文章目录 the python code: the result: overview understand the process: a long example: Correctness: the python code: the code base the vertex(nodes) set and edge se
文章目录
- the python code:
- the result:
- overview
- understand the process:
- a long example:
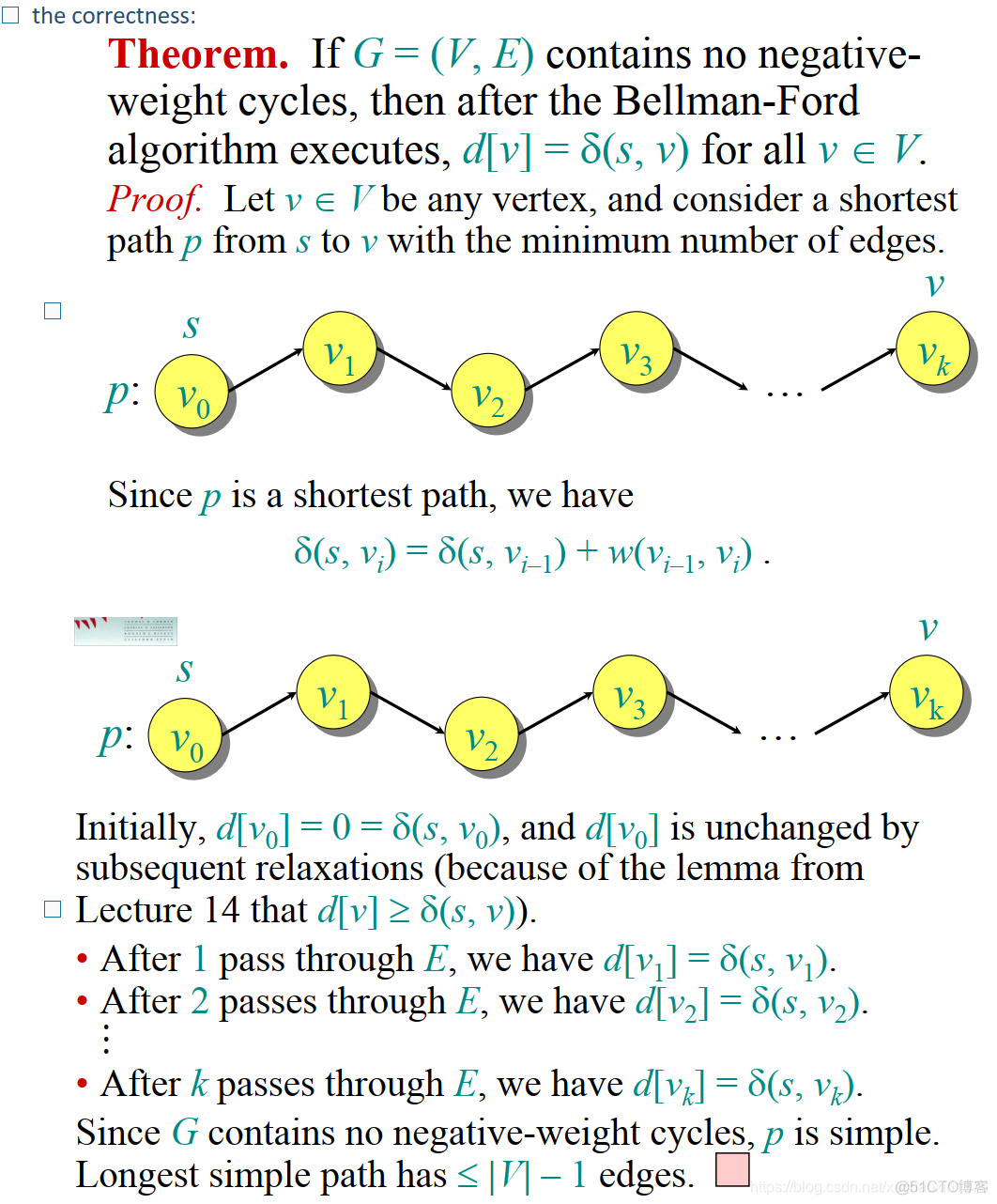
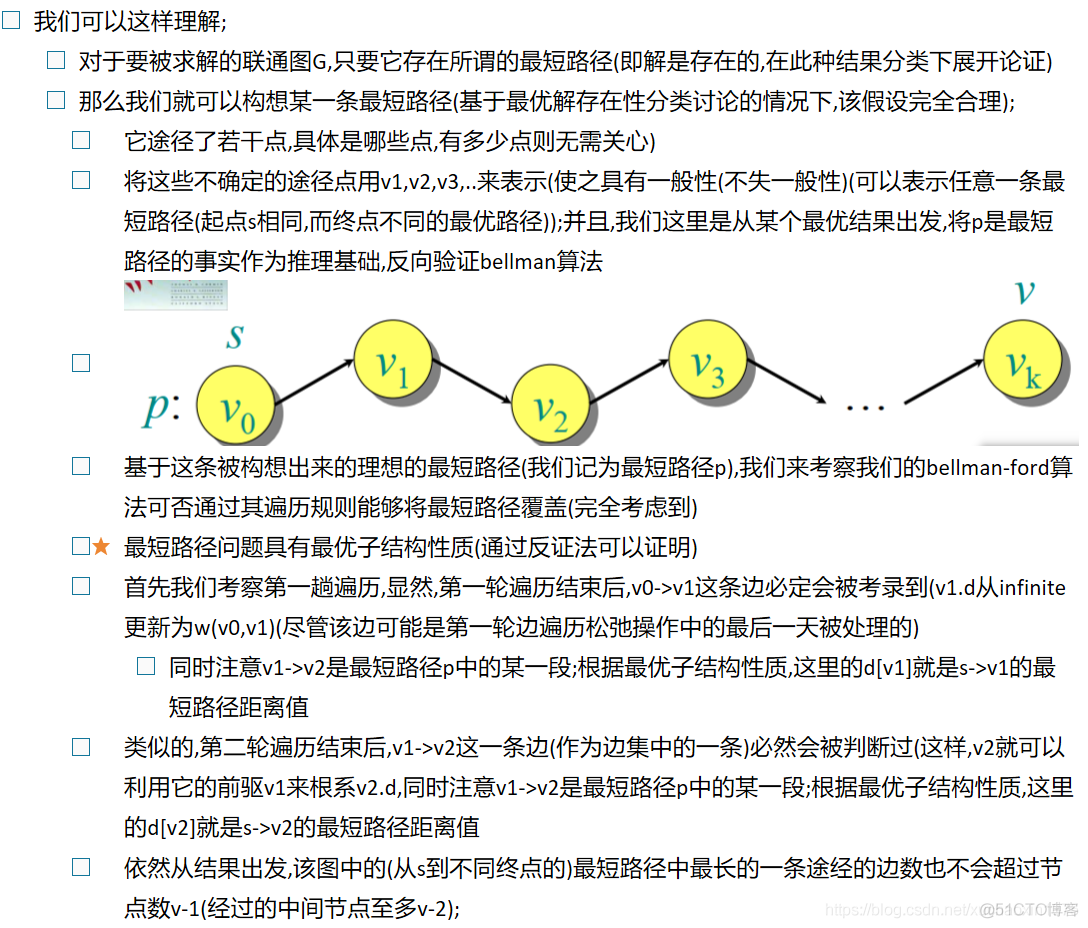
- Correctness:
the python code:
the code base the vertex(nodes) set and edge set seperately
import mathimport logging as l
l.basicConfig(level=l.INFO)
class Edge():
def __init__(self, start, end, weight):
self.start = start
self.end = end
self.weight = weight
class Node():
def __init__(self, sign):
# self.number = number
self.sign = sign
# for initial nodes(vertex) of the graph
self.distance = math.inf
# set the node's precursor:
self.precursor = None
def initalize_source_node(self):
self.distance = 0
return self
class G():
s_node=None
def __init__(self, edges, nodes):
self.edges = edges
self.nodes = nodes
# def generate_nodes(self):
# # get the nodes number(you can custom the number regularity,there use the default simple number system)
# self.nodes = [Node(chr(sign)) for sign in range(ord('A'), ord('E')+1)]
def log_print_nodes(self):
for node in self.nodes:
l.debug(f'{node.sign,node.distance}')
def weight(self, u, v):
for edge in self.edges:
if edge.start == u and edge.end == v:
return edge.weight
return math.inf
def relax(self, edge):
u=edge.start
v=edge.end
l.debug(f'self.weight(u, v):{self.weight(u, v)}')
new_distance= u.distance+self.weight(u, v)
#debug
l.debug(f'{edge.start.sign,edge.end.sign}')
l.debug(f'new_distance:{new_distance}')
if v.distance >new_distance:
v.distance=new_distance
v.precursor=u
# def initialize_single_source(G, source_node):
# # for node in G.nodes:
# # node.distance=0
# # node.precursor=None
# source_node.distance = 0
def bellman_ford(self, s):
G.s_node=s.initalize_source_node()
l.info(f'G.s_node:{G.s_node.sign}')
for i in range(len(self.nodes)-1):
for edge in self.edges:
self.relax(edge)
l.debug(f'{edge.end.distance}')
#debug
self.log_print_nodes()
return self
def print_ford_result(self):
# self.bellman_ford(s)
if not self.is_exist_shortest():
print("there is a nagetive circle.")
