始由HandlerAdapter适配器处理。
-
4、HandlerAdapter会根据Handler来调用真正的处理器开处理请求,并处理相应的业务逻辑。
-
5、处理器处理完业务后,会返回一个ModelAndView对象,Model是返回的数据对象,View是个逻辑上的View。
-
6、ViewResolver会根据逻辑View查找实际的View。
-
7、DispaterServlet把返回的Model传给View。
-
8、通过View返回给请求者(浏览器)
SpringMVC使用

传统的XML配置方式
传统的XML配置方式,需要在webapp/WEB-INF目录下web.xml文件,在文件里面需要配置Context和Servlet,主要是让那个Tomcat Context初始化的时候去初始化Spring容器相关的服务,随后保存在Context实例里面,以供其servlet来使用。
<web-app> <!--上下文参数,在监听器中被使用,实际就是key-value,key=contextConfigLocation写死--> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!--监听器配置,初始化WebApplicationContext--> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!--前端控制器--> <servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springMVC.xml</param-value> </init-param> <!--是启动顺序,让这个Servlet随Servletp容器一起启动。--> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>ContextLoaderListener
ContextLoaderListener可以指定在Web应用程序启动时载入Ioc容器,正是通过ContextLoader来实现的,可以说是Ioc容器的初始化工作。
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener { @Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { //初始化webApplicationCotext initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); } }ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener,其本质是一个Servlet的监听器,Tomcat会优先加载Servlet的监听器组件,以保证在Servlet被创建之前,即Context组件进行初始化的时候,去调用其里面的contextInitialized方法来根据contextConfigLocation去读取并解析Spring容器的配置,去创建并刷新出容器的实例来。
initWebApplicationContext
public class ContextLoader { public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) { //从ServletContext中查找,是否存在以 // WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE为Key的值 if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " + "check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!"); } servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext"); Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that // it is available on ServletContext shutdown. // 创建web上下文,默认是XmlWebApplicationContext if (this.context == null) { this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext); } if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context; // 如果该容器还没有刷新过 if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> // determine parent for root web application context, if any. ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext); cwac.setParent(parent); } // 配置并刷新容器 configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext); } } //将ApplicationContext放入ServletContext中, // 其key为<WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context); ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) { currentContext = this.context; } else if (ccl != null) { //将ApplicationContext放入ContextLoader的全局静态常量Map中, // 其中key为:Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()即当前线程类加载器 currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context); } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } return this.context; } catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex); throw ex; } } }-
该方法会调用configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext)去创建并刷新Spring容器,刷新完成之后,就会将容器的实例保存到Tomcat的Context组件实例里,以供后续要创建出来的DispatcherServlet实例来调用。
-
随后在Servlet里面配置DispatcherServlet,并且给Servlet的contextConfigLocation初始化变量赋值上SpringMVC的配置文件路径,以方便在DispatcherServlet初始化的时候去调用init方法去读取contextConfigLocation里面的配置文件并加载相关的配置。通常情况下会加载RequestMapping标记的类,以及对应的方法和请求路径、请求方法的映射。
注解配置方式
// 完整命名: javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer public interface ServletContainerInitializer { void onStartup(Set<Class<?>> var1, ServletContext var2) throws ServletException; }ServletContainerInitializer 是 Servlet 3.0 新增的一个接口,主要用于在容器启动阶段通过编程风格注册Filter、Servlet以及Listener,以取代通过web.xml配置注册。这样就利于开发内聚的web应用框架。
Servlet3通过SPI的机制允许自定义一个ServletContainerInitializer的实现类,Servlet容器会在启动的时候自动调用实现类的onStartup方法,我们可以在该方法中进行一些Servlet对象的注册。
另外在实现ServletContainerInitializer时还可以通过@HandlesTypes注解定义本实现类希望处理的类型,容器会将当前应用中所有这一类型(继承或者实现)的类放在ServletContainerInitializer接口的集合参数中传递进来。如果不定义处理类型,或者应用中不存在相应的实现类,则集合参数为空。
@HandlesTypes(WebApplicationInitializer.class) public class SpringServletContainerInitializer implements ServletContainerInitializer { @Override public void onStartup(@Nullable Set<Class<?>> webAppInitializerClasses, ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException { List<WebApplicationInitializer> initializers = new LinkedList<>(); // webAppInitializerClasses 就是servlet3.0规范中为我们收集的 WebApplicationInitializer 接口的实现类的class // 从webAppInitializerClasses中筛选并实例化出合格的相应的类 if (webAppInitializerClasses != null) { for (Class<?> waiClass : webAppInitializerClasses) { // Be defensive: Some servlet containers provide us with invalid classes, // no matter what @HandlesTypes says... if (!waiClass.isInterface() && !Modifier.isAbstract(waiClass.getModifiers()) && WebApplicationInitializer.class.isAssignableFrom(waiClass)) { try { initializers.add((WebApplicationInitializer) ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(waiClass).newInstance()); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new ServletException("Failed to instantiate WebApplicationInitializer class", ex); } } } } if (initializers.isEmpty()) { servletContext.log("No Spring WebApplicationInitializer types detected on classpath"); return; } servletContext.log(initializers.size() + " Spring WebApplicationInitializers detected on classpath"); // 这行代码说明我们在实现WebApplicationInitializer可以通过继承Ordered, PriorityOrdered来自定义执行顺序 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(initializers); for (WebApplicationInitializer initializer : initializers) { // 迭代每个initializer实现的方法 initializer.onStartup(servletContext); } } }-
1、通过@HandlesType注解在onStartup方法的参数列表中注入感兴趣的类,即WebApplicationInitializer;
-
2、将WebApplicationInitializer的每个实现类,都新建一个实例,并放入initializers列表中;
-
3、遍历initializers列表,对每个WebApplicationInitializer实例执行其onStartup方法。
WebApplicationInitializer的实现类及其功能
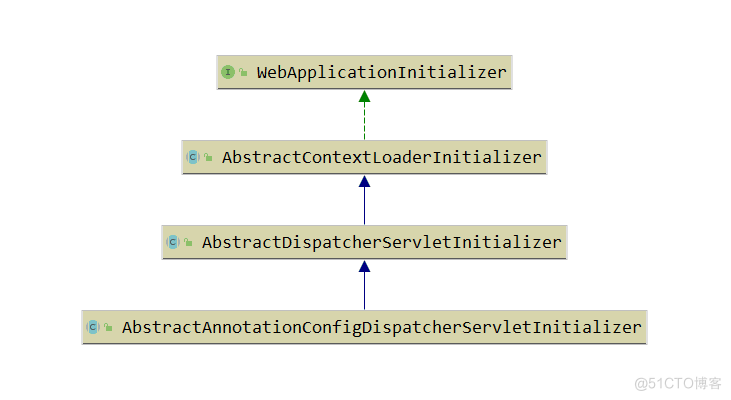
WebApplicationInitializer的实现类有很多,重点看一下AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer
public abstract class AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override @Nullable protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() { Class<?>[] configClasses = getRootConfigClasses(); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) { AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); context.register(configClasses); return context; } else { return null; } } @Override protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() { AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); Class<?>[] configClasses = getServletConfigClasses(); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(configClasses)) { context.register(configClasses); } return context; } @Nullable protected abstract Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses(); @Nullable protected abstract Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses(); }这个类提供了两个方法的实现,以及两个抽象方法供子类继承
-
1、createRootApplicationContext:创建根容器。
-
2、createServletApplicationContext:创建servlet容器。
-
3、getRootConfigClasses:抽象类,用于注册根容器的配置类,相当于spring.xml。
-
4、getServletConfigClasses:抽象的类,用于注册servlet容器的配置类,相当于springmvc.xml。
-
5、它还从AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer类继承了getServletMappings方法,用于注册servlet的映射。
-
6、还从AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer类中继承了getServletFilters方法,用于拦截并处理请求的编码。
因此,我们可以自定义一个WebApplicationInitializer的实现类,继承AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;在servlet容器启动时,会创建spring根容器和servlet容器,代替web.xml配置文件。同时,我们可以看到,在基于注解的springmvc开发中,真正用于代替web.xml的是WebApplicationInitializer,而并不是ServletContainerInitializer,这与本文开头提到的基于注解的servlet开发有些区别。
根容器和servlet容器
- 根容器用于管理@Service、@Repository等业务逻辑层和数据库交互层组件。
- servlet容器用于管理@Controller、视图解析器、拦截器等跟页面处理有关的组件。
使用步骤
-
1、导包或添加依赖:spring-web、spring-webmvc。
-
2、编写数据库访问层、业务逻辑层、控制层等组件,这个跟基于配置文件的springmvc没有区别。
-
3、编写根容器和servlet容器的配置类,这里不需要添加@Configuration注解。
-
4、自定义WebApplicationInitializer,继承AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer。
-
5、在3的实现类中注册根容器和servlet容器的配置类,以及servlet映射。
-
6、在servlet容器中中注册视图解析器、拦截器等组件,用法是使servlet容器配置类实现WebMvcConfigurer接口,然后选择相应的方法进行注册。
添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.6.RELEASE</version> </dependency> compile group: 'org.springframework', name: 'spring-webmvc', version: '5.2.6.RELEASE'自定义springmvc拦截器
/** * 自定义的springmvc拦截器 */ public class CustomedInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { /** * 重写preHandle方法 */ @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("preHandle正在执行..."); return true; } /** * 重写postHandle方法 */ @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("postHandle正在执行..."); } /** * 重写afterCompletion方法 */ @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("afterCompletion正在执行..."); } }SpringRootConfig
根容器的配置类,用于管理数据库访问层、业务逻辑层等组件,相当于spring.xml
@Configuration @ComponentScan("com.yibo.service") public class SpringRootConfig { }MVCConfig
- servlet容器的配置类,用于管理控制层、视图解析器等组件,相当于springmvc.xml
- 可以在其中配置视图解析器、静态资源解析器、拦截器等组件
StartWebApplicationInitializer
自定义的WebApplicationInitializer,用于注册根容器、servlet容器、servlet映射、拦截器、监听器等,相当于web.xml
/** * 自定义web容器启动器 */ public class StartWebApplicationInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { /** * SpringContext中相关的bean * 注册根容器配置类 * @return */ @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class<?>[]{SpringRootConfig.class}; } /** * DispatcherServlet中上下文相关的bean * 注册servlet容器(mvc子容器)配置类 * @return */ @Override protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return new Class<?>[]{MVCConfig.class}; } /** * Servlet请求映射路径 * @return */ @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String[]{"/"}; } /** * 拦截并处理请求的编码 * @return */ @Override protected Filter[] getServletFilters() { CharacterEncodingFilter encodingFilter = new CharacterEncodingFilter(); encodingFilter.setEncoding("UTF-8"); encodingFilter.setForceEncoding(true); return new Filter[]{encodingFilter}; } }参考: https://blog.csdn.net/lqzkcx3/article/details/78507169
https://www.cnblogs.com/dubhlinn/p/10808879.html
