Spring AOP的总体流程
- 1、注册解析AOP的服务
- 2、解析和加载横切逻辑
- 3、将横切逻辑织入目标Bean中
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator继承体系图
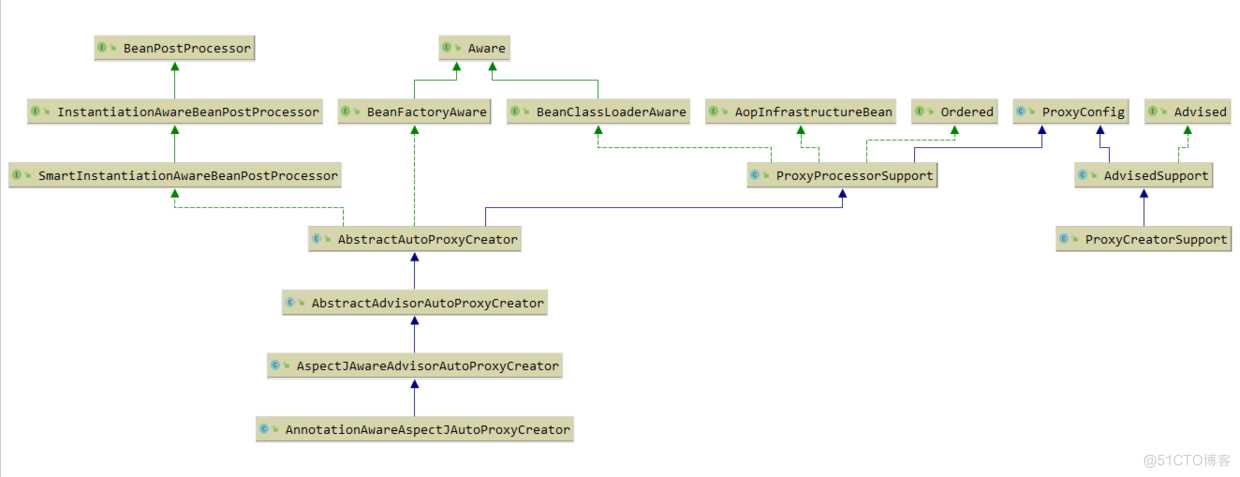
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator既实现了SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 又实现了BeanFactoryAware。就可以对容器做一些事情。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 实现了Order接口,所以先于普通的BeanPostProcessor注册,并对普通BeanPostProcessor也能起作用。
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor,会在Bean被创建之前,在resolveBeforeInstantiation中被调用。
Spring Aop主要是通过AbstractAutoProxyCreator实现的BeanPostProcessor、InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor以及SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口里面的后置处理器方法,来介入到Spring IOC容器的Bean的实例化以及初始化的过程中对Bean进行AOP的处理的。
所以AbstractAutoProxyCreator类里面的实现的容器级别的后置处理器方法便是介入分析的点:
-
横切逻辑的加载主要是在AbstractAutoProxyCreator类中的postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法中,该方法是在Bean的实例化之前被调用的。
-
横切逻辑织入目标Bean中主要是在AbstractAutoProxyCreator类中的postProcessAfterInitialization方法中,该方法是在Bean的实例化之后被调用的。
Spring AOP横切逻辑的织入过程:
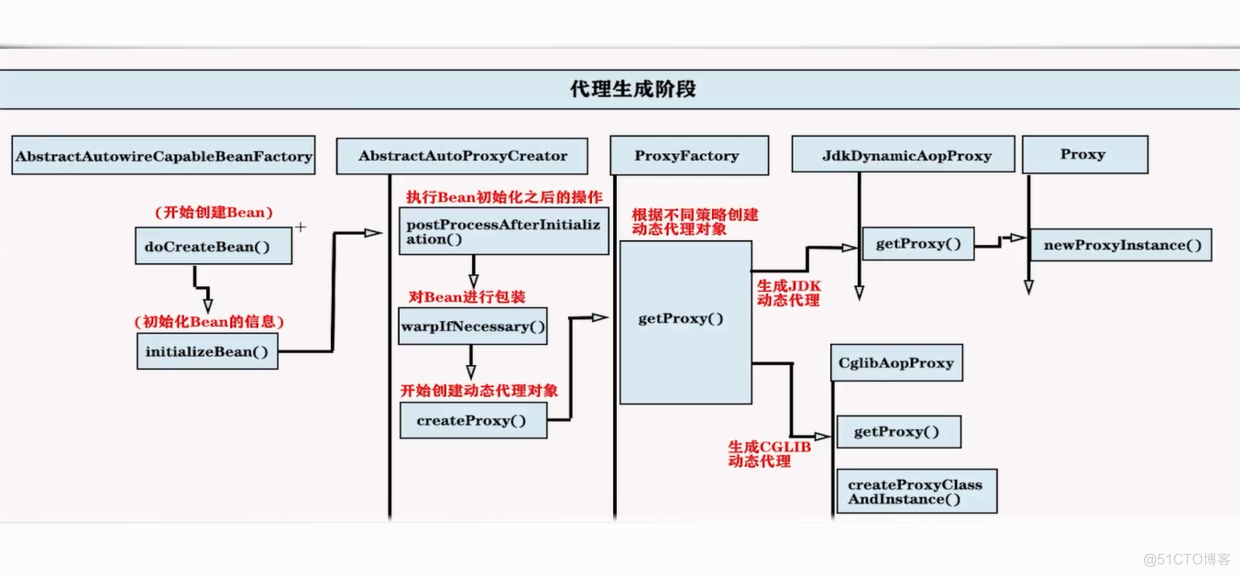
在Spring5AOP——AbstractAutoProxyCreator横切逻辑织入目标Bean中文章中,分析了横切逻辑织入目标Bean中,本文就分析AbstractAutoProxyCreator类中wrapIfNecessary方法中的createProxy方法,创建AOP动态代理。
wrapIfNecessary
- 判断当前bean是否需要被代理,如果需要则创建动态代理类。
-
当执行完getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean方法之后,就可以从候选的Advisor列表里筛选出匹配于当前Bean的Advisor列表,获取到Advisor列表之后就会接着执行后续的创建动态代理的步骤了。
-
由于getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean筛选出匹配的Advisor了,将该Bean对应的cacheKey写入到advisedBeans中,并将对应的值设置为true,表示对该Bean进行过Spring AOP的处理了。
-
之后就会调用createProxy方法去创建目标代理对象实例,创建好动态代理实例之后,就会动态代理实例类型给保存到proxyTypes的缓存里面,并将动态代理实例返回,这样就完成了wrapIfNecessary方法的执行。
-
如果没有getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean没有筛选出匹配的Advisor的话,就证明该Bean不需要织入横切逻辑,此时就会在advisedBeans里给该Bean设置对应的cacheKey和false,以表明该bean是不需要被织入的。
本文重点分析createProxy方法——创建AOP动态代理
public abstract class AbstractAutoProxyCreator extends ProxyProcessorSupport implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor, BeanFactoryAware { protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) { //如果beanFactory是ConfigurableListableBeanFactory的类型,暴露目标类 if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) { AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass); } //创建一个ProxyFactory,当前ProxyCreator在创建代理时将需要用到的字段赋值到ProxyFactory中去 ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(); //将 当前的AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 对象的属性赋值给ProxyFactory对象 proxyFactory.copyFrom(this); // 处理 proxyTargetClass 属性 // 如果希望使用 CGLIB 来代理接口,可以配置 // proxy-target-class="true",这样不管有没有接口,都使用 CGLIB 来生成代理: // <aop:config proxy-target-class="true"></aop:config> if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { // 检查preserveTargetClass属性,判断beanClass是应该基于类代理还是基于接口代理 if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) { // 如果是基于类代理,则将proxyTargetClass赋值为true proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); } else { // 评估bean的代理接口 // 1. 有接口的,调用一次或多次:proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc); // 2. 