else:
for node in self.nodes:
# print()''' '''
print(f'to node:{node.sign},the distance is:{node.distance}')
def is_exist_shortest(self):
for edge in self.edges:
if edge.end.distance>edge.start.distance+edge.weight:
return False
return True
def print_precursor(self,node):
if node.sign==G.s_node.sign:
print(G.s_node.sign,end=" ")
# return
else:
if node.precursor==None:
print(G.s_node.sign,"->",node.sign,"(the node is not accessible)",end=" ")
else:
self.print_precursor(node.precursor)
print(node.sign,end=" ")
def print_path(self):
for node in self.nodes:
# print(node.sign)
self.print_precursor(node)
print()
def generate_nodes():
# get the nodes number(you can custom the number regularity,there use the default simple number system)
nodes = [Node(chr(sign)) for sign in range(ord('A'), ord('E')+1)]
return nodes
#debug:print nodes:
def print_nodes():
for node in nodes:
print(node.sign,node.distance)
# print_nodes()
def get_node_instance(sign):
for node in nodes:
if node.sign==sign:
return node
#throw exception
return None
# get the edges parameters to instantiate the edge nodes ,put the edges to the list edges;
def generate_edges():
while(True):
line = input("input node:")
if line == "0":
break
edge_param = line.split(",")
start, end, weight = edge_param[0], edge_param[1], int(edge_param[2])
start_node=get_node_instance(start)
end_node=get_node_instance(end)
# print(end_node.sign)
edges.append(Edge(start_node,end_node , weight))
return edges
'''debug the edges is right: '''
def print_edges():
for edge in edges:
# print(edge.start.sign,edge.end.sign,edge.weight)
l.info((edge.start.sign,edge.end.sign,edge.weight))
# print_edges()
nodes=[]
nodes=generate_nodes()
edges = []
edges=generate_edges()
G=G(edges,nodes)
# G.print_nodes()
source_node=input("input the source node you want:(from 'A'~'E')\n")
G.bellman_ford(get_node_instance(source_node))
G.print_ford_result()
G.print_path()
'''
test data:
A,B,-1
A,C,4
B,C,3
D,C,5
D,B,1
B,D,2
B,E,2
E,D,-3
0
'''
the result:
source A: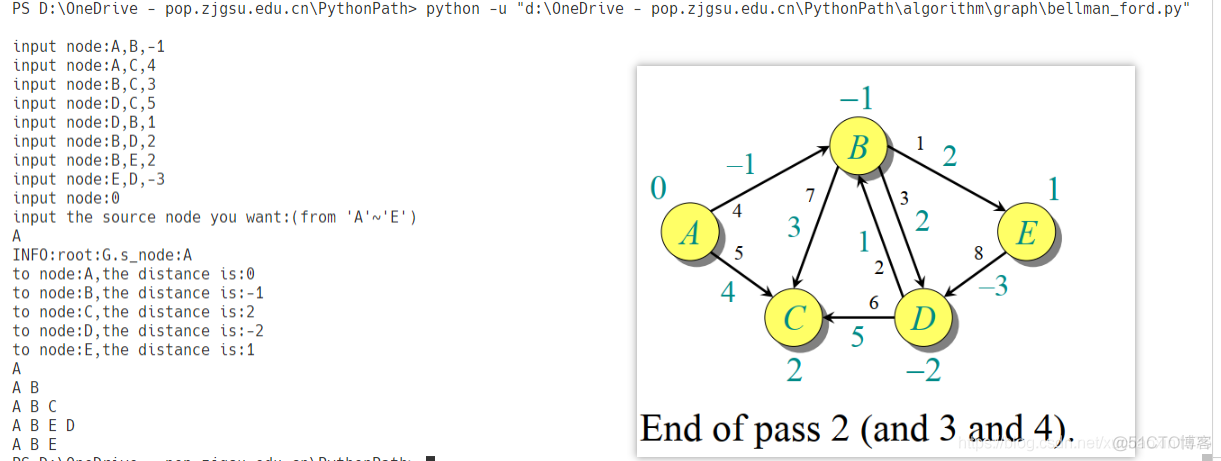
source D: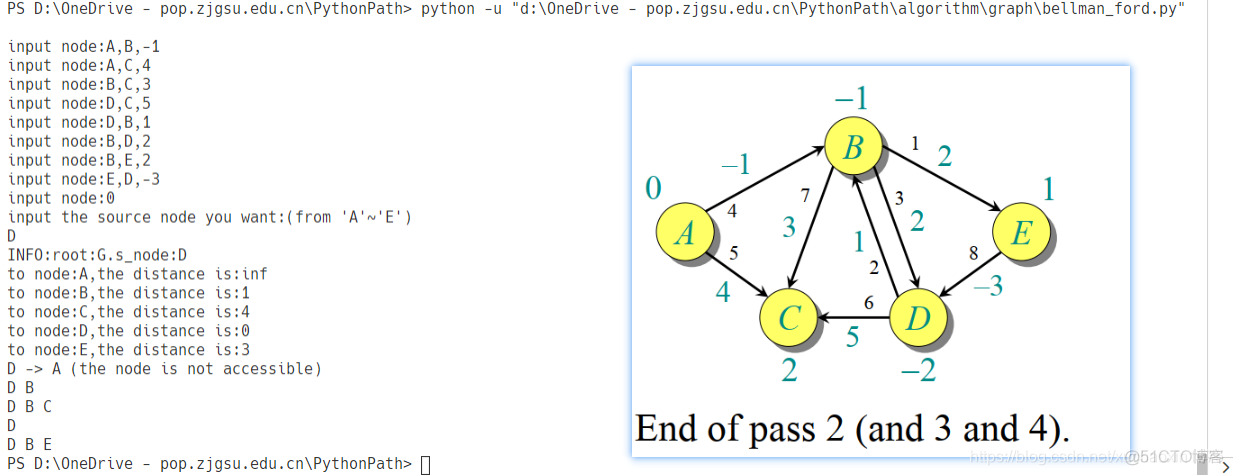
overview

understand the process:

a long example:
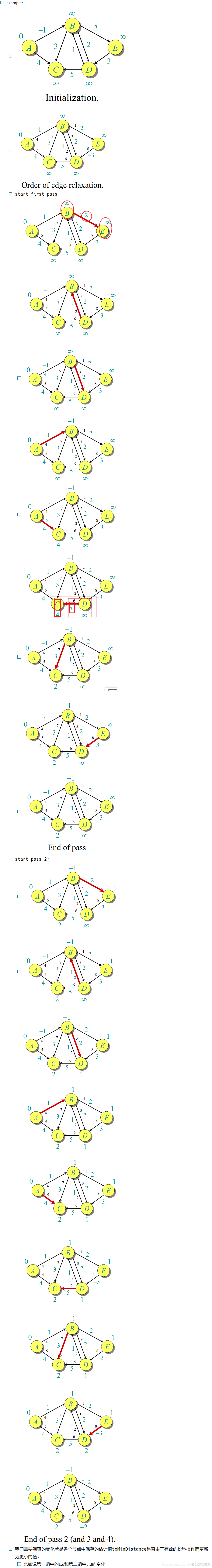
Correctness: