C语言函数大全 本篇介绍C语言函数大全-- w 开头的函数 1. wcsdup 1.1 函数说明 函数声明 函数功能 wchar_t *wcsdup(const wchar_t *str); 用于复制宽字符字符串 参数: str : 待复制的宽字符串 返回
C语言函数大全
本篇介绍C语言函数大全-- w 开头的函数
1. wcsdup
1.1 函数说明
wchar_t *wcsdup(const wchar_t *str);
用于复制宽字符字符串
参数:
- str : 待复制的宽字符串
返回值:
- 如果成功复制,则返回指向该内存块的指针;
- 如果内存分配失败,函数将返回
NULL。
1.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void)
{
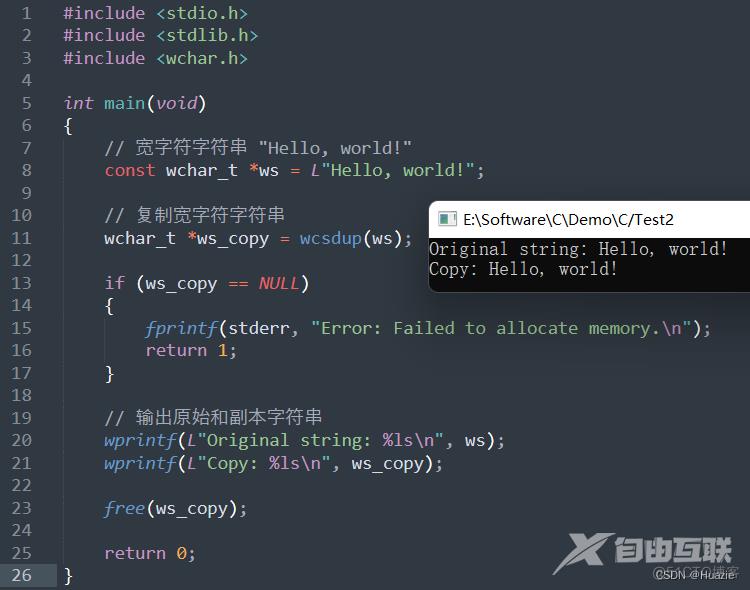
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, world!"
const wchar_t *ws = L"Hello, world!";
// 复制宽字符字符串
wchar_t *ws_copy = wcsdup(ws);
if (ws_copy == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Error: Failed to allocate memory.\n");
return 1;
}
// 输出原始和副本字符串
wprintf(L"Original string: %ls\n", ws);
wprintf(L"Copy: %ls\n", ws_copy);
// 释放由 wcsdup() 函数分配的内存空间
free(ws_copy);
return 0;
}
1.3 运行结果
2. wcsicmp
2.1 函数说明
int wcsicmp(const wchar_t *s1, const wchar_t *s2);
用于比较两个宽字符字符串的大小写不敏感的差异
参数:
- s1 : 待比较的宽字符串1
- s2 : 待比较的宽字符串2
返回值:
- 如果
s1指向的字符串按字典顺序小于s2指向的字符串(忽略大小写),则函数返回一个负整数;- 如果
s1等于s2,则函数返回0;- 如果
s1指向的字符串按字典顺序大于s2指向的字符串(忽略大小写),则函数返回一个正整数。
2.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void)
{
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, huazie!"
const wchar_t *ws1 = L"Hello, huazie!";
// 宽字符字符串 "hello, HUAZIE!"
const wchar_t *ws2 = L"hello, HUAZIE!";
int cmp_result = wcsicmp(ws1, ws2);
// 输出比较结果
if (cmp_result < 0)
{
wprintf(L"%ls is less than %ls.\n", ws1, ws2);
}
else if (cmp_result == 0)
{
wprintf(L"%ls is equal to %ls.\n", ws1, ws2);
}
else
{
wprintf(L"%ls is greater than %ls.\n", ws1, ws2);
}
return 0;
}
2.3 运行结果

3. wcsicoll
3.1 函数说明
int wcsicoll(const wchar_t *s1, const wchar_t *s2);
用于比较两个宽字符字符串的大小写不敏感的差异, 并考虑当前本地环境的语言和排序规则
参数:
- s1 : 待比较的宽字符串1
- s2 : 待比较的宽字符串2
返回值:
- 如果
s1指向的字符串按字典顺序小于s2指向的字符串(忽略大小写),则函数返回一个负整数;- 如果
s1等于s2,则函数返回0;- 如果
s1指向的字符串按字典顺序大于s2指向的字符串(忽略大小写),则函数返回一个正整数。
3.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <locale.h>
int main(void)
{
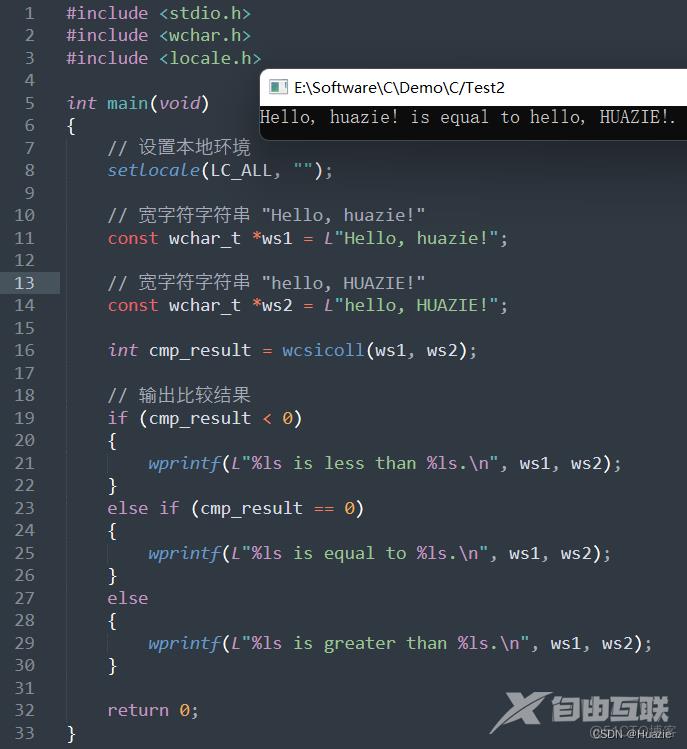
// 设置本地环境
setlocale(LC_ALL, "");
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, world!"
const wchar_t *ws1 = L"Hello, huazie!";
// 宽字符字符串 "hello, WORLD!"
const wchar_t *ws2 = L"hello, HUAZIE!";
int cmp_result = wcsicoll(ws1, ws2);
// 输出比较结果
if (cmp_result < 0)
{
wprintf(L"%ls is less than %ls.\n", ws1, ws2);
}
else if (cmp_result == 0)
{
wprintf(L"%ls is equal to %ls.\n", ws1, ws2);
}
else
{
wprintf(L"%ls is greater than %ls.\n", ws1, ws2);
}
return 0;
}
注意: 在使用
wcsicoll()函数前,需要先调用setlocale()函数设置本地环境。
3.3 运行结果
4. wcslwr
4.1 函数说明
wchar_t *wcslwr(wchar_t *str);
用于将宽字符字符串转换为小写字母形式
参数:
- str : 待转换的宽字符串
4.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void)
{
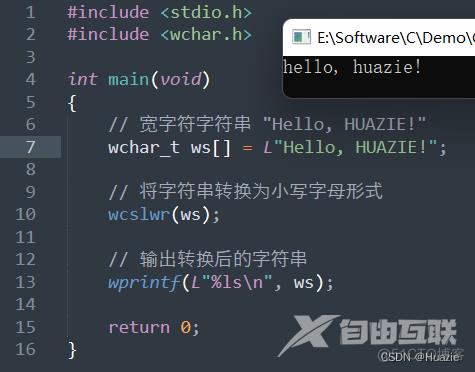
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, HUAZIE!"
wchar_t ws[] = L"Hello, HUAZIE!";
// 将字符串转换为小写字母形式
wcslwr(ws);
// 输出转换后的字符串
wprintf(L"%ls\n", ws);
return 0;
}
4.3 运行结果
5. wcspbrk
5.1 函数说明
wchar_t *wcspbrk(const wchar_t *str, const wchar_t *charset);
用于在宽字符字符串中查找指定字符集中任意一个字符第一次出现的位置
参数:
- str : 要搜索的宽字符字符串
- charset : 要搜索的宽字符集合
wcspbrk()函数会将str指向的宽字符字符串中的每个字符与charset指向的宽字符集合中的字符进行比较,直到找到其中任意一个相同的字符为止。 返回值:
- 如果找到了这样的字符,则函数返回指向该字符的指针;
- 否则,函数返回
NULL。
5.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void)
{
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, huazie!"
const wchar_t *ws = L"Hello, huazie!";
// 查找第一个出现在 "abcd" 中的字符
wchar_t *result = wcspbrk(ws, L"abcd");
if (result == NULL)
{
wprintf(L"No matching character found.\n");
}
else
{
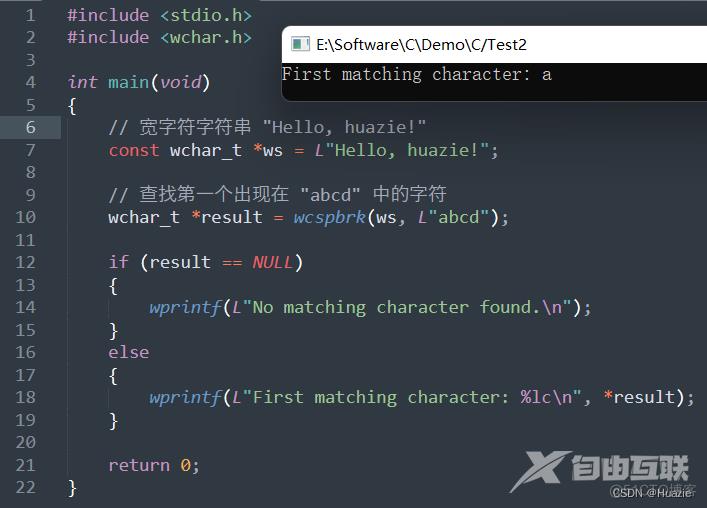
wprintf(L"First matching character: %lc\n", *result);
}
return 0;
}
5.3 运行结果
6. wcsnicmp
6.1 函数说明
int wcsnicmp(const wchar_t *s1, const wchar_t *s2, size_t n);
用于比较两个宽字符字符串的前若干个字符的大小写不敏感的差异
参数:
- s1 : 待比较的宽字符串1
- s2 : 待比较的宽字符串2
- n : 要比较的字符数目
返回值:
- 如果
s1指向的字符串按字典顺序小于s2指向的字符串(忽略大小写),则函数返回一个负整数;- 如果
s1等于s2,则函数返回0;- 如果
s1指向的字符串按字典顺序大于s2指向的字符串(忽略大小写),则函数返回一个正整数。
6.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void)
{
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, huazie!"
const wchar_t *ws1 = L"Hello, huazie!";
// 宽字符字符串 "HELLO, HUAZIE!"
const wchar_t *ws2 = L"HELLO, HUAZIE!";
int cmp_result = wcsnicmp(ws1, ws2, 5);
// 输出比较结果
if (cmp_result < 0)
{
wprintf(L"%ls is less than %ls.\n", ws1, ws2);
}
else if (cmp_result == 0)
{
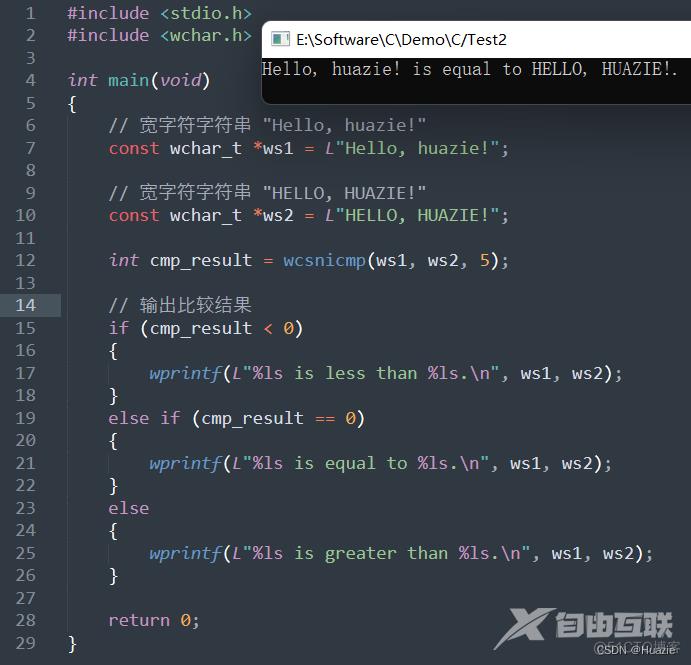
wprintf(L"%ls is equal to %ls.\n", ws1, ws2);
}
else
{
wprintf(L"%ls is greater than %ls.\n", ws1, ws2);
}
return 0;
}
6.3 运行结果
7. wcsnset
7.1 函数说明
wchar_t *wcsnset(wchar_t *str, wchar_t ch, size_t n);
用于将宽字符字符串中的前若干个字符设置为指定字符
参数:
- s1 : 要修改的宽字符字符串
- s2 : 要设置的宽字符
- n : 要设置的宽字符数目
7.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void)
{
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, huazie!"
wchar_t ws[] = L"Hello, huazie!";
// 将前五个字符设置为 '*'
wcsnset(ws, L'*', 5);
// 输出修改后的字符串
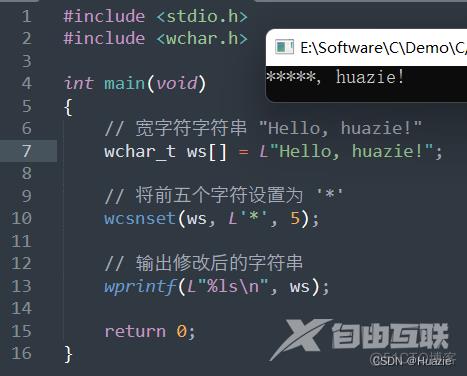
wprintf(L"%ls\n", ws);
return 0;
}
7.3 运行结果
8. wcsrev
8.1 函数说明
wchar_t *wcsrev(wchar_t *str);
用于将宽字符字符串反转
参数:
- s1 : 要反转的宽字符字符串
8.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void)
{
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, huazie!"
wchar_t ws[] = L"Hello, huazie!";
// 反转字符串
wcsrev(ws);
// 输出反转后的字符串
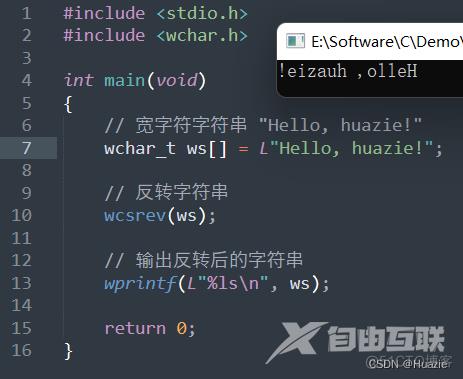
wprintf(L"%ls\n", ws);
return 0;
}
8.3 运行结果
9. wcsset
9.1 函数说明
wchar_t *wcsset(wchar_t *str, wchar_t ch);
用于将宽字符字符串中的所有字符设置为指定字符
参数:
- str : 要修改的宽字符字符串
- ch : 要设置的宽字符
9.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void)
{
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, huazie!"
wchar_t ws[] = L"Hello, huazie!";
// 输出修改前的字符串
wprintf(L"Before: %ls\n", ws);
// 将字符串中的每个字符都设置为 '#'
wcsset(ws, L'#');
// 输出修改后的字符串
wprintf(L"After : %ls\n", ws);
return 0;
}
注意:
wcsset()函数会修改原始字符串,因此需要在操作前确保原始字符串可以被修改。
9.3 运行结果
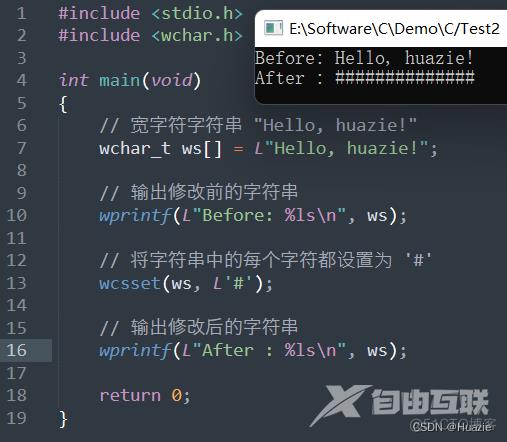
10. wcstoll
10.1 函数说明
long int wcstoll(const wchar_t* str, wchar_t** endptr, int base);
用于将宽字符串转换为长整形
参数:
- str : 要转换成长整型的宽字符串
- endptr : 一个指向指针的指针,可用于检测是否发生了转换错误,并且返回第一个无法被识别的宽字符位置。当该值为
nullptr时,不会返回无法被识别的宽字符位置- base : 进制数,默认为 10
10.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main()
{
const wchar_t* str = L"123456789";
//const wchar_t* str = L"12345a6789";
//const wchar_t* str = L"a123456789";
wchar_t* endptr;
long int num;
num = wcstoll(str, &endptr, 10);
wprintf(L"The number is %ld\n", num);
return 0;
}
10.3 运行结果
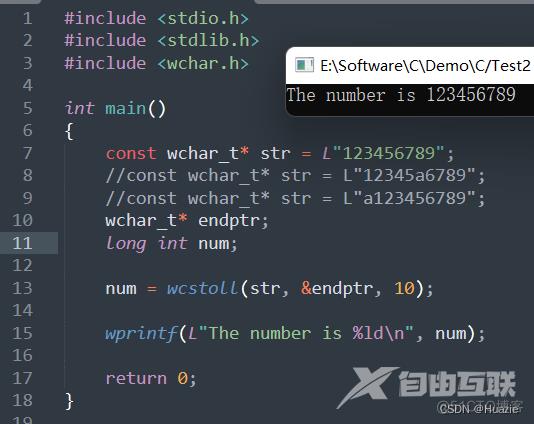

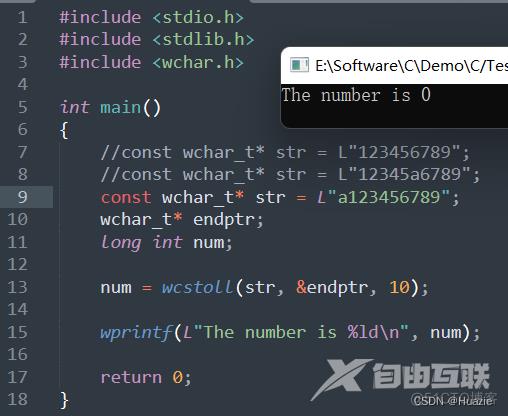
11. wcstoull
11.1 函数说明
unsigned long long int wcstoull(const wchar_t* str, wchar_t** endptr, int base);
用于将宽字符串转换为无符号长整型
参数:
- str : 要转换成无符号长整型的宽字符串
- endptr : 一个指向指针的指针,可用于检测是否发生了转换错误,并且返回第一个无法被识别的宽字符位置。当该值为
nullptr时,不会返回无法被识别的宽字符位置- base : 进制数,默认为 10
11.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main()
{
const wchar_t* str = L"123456789";
//const wchar_t* str = L"12345a6789";
//const wchar_t* str = L"a123456789";
wchar_t* endptr;
unsigned long long int num;
num = wcstoull(str, &endptr, 10);
wprintf(L"The number is %llu\n", num);
return 0;
}
wcstoull() 函数的用法和 wcstoll() 函数类似,不再赘述了。
11.3 运行结果
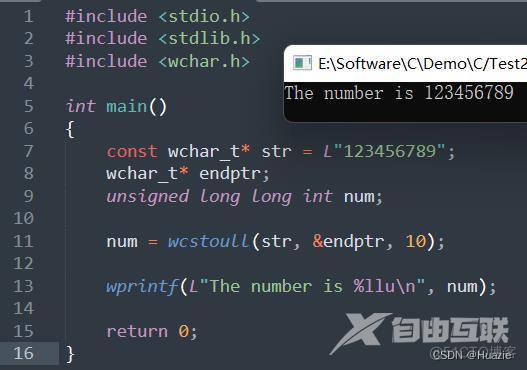
12. wcsupr
12.1 函数说明
wchar_t* wcsupr(wchar_t* str);
用于将宽字符串转换为大写
参数:
- str : 要转换为大写的宽字符串
12.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main(void)
{
// 宽字符字符串 "Hello, huazie!"
wchar_t ws[] = L"Hello, huazie!";
// 将宽字符串转换为大写字母形式
wcsupr(ws);
// 输出转换后的字符串
wprintf(L"%ls\n", ws);
return 0;
}
12.3 运行结果
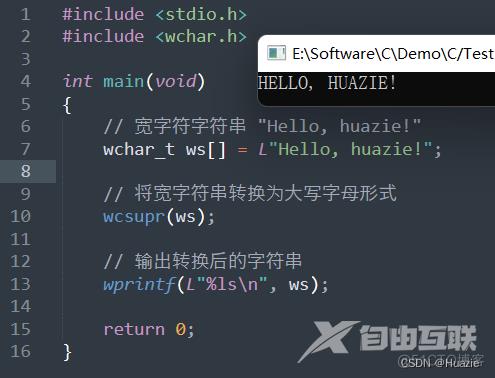
13. wctrans
13.1 函数说明
wctrans_t wctrans(const char* property);
用于创建字符转换描述符
wint_t towctrans(wint_t wc, wctrans_t desc);
通过 wctrans() 函数创建的字符转换描述符,可以将一个字符或字符串进行指定类型的转换。
wctrans 参数:
- property : 转换属性名称
towctrans 参数:
- wc : 待转换的字符
- desc : 转换描述符
13.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wctype.h>
#include <wchar.h>
int main() {
// 创建一个转换描述符,用于将小写字母转换为大写字母
wctrans_t to_upper = wctrans("toupper");
// 使用转换描述符将 wchar_t 类型字符串中的所有小写字母转换为大写字母
wchar_t str[] = L"hello huazie";
for (int i = 0; str[i] != L'\0'; i++) {
str[i] = towctrans(str[i], to_upper);
}
// 输出结果:"HELLO WORLD"
wprintf(L"%ls\n", str);
return 0;
}
13.3 运行结果
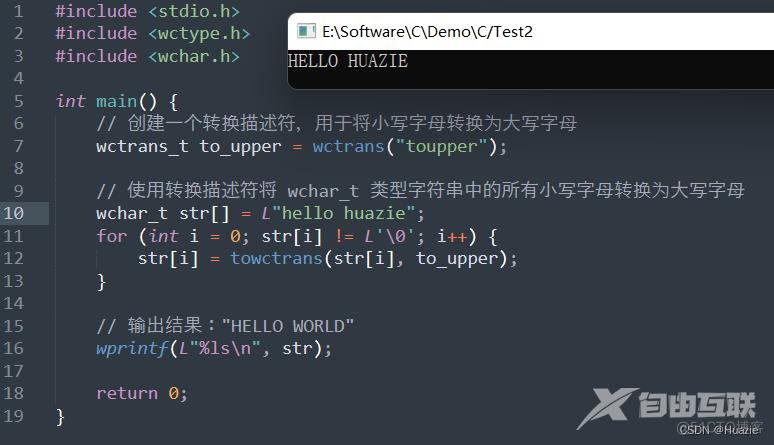
14. wmempcpy
14.1 函数说明
wchar_t* wmempcpy(wchar_t* dest, const wchar_t* src, size_t n);
用于将将源宽字符串的前 n 个字节的内容拷贝到目标字符串中
参数:
- dest : 目标宽字符串
- src : 源宽字符串
- n : 要拷贝的字节数
14.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
const wchar_t* src = L"Hello, Huazie!";
wchar_t dest[20];
wprintf(L"Original string: %ls\n", src);
// 将源字符串内容拷贝到目标字符串中
wchar_t* ptr = wmempcpy(dest, src, wcslen(src) * sizeof(wchar_t));
*ptr = L'\0';
wprintf(L"Copied string: %ls\n", dest);
return 0;
}
14.3 运行结果
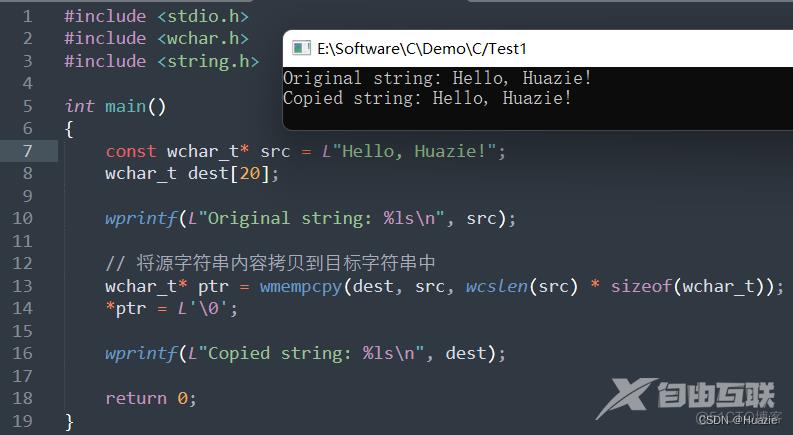
15. wmemmove
15.1 函数说明
wchar_t* wmemmove(wchar_t* dest, const wchar_t* src, size_t n);
将源宽字符串中指定数量的字节复制到目标宽字符串中,即使目标内存和源内存重叠
参数:
- dest : 目标宽字符串
- src : 源宽字符串
- n : 要移动的字节数
15.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <wchar.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
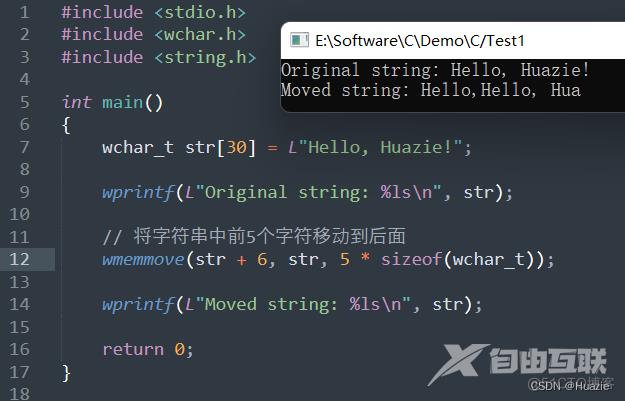
wchar_t str[30] = L"Hello, Huazie!";
wprintf(L"Original string: %ls\n", str);
// 将字符串中前5个字符移动到后面
wmemmove(str + 6, str, 5 * sizeof(wchar_t));
wprintf(L"Moved string: %ls\n", str);
return 0;
}
15.3 运行结果