没有接口的,调用:proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory); } } // 这个方法主要来对前面传递进来的横切逻辑实例进行包装 // 注意:如果 specificInterceptors 中有 Advice 和 Interceptor,它们也会被包装成 Advisor // 方法会整理合并得到最终的advisors (毕竟interceptorNames还指定了一些拦截器的) // 至于调用的先后顺序,通过方法里的applyCommonInterceptorsFirst参数可以进行设置, // 若applyCommonInterceptorsFirst为true,interceptorNames属性指定的Advisor优先调用。默认为true Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); // 将advisors添加到proxyFactory proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors); // 设置要代理的类,将targetSource赋值给proxyFactory的targetSource属性,之后可以通过该属性拿到被代理的bean的实例 proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource); // 这个方法是交给子类的,子类可以继续去定制此proxyFactory customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); // 用来控制proxyFactory被配置之后,是否还允许修改通知。默认值为false(即在代理被配置之后,不允许修改代理类的配置) proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); // 设置preFiltered的属性值,默认是false。子类:AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator修改为true // preFiltered字段意思为:是否已为特定目标类筛选Advisor // 这个字段和DefaultAdvisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice获取所有的Advisor有关 //CglibAopProxy和JdkDynamicAopProxy都会调用此方法,然后递归执行所有的Advisor if (advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true); } // 使用proxyFactory获取代理 return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader()); } }evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory)
- 根据被代理beanClass是否实现了接口,来评估是调用CGLIB还是JDK动态代理。
buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors)
- 对横切逻辑实例进行包装
resolveInterceptorNames
- 解析interceptorNames而来得Advisor数组
wrap
- this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(next)
- 将满足不是正在创建中的横切逻辑实例,给统一转换成Advisor
- 接着回到createProxy方法中,在执行完buildAdvisors方法之后,就能获取到所有的适配于被代理Bean的Advisor列表,
proxyFactory.getProxy
- 使用proxyFactory获取代理
createAopProxy()
- 首先获取AopProxy对象,其主要有两个实现:JdkDynamicAopProxy和ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
getAopProxyFactory()
- 获取AopProxyFactory
createAopProxy
- createAopProxy(this)
- 创建AopProxy
-
这边创建 AopProxy 的参数 config(AdvisedSupport)实际上是proxyFactory 对象。
-
具体为:AbstractAutoProxyCreator 中的 proxyFactory.getProxy 发起的调用,在 ProxyCreatorSupport 使用了 this 作为参数调用了本方法,这边的 this 就是发起调用的 proxyFactory对象,而 proxyFactory 对象中包含了要执行的的拦截器(Advisor)。
-
无论是创建 JDK 动态代理还是 CGLIB 代理,都会传入 config 参数,该参数会被保存在 advised(AdvisedSupport)变量中。
JDK 动态代理、CBLIB 代理构造函数
final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable { public JdkDynamicAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null"); if (config.getAdvisors().length == 0 && config.getTargetSource() == AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) { throw new AopConfigException("No advisors and no TargetSource specified"); } this.advised = config; } } class ObjenesisCglibAopProxy extends CglibAopProxy { public ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) { super(config); } } class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable { public CglibAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { Assert.notNull(config, "AdvisedSupport must not be null"); if (config.getAdvisors().length == 0 && config.getTargetSource() == AdvisedSupport.EMPTY_TARGET_SOURCE) { throw new AopConfigException("No advisors and no TargetSource specified"); } this.advised = config; this.advisedDispatcher = new AdvisedDispatcher(this.advised); } }getProxy(classLoader)
- 获取代理对象实例
JdkDynamicAopProxy#getProxy
final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable { @Override public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); } // 1.拿到要被代理对象的所有接口 Class<?>[] proxiedInterfaces = AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised, true); findDefinedEqualsAndHashCodeMethods(proxiedInterfaces); // 2.通过classLoader、接口、InvocationHandler实现类,来获取到代理对象 return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, proxiedInterfaces, this); } }最终,通过 JDK 动态代理的类被调用时,会走到 JdkDynamicAopProxy#invoke 方法。
JdkDynamicAopProxy#invoke
final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable { @Override @Nullable public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.targetSource; Object target = null; try { //若是equals方法不需要代理 if (!this.equalsDefined && AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the equals(Object) method itself. return equals(args[0]); } //若是hashCode方法不需要代理 else if (!this.hashCodeDefined && AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method)) { // The target does not implement the hashCode() method itself. return hashCode(); } // 如果当前方法是Spring织入的DecoratingProxy接口中的方法,则返回目标对象的Class类型 else if (method.getDeclaringClass() == DecoratingProxy.class) { // There is only getDecoratedClass() declared -> dispatch to proxy config. return AopProxyUtils.ultimateTargetClass(this.advised); } //如果被代理的对象本身就实现了Advised接口,则证明该类里面的方法已经被代理了,直接执行即可 else if (!this.advised.opaque && method.getDeclaringClass().isInterface() && method.getDeclaringClass().isAssignableFrom(Advised.class)) { // Service invocations on ProxyConfig with the proxy config... return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.advised, method, args); } Object retVal; //是否将动态代理暴露给AopContext if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { // Make invocation available if necessary. oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } // Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, // in case it comes from a pool. //获取我们的目标对象 target = targetSource.getTarget(); Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null); // Get the interception chain for this method. //把aop的advisor转化为拦截器链 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); // Check whether we have any advice. If we don't, we can fallback on direct // reflective invocation of the target, and avoid creating a MethodInvocation. if (chain.isEmpty()) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor so we know it does // nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot swapping or fancy proxying. // chain 是空的,说明不需要被织入横切逻辑,直接执行被代理的方法实例本身 Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse); } else { // We need to create a method invocation... // 获取目标对象的调用链逻辑,并且对该链进行调用 MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); // Proceed to the joinpoint through the interceptor chain. retVal = invocation.proceed(); } // Massage return value if necessary. Class<?> returnType = method.getReturnType(); if (retVal != null && retVal == target && returnType != Object.class && returnType.isInstance(proxy) && !RawTargetAccess.class.isAssignableFrom(method.getDeclaringClass())) { // Special case: it returned "this" and the return type of the method // is type-compatible. Note that we can't help if the target sets // a reference to itself in another returned object. // 判断返回值如果为目标对象,并且当前方法的返回值类型是当前代理对象的类型,那么就将 // 当前代理对象返回。这里的逻辑的实际意思简单的说就是,如果返回值是目标对象,那么 // 就将当前代理对象返回 retVal = proxy; } else if (retVal == null && returnType != Void.TYPE && returnType.isPrimitive()) { // 如果返回值满足其为空,不是Void类型,并且是基本数据类型,那么就抛出异常, // 因为基本数据类型的返回值必然不为空 throw new AopInvocationException( "Null return value from advice does not match primitive return type for: " + method); } return retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { // Must have come from TargetSource. // 如果TargetSource不是静态的, // 则调用其releaseTarget()方法将生成的目标对象释放 targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. // 处理AopContext中保存的当前代理对象 AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } } }getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
- List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass)
- 把aop的advisor转化为拦截器链
可以看出上面方法用到缓存的,假设现在缓存没有相应的拦截器, 则到 AdvisorChainFactory 的相应方法中获取,继续跟踪AdvisorChainFactory,进入DefaultAdvisorChainFactory中的相应方法,比较长。
getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
- cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(this, method, targetClass)
- 缓存没有,则尝试通过advisorChainFactory去创建调用链。
如果aop的advisor转化为拦截器链为空,说明不需要被织入横切逻辑,直接执行被代理的方法实例本身。
###invokeJoinpointUsingReflection
- 目标对象方法的调用
- AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(target, method, argsToUse)
- 其实是通过AopUtils的方法调用,使用反射机制来对目标对象的方法进行的。
如果aop的advisor转化为拦截器链不为空,获取目标对象的调用链逻辑,并且对该链进行调用。
- 如果存在拦截器,则创建一个 ReflectiveMethodInvocation,代理对象、被代理对象、方法、参数、被代理对象的 Class、拦截器链作为参数。这边 ReflectiveMethodInvocation 已经持有了被代理对象、方法、参数,后续就可以直接使用反射来调用被代理的方法了。
ReflectiveMethodInvocation 构造函数
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable { protected ReflectiveMethodInvocation( Object proxy, @Nullable Object target, Method method, @Nullable Object[] arguments, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass, List<Object> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers) { this.proxy = proxy; this.target = target; this.targetClass = targetClass; this.method = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method); this.arguments = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, arguments); this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers = interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers; } } // 获取目标对象的调用链逻辑,并且对该链进行调用 MethodInvocation invocation = new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain); retVal = invocation.proceed();ReflectiveMethodInvocation#proceed() 拦截器方法执行
- 看看拦截器对象,即ReflectiveMethodInvocation中proceed()方法的调用,
该方法是一个责任链的方法,会按索引执行所有的拦截器。
-
如果所有拦截器都执行完毕(index是从-1开始,所以跟size - 1比较),则直接使用反射调用连接点(也就是我们原本的方法)。
-
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor 前置通知
-
AspectJAfterAdvice 后置通知
-
AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor 返回通知
-
AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice 异常通知
以上拦截器方法都在invoke()方法中执行
递归调用拦截器
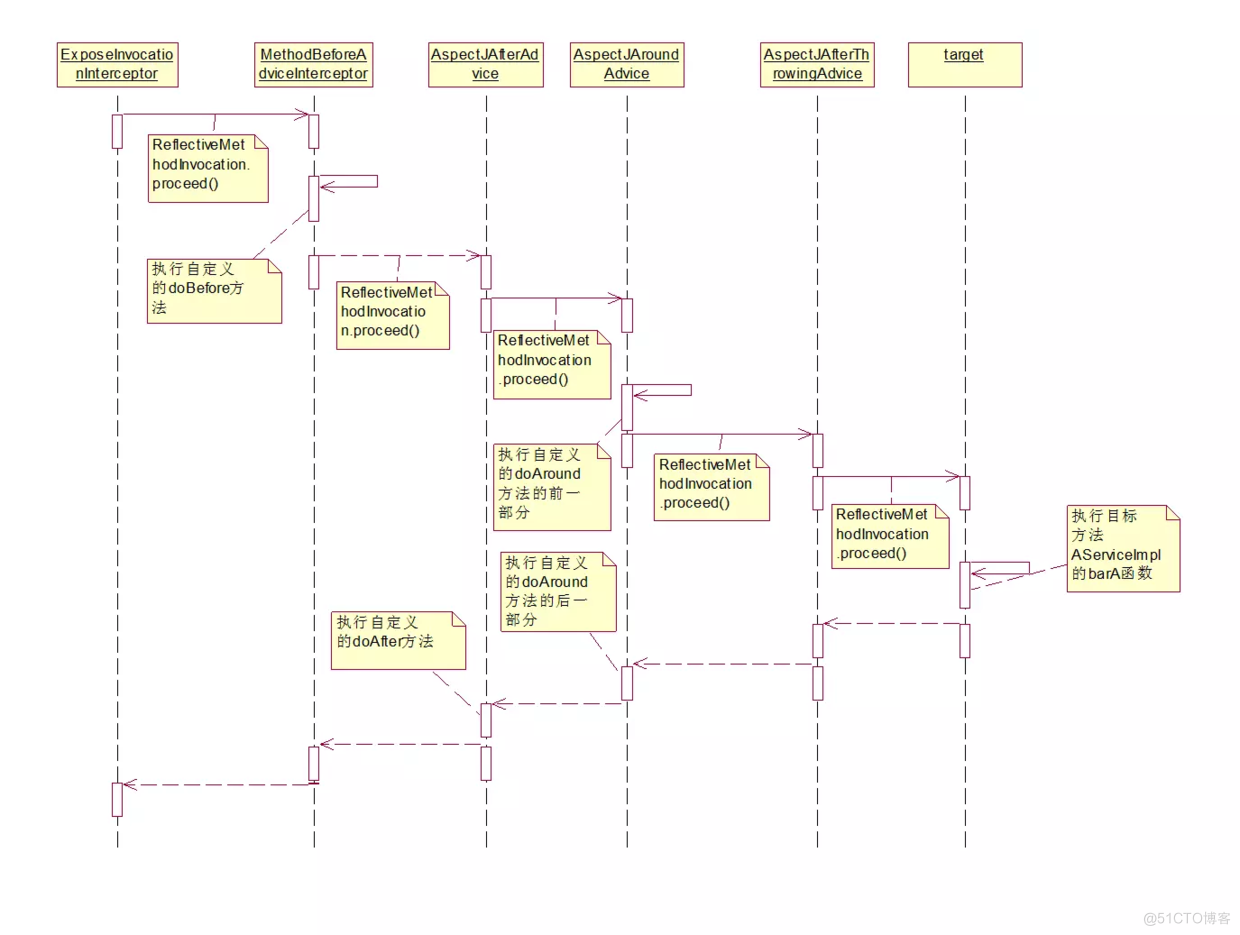
invokeJoinpoint 执行目标方法
public class ReflectiveMethodInvocation implements ProxyMethodInvocation, Cloneable { @Nullable protected Object invokeJoinpoint() throws Throwable { // 反射执行连接点,也就是原方法,target为被代理的对象实例、method为执行的方法、arguments为方法参数 return AopUtils.invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(this.target, this.method, this.arguments); } } public abstract class AopUtils { @Nullable public static Object invokeJoinpointUsingReflection(@Nullable Object target, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { // Use reflection to invoke the method. // 通过反射机制来获得相应的方法,并调用invoke try { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method); return method.invoke(target, args); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { // Invoked method threw a checked exception. // We must rethrow it. The client won't see the interceptor. throw ex.getTargetException(); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw new AopInvocationException("AOP configuration seems to be invalid: tried calling method [" + method + "] on target [" + target + "]", ex); } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) { throw new AopInvocationException("Could not access method [" + method + "]", ex); } } }CglibAopProxy#getProxy
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable { @Override public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); } try { // 1.拿到要代理目标类 Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass(); Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy"); // proxySuperClass默认为rootClass Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass; // 这里判断rootClass是否是Cglib代理所产生的类(内部判断rootClass的className是否包含$$) // 如果rootClass是被Cglib代理过的,获取rootClass的父类作为proxySuperClass if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) { proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass(); Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces(); for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) { // 将父类的接口也添加到advised的interfaces属性 this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface); } } // Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary. // 方法校验,final方法不能被代理,记录日志 // 2.校验proxySuperClass,主要是校验方法是否用final修饰、跨ClassLoader的包可见方法,如果有将警告写入日志 validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader); // Configure CGLIB Enhancer... // 3.创建和配置Cglib Enhancer Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer(); if (classLoader != null) { enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader); if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader && ((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) { enhancer.setUseCache(false); } } // superclass为被代理的目标类proxySuperClass,通过名字可以看出,生成的代理类实际上是继承了被代理类 enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass); enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised)); enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE); enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader)); // 4.获取所有要回调的拦截器 // 通过callbacks设置拦截器链 // spring在这里考虑了很多种情况,将所有callback放到一个数组中。 // 而在某些特定场景下,spring还对回调进行了优化,生成新的回调函数,追加到callbacks数组中。 Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass); Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length]; for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) { types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass(); } // fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above // 设置回调过滤器,修正后的拦截器map和偏移量在这里传进去 // 在上面调用getCallbacks之后,此时仅填充fixedInterceptorMap enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter( this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset)); enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types); // Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance. // 生成代理类实例 // 5.生成代理类并创建代理实例,返回代理实例 return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks); } catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() + ": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class", ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { // TargetSource.getTarget() failed throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex); } } }getCallbacks
- 获取所有要回调的拦截器
最终,通过 CGLIB 代理的类被调用时,会走到 DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept 方法。
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable { private static class DynamicAdvisedInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable { private final AdvisedSupport advised; public DynamicAdvisedInterceptor(AdvisedSupport advised) { this.advised = advised; } @Override @Nullable public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable { Object oldProxy = null; boolean setProxyContext = false; Object target = null; TargetSource targetSource = this.advised.getTargetSource(); try { if (this.advised.exposeProxy) { // Make invocation available if necessary. oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy); setProxyContext = true; } // Get as late as possible to minimize the time we "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool... target = targetSource.getTarget(); Class<?> targetClass = (target != null ? target.getClass() : null); // 这里获取拦截器链的方式与jdk动态代理方式调用了同一个方法 List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass); Object retVal; // Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is, // no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target. if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) { // We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly. // Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know // it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot // swapping or fancy proxying. // chain 是空的,说明不需要被织入横切逻辑,直接执行被代理的方法实例本身 Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args); retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse); } else { // We need to create a method invocation... // 获取目标对象的调用链逻辑,并且对该链进行调用 retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed(); } //处理返回值,并返回。 retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal); return retVal; } finally { if (target != null && !targetSource.isStatic()) { // 如果TargetSource不是静态的, // 则调用其releaseTarget()方法将生成的目标对象释放 targetSource.releaseTarget(target); } if (setProxyContext) { // Restore old proxy. // 处理AopContext中保存的当前代理对象 AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy); } } } } }-
DynamicAdvisedInterceptor#intercept(),该方法中通过List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass)获取一个List拦截链,这里获取拦截器链的方式与上面分析jdk动态代理方式调用了同一个方法。
-
然后通过retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed()方法执行对应的拦截链进行执行处理。
-
最后通过processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal)处理返回值,并返回。
-
整体过程完全采用动态代理模式来实现。
CglibMethodInvocation构造函数
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable { private static class CglibMethodInvocation extends ReflectiveMethodInvocation { @Nullable private final MethodProxy methodProxy; public CglibMethodInvocation(Object proxy, @Nullable Object target, Method method, Object[] arguments, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass, List<Object> interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers, MethodProxy methodProxy) { super(proxy, target, method, arguments, targetClass, interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers); // Only use method proxy for public methods not derived from java.lang.Object this.methodProxy = (Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers()) && method.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class && !AopUtils.isEqualsMethod(method) && !AopUtils.isHashCodeMethod(method) && !AopUtils.isToStringMethod(method) ? methodProxy : null); } } }CglibMethodInvocation#proceed()
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable { private static class CglibMethodInvocation extends ReflectiveMethodInvocation { @Override @Nullable public Object proceed() throws Throwable { try { return super.proceed(); } catch (RuntimeException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Exception ex) { if (ReflectionUtils.declaresException(getMethod(), ex.getClass())) { throw ex; } else { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(ex); } } } } }CglibMethodInvocation中的proceed方法最终调用到了ReflectiveMethodInvocation类中的proceed方法,该方法在前面JDK动态代理中解析过。
至此,创建 AOP 代理,以及AOP的调用,已经介绍完毕。
总结:
-
1、@EnableAspectJAutoProxy 会注册一个AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
-
2、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator是一个InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
-
3、创建流程:
- A、registerBeanPostProcessors() 注册后置处理器,创建AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
- B、finishBeanFactoryInitialization 初始化剩下的单实例Bean
- a、创建Bean和切面
- b、AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator拦截创建过程
- c、创建完Bean判断是否需要增强。通过BeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization,wrapIfNecessary() 包装代理对象
-
4、执行目标方法
- A、获取拦截器链(advisor包装为Interceptor)
- B、递归调用拦截器链
- 前置通知、目标方法、后置通知、返回通知、异常通知
参考: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/104521455
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000015830477
https://blog.csdn.net/fuli_mouren/article/details/45244453
http://www.mamicode.com/info-detail-890966.html
